Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: Stubble burning, air pollution, 15-Point Winter Action Plan, Punjab Pollution Control Board (PPCB), Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981, and Air Quality Index (AQI).
Relevancy for Mains: Stubble burning in Punjab, challenges associated with crop burning, and policy interventions by the central government to reduce stubble burning. |
Stubble Burning in Punjab
- Farmers across Punjab face the challenge of managing nearly 20 million tonnes of paddy straw. It is estimated that over 15 million tonnes of paddy straw is burnt in the open fields.
- According to the Punjab Pollution Control Board (PPCB), 656 cases of farm fire occurrence have been reported in the State till October 4, 2023.
- By comparison, the same period last year saw only 415 such incidents.
- According to Punjab’s State Action Plan, the government is committed to reducing paddy stubble burning incidents by half.
- In Punjab, the ban and action against people burning crop residue are regulated under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
What is stubble burning?
- Stubble burning is a practice of removing agricultural waste from the field by setting on fire the straw stubble (parali) that is left on the land after harvesting of grains like paddy, wheat etc.
- Paddy stubble burning is practised mainly in the Indo-Gangetic plains of Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh to clear the fields for rabi crop sowing.
- The paddy crop is harvested between the first and last weeks of October and wheat is sown from the first week of November until the middle of December.
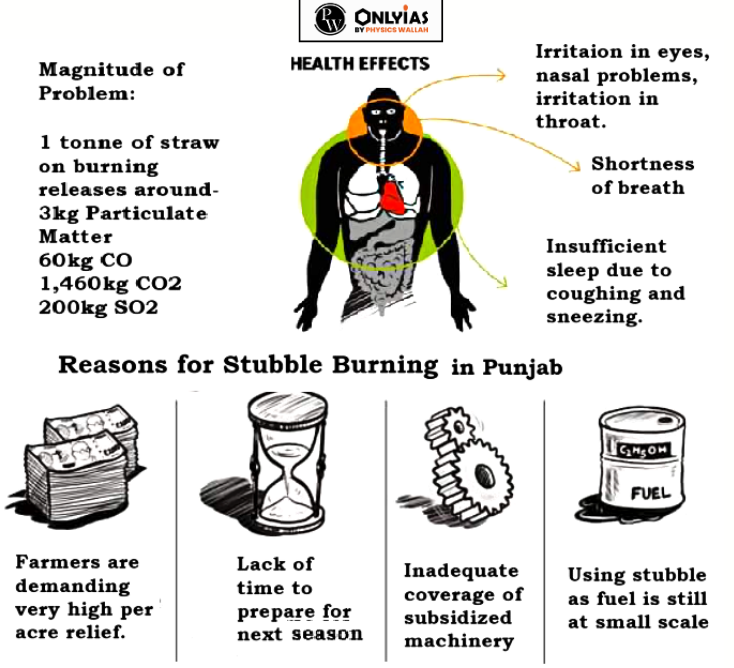
- Although rice and wheat account for large volumes of crop residues, sugarcane leaves are also burnt on fields.
- Burning crop residue is a crime under Section 188 of the IPC and under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act.
Also read: POLLUTION AND ITS EFFECTS ON HEALTH
What are the challenges associated with stubble burning?

- Air Pollution: Stubble burning in North India is seen as a major cause of air pollution affecting the Air Quality Index (AQI). Each year, air pollution levels rise and the AQI reaches a ‘severe’ and ‘hazardous’ level.
- Heat Penetration: Stubble burning generates heat that penetrates the soil, causing an increase in soil erosion, loss of useful microbes and moisture, leading to soil degradation and loss of soil fertility.
- For instance, the heat from burning paddy straw penetrates 1 centimeter into the soil, elevating the temperature to around 400 Celsius.
- Lack of Political Will: As farmers are an important political constituency, the state government adopted a soft approach.
- In recent years, the government has developed a framework and action plan for effective prevention and control of stubble burning, their successful implementation and enforcement remains a challenge.
- For instance, following the National Green Tribunal (NGT) order of 2015 banning stubble burning, the PPCB has been imposing penalties on farmers, still, the cases are rising.
- Lack of Viable Alternatives: Although farmer outfits in Punjab are against the burning of stubble, they would continue with the status quo without a viable alternative or financial incentive.
- Harmful Health Impacts: Stubble burning emits toxic pollutants in the atmosphere containing harmful gases like Carbon Monoxide (CO), methane (CH4), carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and volatile organic compounds (VOC).
- These pollutants disperse in the surroundings and eventually affect air quality and people’s health by forming a thick blanket of smog (fog with soot or smoke).
- Global Warming: Pollution and greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) lead to global warming. These are also responsible for the haze in Delhi and the melting of Himalayan glaciers.
ALSO READ: CLIMATE CHANGE & MITIGATION STRATEGIES
What are the policy interventions by the central government to reduce stubble burning?
National Air Quality Index (NAQI)
- Air Quality Index is a tool for effectively communicating air quality status to people in terms that are easy to understand.
