Context: Shadow banks must review how they lend money as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) strengthens norms and squeezes their credit lines.
RBI’s Report Highlights Risks in NBFCs
- Recently, the RBI increased the risk weights for Non-bank financial companies (NBFCs) (and Banks) by 25 percentage points to 125% on retail loans.
- Risk Weights: Banks need to set aside capital for every loan.
- The RBI’s ‘Financial Stability Report‘ of June 2023 drew attention to NBFCs’ personal loan growth: It rose year-on-year by 31.3 percent while the industry grew slower by 12.7 percent hinting towards issue asset quality.
What is Shadow Banking?
- The shadow banking system consists of lenders, brokers, and other credit intermediaries outside traditional regulated banking.
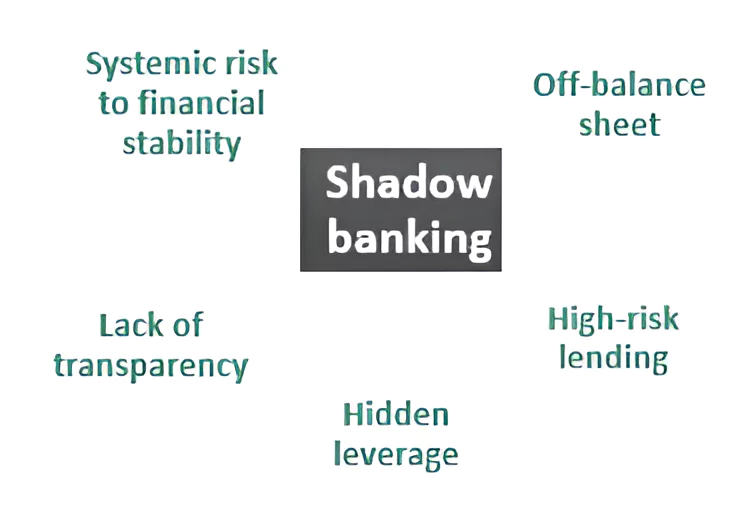
- Shadow banking is generally unregulated and not subject to the same risk, liquidity, and capital restrictions as traditional banks.
- The term ‘shadow bank’ was coined by Paul McCulley in 2007.
- Examples of shadow lenders include Special Purpose Entities, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), Hedge Funds, etc.
- In India, the crisis of the NBFCs that was triggered by the liquidity problems of IL&FS in 2018, has brought back attention to the shadow banking sector.
ALSO READ: BANKING SECTOR OF INDIA
Source: Business Standard
![]() 4 Dec 2023
4 Dec 2023
