Context: According to SBI research Ecowrap, better connection with credit dispensation, increased savings through PM Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) and higher participation share in MGNREGA is ushering in sustainable empowerment of women across states.
Role Played by Trinity Acts in Empowering Women in India:
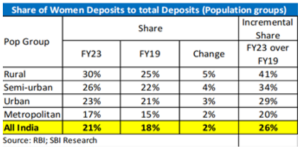
- Deposits with Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCB): According to RBI’s 2023 report, overall deposits of Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) increased by 10.2%.
- The per capita women deposits increased by Rs 4,618 in the last five years.
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs): Women deposits account for 50% share in incremental deposits in RRBs during FY19 and FY23.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA): Almost all major states have women participation of more than 33% in the financial year 2023.
- However, in some of the states it was less than the national average of 57.4%.
- PMJDY: Currently 55% of total PMJDY beneficiaries are women.
- In southern states, the share of MGNREGA and PMJDY is more than the national average.
- Positive Correlation: In states where women participation in MGNREGA is low, women beneficiaries in PMJDY are also low.
Challenges Associated with the Trinity Acts:
- Credit Dispensation:
- Financial Exclusion: Women in this segment lack regular cash flows and are not involved in paid economic activity.
- Structural Barriers: Related to mobility, oppressive gender roles, and lack of financial and digital literacy.
- Dormant Account Holders: Many women lack use-case and opened an account either due to the government’s financial inclusion drive or peer pressure or both.
- Social norms: Their accounts are used by someone else in the family (primarily their husbands). For a typical financial transaction, their role is limited to authentication.
- MGNREGA:
- Personal and Family Problems:
- Children Left Uncared: Children were either left with the family members or were brought to the work site, so they were unattended.
- Domestic work neglected: No extra work can be taken up due to fatigue and debility leading to non-cooperation from family members.
- Operational Problems: Delays in issuing job card and huge delay in work payment followed by wages not provided according to MGNREGA act.
- For instance, the measurement of earth works is sometimes not proper which causes delay in the payment.
- Worksite Problems: Most important problems faced by the women workers were lack of safe drinking water and no shade during rest period.
- MGNREGA works are taken up during slack season i.e. summers when water requirement is high and there is a scarcity of water in rural areas.
- PM Jan Dhan Yojana:
- Multiple Accounts, Single Holder: An individual has opened more than one account in various banks.
- Although the number of bank accounts has crossed 50 crores with total deposits exceeding ₹2 lakh crore, many existing bank users have opened accounts to benefit from insurance and overdraft facilities.
- Digital Divide: Low engagement and inactive accounts are possible explanations for women’s low credit adoption in India.
- NFHS-5 Data: Digital access ownership of a mobile phone is 65 percent among women 25-29.
Way Forward
- Microcredit and Entrepreneurship: According to RBI, microfinance are collateral free loans given to households having annual income up to Rs. 3 lakh. This can help boost entrepreneurship and small business developments in India.
- Digital Financial Inclusion: Increasing access to financial services by minimising demand and supply side barriers.More centers of financial literacy may be established to bring excluded women under financial inclusion. For example, a gender-sensitive interface will be critical to address the supply side barriers.
- Safe and Accessible Work Sites: This includes providing proper sanitation facilities, safe drinking water, etc. at work sites to promote women’s participation.
- Childcare Facilities: Ensuring proper childcare facilities will ensure that children of women workers do not remain unattended. For example, the Karnataka government is opening around 4,000 “Koosian Mane” creches for children of women workers under MGNREGA.
- Self Help Groups (SHG): They allow exposure to financial services , help develop skills, and facilitate transactions. For example, the Bank Sakhis programme by the National Rural Livelihoods Mission has improved women’s exposure to financial services, in turn driving up transactions in rural India.
- Improved Decision Making: Increasing women literacy, growing economic pressure, and the burning desire to gain economic and social independence are pushing womenfolk to take up gainful careers. Researches have shown that having women on boards provides genuine value addition to decision-making.
Conclusion
- “Millions of women in our hamlets know what unemployment means. Give them access to economic activities and they will have access to power and self- confidence to which they hitherto have been strangers,” said Mahatma Gandhi in Young India (1930).
- We have a distance to go, especially in the larger society, whose attitudes determine how women are viewed and valued, including in corporate life.
- Thus, efforts should be made to include more women in MGNREGA and PMJDY so that all women are brought under the formal banking system thus ensuring credit dispensation.
![]() 1 Sep 2023
1 Sep 2023
