Researchers have used James Webb Space Telescope observations to conduct detailed examinations of the atmospheric conditions on brown dwarfs, specifically a pair that orbit each other around six light years from Earth, quite close by cosmic standards.
- A light-year is the distance light travels in a year, 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km).
About the Findings on Atmospheric Conditions on Brown Dwarfs
The two brown dwarfs examined by Webb formed about 500 million years ago. Each has a diameter comparable to Jupiter’s. One is 35 times more massive than Jupiter, and the other 30 times. As per researchers, in this study, they created the most detailed ‘weather maps’ for any brown dwarf to date.
- On Weather Change: The Webb data provided a three-dimensional look at how the weather changed over the course of a brown dwarf’s rotation.
- The larger of the two taking seven hours and the smaller five hours with multiple layers of clouds found at different atmospheric depths.
- Atmosphere: It is highly complex. Webb helps to understand these atmospheres by providing unprecedented wavelength range and sensitivity.
- These different wavelengths allow researchers to monitor the atmosphere from very deep to very shallow.
- If one could actually directly see the cloud-top structure, then probably would be able to see bands and vortices, like the Great Red Spot similar to Jupiter.
- Gases Present: Both have atmospheres dominated by hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of water vapor, methane and carbon monoxide.
- Temperature: The temperature at their cloud tops was about 1,700 degrees Fahrenheit (925 degrees Celsius), similar to a candle flame.
- Significance: In the future, similar techniques could be used to study weather on potentially habitable exoplanets (planets beyond our solar system).
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Brown Dwarfs
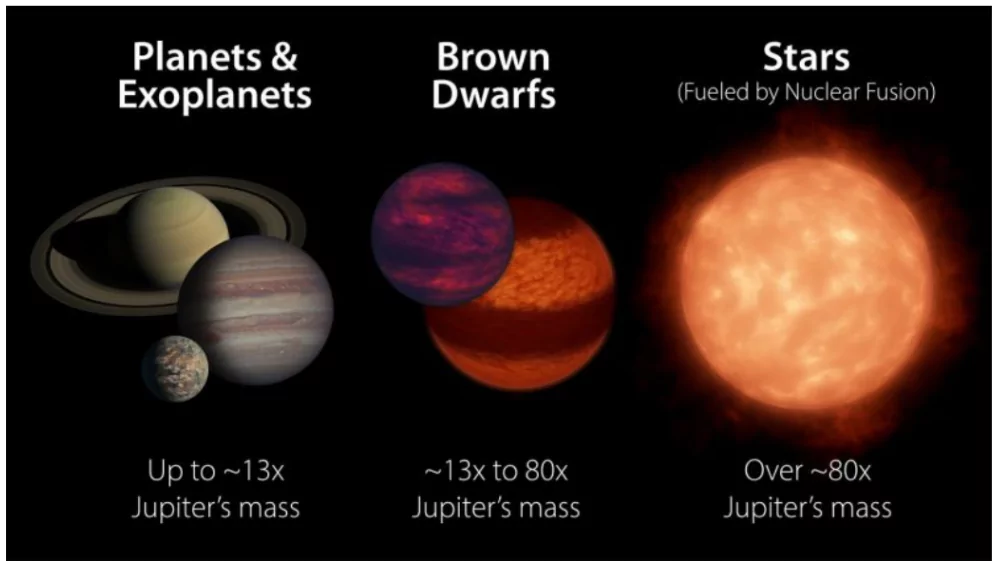
These are celestial bodies that are bigger than a planet but smaller than a star – closest to us and are relatively common and about 1,000 are known.
- Size: Range between that of a giant planet like Jupiter and a small star and mass is up to 80 times greater than Jupiter’s. By comparison, the sun’s mass is about 1,000 times greater than Jupiter’s.
- Composition: Their composition is similar to gas giant planets like Jupiter.
- Clouds by Precipitation: Like planets, but unlike stars, brown dwarfs can also have clouds made out of precipitates in their atmospheres.
- Unlike Earth’s water clouds, the clouds on brown dwarfs are much hotter and likely made up of hot silicate particles – kind of like a very hot Saharan dust storm.
- Composed Elements: They retain lighter elements such as hydrogen and helium more effectively than planets and have a relatively low metal content.
- Emit Light: They give off their own light due to their sheer heat, just like embers in a fire glowing red because of how hot they are.
- Unlike stars, brown dwarfs do not have nuclear fusion occurring at their core.
- They do not have enough mass for their cores to burn nuclear fuel and radiate starlight, which is why they are sometimes referred to as “failed stars”.
About James Webb Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope is an orbiting infrared observatory that will complement and extend the discoveries of the Hubble Space Telescope, with longer wavelength coverage and greatly improved sensitivity.
- Developed by: NASA with the assistance of the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.
- Launched in: It was launched in 2021, with the mission duration of 5-10 years.
- Location in Space: It is placed at Lagrange point 2, approximately 1.5 million km beyond Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
- Size: Webb’s primary mirror is approximately 6.5 metres in diameter, giving it a significantly larger collecting area than the mirrors of the current generation of space telescopes.
- Wavelength: It will provide wavelength coverage from 0.6 to 28 microns (the infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum).
- Objectives:
- Search for the first galaxies and luminous objects formed after the Big Bang.
- Determine how galaxies evolved from their formation until now.
- Observe the formation of stars from the first stages to the formation of planetary systems.
- Measure the physical and chemical properties of planetary systems, including our own Solar System, and investigate the potential for life in those systems.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
![]() 24 Jul 2024
24 Jul 2024
