According to the World Health Organisation, more than 2.2 billion people worldwide experience some forms of vision impairment.
- An estimated 5.5 million people suffer from IRDs around the world, with a prevalence rate of one in 3,450.
- Studies have revealed significantly higher prevalence of such cases in India
- one in 372 individuals in rural South India,
- one in 930 in urban South India,
- and one in 750 in rural Central India affected by these conditions.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
What are Inherited Retinal Diseases (IRDs)?
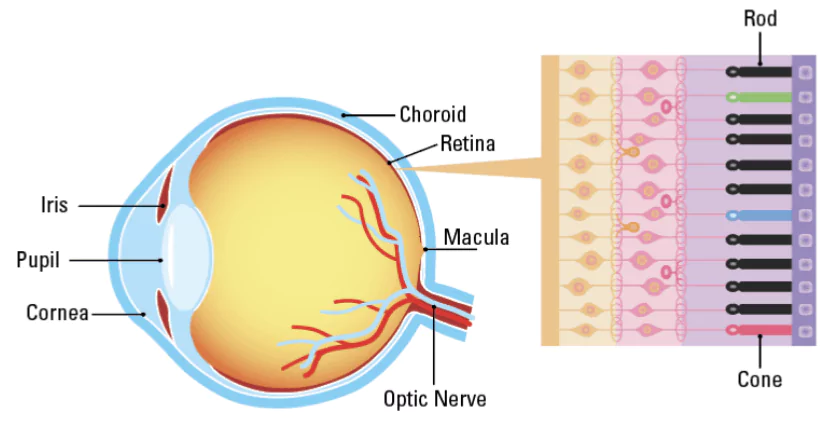
- IRDs are genetic disorders causing progressive vision loss, often leading to blindness.
- Caused by mutations in 300+ genes responsible for retinal function.
- Some individuals lose vision early, while others experience gradual deterioration.
- Early intervention can slow or prevent blindness in some cases.
How do Genes Affect Vision?
- The body is made up of cells, each containing a nucleus with chromosomes made of DNA.
- DNA contains genes, which provide instructions for making proteins essential for body functions.
- A change (mutation) in a gene can cause proteins to function incorrectly or be missing.
- Faulty proteins in the retina lead to IRDs and vision loss.
Risk Factors for IRDs
IRDs follow different inheritance patterns:
- Autosomal Dominant: The defective gene is located on an autosome (non-sex chromosome).
- A person inherits one faulty dominant gene from a parent and one normal gene from the other.
- The faulty dominant gene causes the disorder.
- Autosomal Recessive: Both copies of the gene (one from each parent) must be defective.
- Parents are usually asymptomatic carriers.
- 25% chance of inheriting the disease if both parents are carriers.
- X-linked Disorders: The defective gene is located on the X chromosome.
- Males (XY) are more severely affected as they have only one X.
- Females (XX) may be carriers or show milder symptoms.
- Mitochondrial Inheritance: Mutations occur in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), inherited exclusively from the mother (sperm do not contribute mitochondria).
- Can affect multiple organs, including the eyes.
What is RNA-Based Therapy?
- RNA-based therapies offer a safer alternative to gene therapy as they do not alter DNA permanently.
- These therapies temporarily modify gene expression, reducing long-term risks.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Types of RNA-Based Therapies
- Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs)
- Used successfully for spinal muscular atrophy and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
- Being tested for Stargardt disease, Leber congenital amaurosis, and retinitis pigmentosa.
- RNA-Editing with ADAR Enzymes
- Corrects specific mutations at the RNA level.
- Can restore protein production in retinal cells without altering DNA.
- Suppressor tRNA Therapy
- Bypasses stop-codon mutations that disrupt protein synthesis.
- Helps in producing full-length proteins to restore retinal function.
- Small Molecule RNA Therapy (PTC124/Ataluren)
- Used for cystic fibrosis and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
- Clinical trials underway for treating aniridia (a rare eye disease).
India’s Role in Precision Medicine
- What is Precision Medicine?
- It tailors treatments based on a person’s genetics, lifestyle, and environment.
- Aims for personalized care instead of a one-size-fits-all approach.
- Need for Genetic Research in India
- Over 300 genes are linked to IRDs, but India lacks large-scale studies on genetic mutations in its population.
- No major study (500+ patients) has mapped genetic variations in Indian IRD patients.
- Identifying common genetic mutations is crucial for developing effective treatments.
- Challenges in India
- Genetic variations differ across communities in India, making research complex.
- Barriers include:
- Low awareness among doctors and patients.
- Limited access to genetic counseling.
- Insufficient research funding.
- Lack of diagnostic infrastructure, especially in rural areas.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 30 Jan 2025
30 Jan 2025