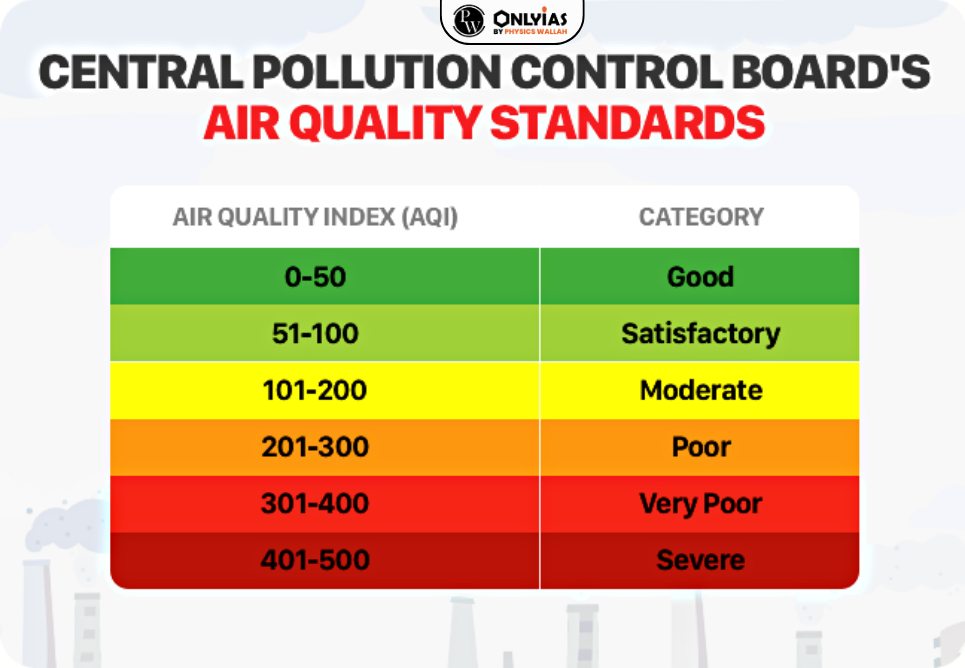
|
- National Policy for Management of Crop Residues: Control of burning of crop residue by promotion of in-situ management (incorporation in soil, mulching) of crop residue.
- Waste to Energy Programme under the Umbrella scheme of the National Bioenergy Programme: It supports the setting up of Waste to Energy projects for the generation of biogas, bioCNG, power, and syngas from urban, industrial and agricultural residues.
- Promotion of agricultural mechanization for in-situ crop residue management in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and NCT of Delhi.
- It aims to address air pollution and subsidize machinery required for in-situ crop residue management.
- Crop Residue Management Guidelines: For efficient ex-situ management of paddy straw generated, surplus paddy straw will be collected and biomass collection depots will be built in the States of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- It would generate employment opportunities, reduce air pollution, and would result in new investments in biomass to the biofuel and energy sectors.
Way Forward
- Subsidizing Innovative Farm Technologies: Recent innovations like happy seeder, rotavator, baler, paddy straw chopper, etc. are costly but they could help farmers to manage crop residues effectively. New and Improved seed varieties: Using improved varieties of rice and wheat crops, particularly short-duration crop varieties.
- For example, Pusa Basmati-1509 and PR-126 mature quickly and also improve the quality of the soil.
- Using Bio-Waste Decomposers: These decomposers contain agricultural micro-organisms which increase the Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR).
- For instance, using Pusa-bio-decomposer, developed by the scientists at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute, which turns crop residue into manure in 15-20 days by accelerating the decomposition process.
- Sustainable farm management practices: Such measures include the production of biochar in-situ management with mechanical intensification. These measures could not only manage the crop residues but also help control GHG emissions.
- Educating and Empowering the Stakeholders: It could be an important step to make farmers feel that they are also responsible for the crop residue and empower them to better utilize agricultural waste for financial and environmental gains.
Best Practices:
- The Punjab government instructed brick kiln owners to replace at least 20 percent of coal with paddy straw pellets for fuel after the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) introduced a scheme to reduce pollution and use of fossil fuel.
- Chattisgarh Gauthans Model: As a goodwill gesture the paddy growers are donating the crop residues in thousands of Gauthans (cattle shed premises for conservation and augmenting livestock) where it is used as fodder.
|
Conclusion
To solve the problem of stubble burning in Punjab, everyone needs to work together. We should encourage farmers to use new and eco-friendly farming methods, teach and support them, and put effective rules in place to reduce the harm to the environment and people’s health.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
What is/are the advantage/ advantages of zero tillage in agriculture?
- Sowing of wheat is possible without burning the residue of previous crop.
- Without the need for nursery of rice saplings, direct planting of paddy seeds in the wet soil is possible.
- Carbon sequestration in the soil is possible.
Select the correct answer
using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Ans: D |
![]() 7 Oct 2023
7 Oct 2023


