Context:
- This article is based on an Editorial “Breaking the ice: How India can help save the Arctic” which was published in the Indian Express. This article expresses concerns over the impact of climate change on the Arctic Region and highlights India’s role in maintaining a balance between the competing interests of the Global North and the Global South, which is essential to protect the global climate including Arctic too.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Arctic Region, Northern Sea and Changes in the Arctic Region – How India can help save the Arctic Region.
Relevancy for Mains: Changes in the Arctic Region, Impact of climate change on the Arctic Region – How India can help save the Arctic Region. |
What are the reasons for the changes in the Arctic region?
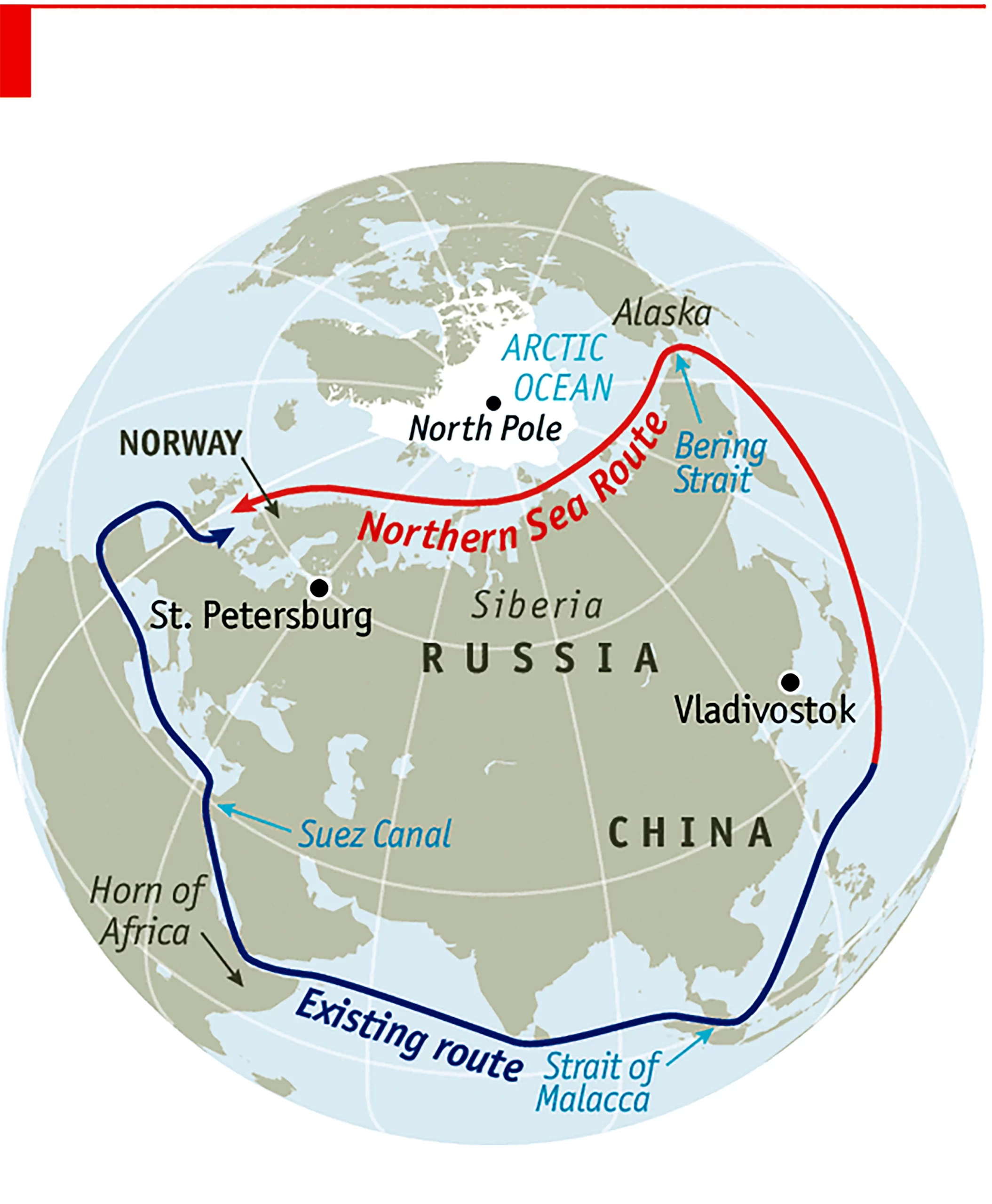
- Rapid Development: Russia is commercializing and expanding trade channels along the Northern Sea Route, while continuing to use and transport high-polluting heavy fuel oil through Arctic waters.
- Growing Geopolitical Tensions: Other Arctic countries are also planning oil and gas development endeavors.
- No Accountability and Monitoring: The only current governance mechanism, the Arctic Council, has been suspended due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine and has made it more difficult to hold countries accountable and to monitor wider activity contributing to changes in the Arctic.
- The Arctic Council: The Arctic Council is a group of eight countries (the US, Russia, Norway, Finland, Sweden, Canada, Denmark, and Iceland) with primary capacity for protecting or exploiting the vital ecosystem.
- Less Inclusive: The Arctic Council does not have any member from the Global South, though some has observer status like India.
Challenges with Continued Arctic Changes
- Faster Warming: The Arctic is warming at a rate four times faster than the global average.
- Ice Loss: It is leading to an unprecedented loss of sea ice, as well as the melting of permafrost.
- Unleashing of Stored Carbon: It risks losing the North Pole’s “great white shield” and releases huge quantities of stored carbon.
- Catastrophic Effects: This can trigger multiple catastrophic and irreversible climate tipping points.
- A tipping point is a critical threshold that, when crossed, leads to large, accelerating and often irreversible changes in the climate system.
- Impact on Global South and India:
- Variation in Rainfall: Recent research shows an intricate correlation between the melting of Arctic sea ice and extreme rainfall events during the Indian summer monsoon, which is crucial to agriculture and livelihoods, making up 80 per cent of South Asia’s rainfall.
How India Can Help Save the Arctic Region – Opportunity and Role for India
- Voice of the Global South: The active involvement of India as a member of the Arctic Council to voice the concerns of the Global South could help push for an end to further exploitation.
- Build Consensus: India holds the potential to forge a united approach to safeguarding crucial global ecosystems, especially the Arctic.
- The New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration demonstrated India’s ability to resolve the conflicting interests of the Global North and the Global South.
- India has a further opportunity to exercise this bridge-building capacity at its proposed virtual G20 Summit, where it can raise the Arctic as part of a constructive conversation on climate governance.
Also read: Antarctica Ice Shelves: 40% Volume Loss in 25 Years
Conclusion:
Climate emergency knows no boundary and impacts in one region can affect the rest of the world, hence, a disproportionate impact on the Global South, consensus-based collective action to mitigate climate impacts in the Arctic is critical.
| Prelims Question (2015)
The term ‘IndARC’, sometimes in the news, is the name of:
(a) An indigenously developed radar system inducted into Indian Defence
(b) India’s satellite to provide services to the countries of Indian Ocean Rim
(c) A scientific establishment set up by India in Antarctic region
(d) India’s underwater observatory to scientifically study the Arctic region
Ans: (d) |
![]() 30 Oct 2023
30 Oct 2023


