Context: A bench of 7 Judges of the Supreme Court has unanimously held that unstamped arbitration agreements were legally enforceable, and the lack of proper stamping does not render an arbitration contract invalid, thus overruling its earlier judgement passed in April 2023.
More about News:
- Legal Issue: The present case was based on the question of whether the Court should check the legal validity and stamping of the arbitration document before assigning an arbitrator.
- If two disagreeing parties can not concur on who the arbitrator will be, they can seek the court’s direction to appoint the arbitrator.
What is Stamping?
- Stamping refers to the act of paying stamp duty on the value of the agreement as per the Stamps Act, 1899.
- The quantum of stamp duty varies depending on the nature and geographical location of the agreement.
- While the central government fixes stamp duties on some agreements, state governments are empowered to fix stamp duties on some agreements executed within their borders.
|
- Previous Judgment: The previous judgment by majority of 3:2 held that documents without a valid stamp, can not be recognised as a legal documents.
- The judgment thus led to freezing the process of arbitration in such cases.
- Recent Judgment: The latest judgment overrules the previous verdict, holding that insufficient stamping is a curable defect and can not be a ground to stop the arbitration process.
What is Arbitration?
- Meaning: It is one of the types of Alternative Dispute Resolution, where the parties submit their dispute to a mutually agreed arbitrator outside the court. This arbitrator then makes a binding decision on the dispute.
- Characteristics:
-
- Arbitration is consensual and can occur only if both parties have agreed to it.
- The arbitrator’s or arbitral tribunal’s decision is final and easy to enforce.
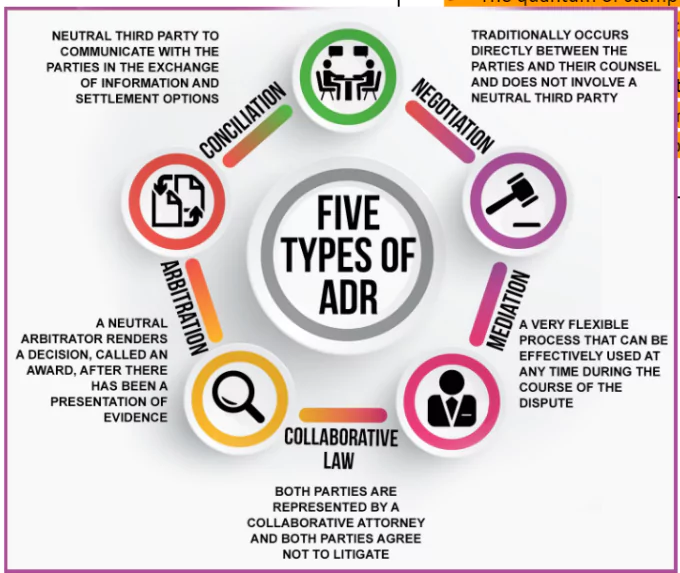
What are Alternative Dispute Resolution?
- Alternative dispute resolution, or ADR, is a process in which a neutral third party—a mediator or arbitrator—helps parties who are embroiled in a dispute come to an agreement without going through the court-based adversarial dispute resolution.
- Types of ADR: See Image.
How can the Supreme Court review its own decision?
- Under Article 137, the Constitution has empowered SC to review any judgment or order pronounced by it. Therefore, the Supreme Court can review any of its earlier judgments.
- For example– the Historic Judgement of the Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973), reviewed and overruled its judgment in the Golak Nath case (1967)
- Under Article 142, the Constitution confers unique power on the Supreme Court to do ‘complete justice’ between the parties. Therefore, the court can review its own decision, if it is required for complete justice.
Source: Hindustan Times
![]() 14 Dec 2023
14 Dec 2023
