Context
India has emerged as the world’s fastest growing major economy in 2023, according to the United Nations.
- India’s Economic growth rate is 6.8% in FY 2023, with formal unemployment at a 12-year low of 4.1%.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Key Highlights of the United Nations Survey
India’s Economy
- World’s Fastest growing major economy: India achieved an impressive economic growth rate of 6.8% in FY 2023, making it the world’s fastest growing major economy though economic revival was concentrated in few large economies.
- Domestically driven growth: India’s economic success is primarily driven by domestic factors, with less reliance on external exposure to developed nations or China.
- Infrastructure boost: Government spending on infrastructure played a significant role in propelling growth, with gross fixed capital formation increasing by 6%, reaching 34% of GDP in the final quarter of FY23.
- Favorable demographics: India’s young population (600 million youth aged 15-24 years) presents a tremendous opportunity to boost domestic demand.
- This demographic advantage contrasts with rapidly aging populations in some regional economies like China, Japan, and South Korea.
- Gender equality gap: The UN urges India to improve gender equality and integrate women’s participation in the workforce, particularly in sectors like manufacturing and tourism.
- This requires better data collection and analysis to inform gender-inclusive economic policies.
- GST reforms success: The UN commends India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) reform for simplifying the indirect tax system and reducing compliance burdens.
- Rice export ban impact: In July 2023, India temporarily banned some rice exports, which made the prices of food rise even higher in the region.
 This happened at a time when food prices were already high due to weather issues caused by El Nino.
This happened at a time when food prices were already high due to weather issues caused by El Nino.
- Climate change concerns: The UN warns that India could lose 5.8% of daily working hours due to heat stress by 2030, especially impacting outdoor workers in agriculture and construction.
- This highlights the need for climate change mitigation efforts.
Global Economy
-
Output Growth in Other Economies:
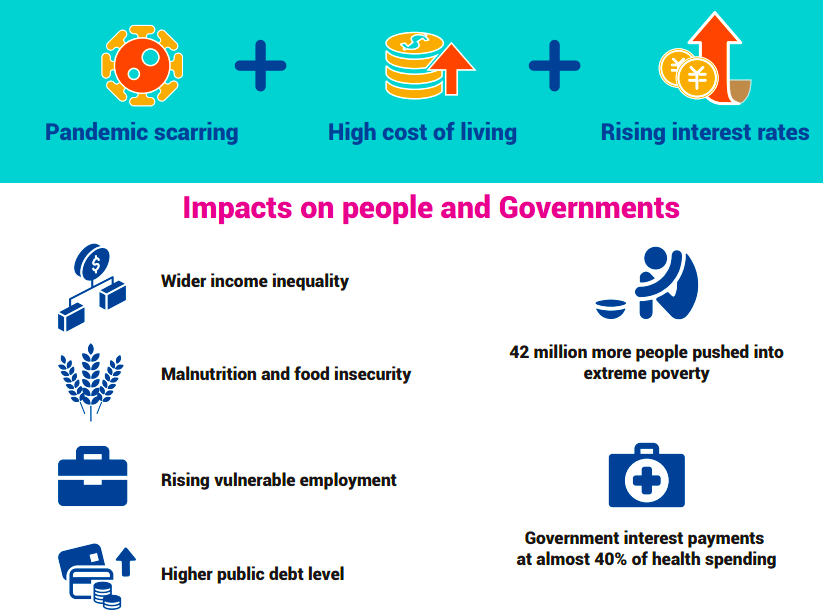
- The growth of output was slow in other economies because of high living cost, rise in economic uncertainty, and weak external demand.
-
Income Inequality/ People’s Purchasing Power:
- High inflation and poor job opportunities have decreased individual’s buying capacity and their ability to face shocks.
- COVID 19 pandemic and high cost of living are the major factors behind rising income inequality. These pushed around 42 million more people in the poverty cycle.
-
Global Near-term Economic Outlook:
-
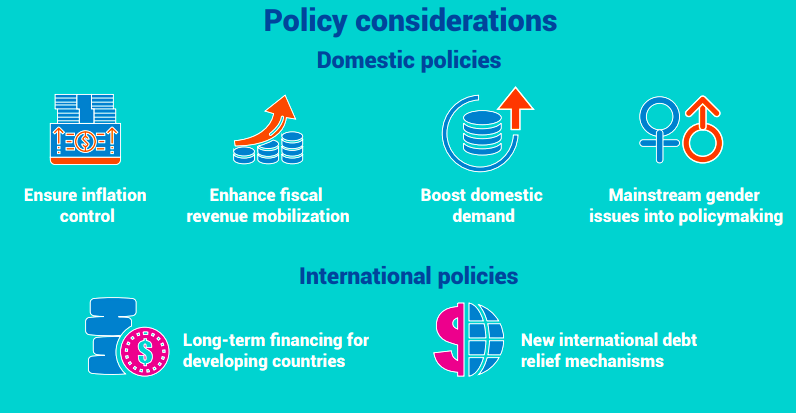
- Inflation is still high. In addition to it, fiscal conditions are also not favourable. Apart from this, there are various risks such as the impact of China’s economic slowdown, rise in geopolitical tensions, and trade disruptions in the Asia-Pacific region.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
-
High borrowing costs in Asia Pacific Region:
- During 2019 to 2022, interest payment of the government was about 28 and 38 percent of public spending on education and health care.
 ESCAP analysis: According to this analysis, there is a need to manage sustained macroeconomic and inflation stability, strong fiscal positions and financial market liquidity as these are crucial in keeping low borrowing rates.
ESCAP analysis: According to this analysis, there is a need to manage sustained macroeconomic and inflation stability, strong fiscal positions and financial market liquidity as these are crucial in keeping low borrowing rates.
-
Global Working Hour Loss:
- Globally, about 2.2% of working hours are estimated to be lost due to rising temperatures.
- In developing countries, total output losses due to heat stress are estimated to range from 1.5% to 4.0% of GDP annually.
-
Labor Productivity and Social Welfare Strategies:
- Nations with limited savings should focus on raising productivity by making investments in education, skills training, technology adoption, and infrastructure development.
- It will help in reducing precautionary savings and boost financial accessibility and literacy.
Benefits of India’s Strong Economic Performance in 2023 (as per the UN Report):
- Low Unemployment: India’s impressive growth rate will create more jobs, investment, and overall prosperity, leading to a fall in unemployment rate.
- Strong domestic demand: A large young population creates a strong domestic market for businesses to sell to within India.
- Less reliance on external factors: India’s economic success is less vulnerable to global slowdowns or trade issues compared to other economies.
- Simpler tax system: The GST reforms has streamlined the tax system, making it easier for businesses to operate.
Challenges for India to Address
India has various challenges to face
- Climate change: Rising heat stress could significantly impact worker productivity, particularly in outdoor jobs.
- Gender equality gap: There is a need to improve gender equality and integrate women’s participation in the workforce for full utilization of women’s talents in the workforce to increase economic potential.
- Food security: The rice export ban highlights the need for India to ensure food security for its own population.
Also Read: India Employment Report 2024
![]() 8 Apr 2024
8 Apr 2024
 This happened at a time when food prices were already high due to weather issues caused by El Nino.
This happened at a time when food prices were already high due to weather issues caused by El Nino.
 ESCAP analysis: According to this analysis, there is a need to manage sustained macroeconomic and inflation stability, strong fiscal positions and financial market liquidity as these are crucial in keeping low borrowing rates.
ESCAP analysis: According to this analysis, there is a need to manage sustained macroeconomic and inflation stability, strong fiscal positions and financial market liquidity as these are crucial in keeping low borrowing rates.