Context: This article is based on an Editorial “Food versus Fuel: What’s happening with Centre’s ethanol blending scheme” which was published in the Indian Express. The government recently restricted the sweetener’s diversion for ethanol production in order to increase domestic supply after banning sugar exports.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Biofuels, National Policy on Biofuels, Ethanol Blending, and E20 Petrol
Relevancy for Mains: India’s Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP): Need, Significance, Challenges and Way Forward. |
Why has the government banned sugarcane for ethanol production?
- Estimated Fall in Sugar Production: The decision comes in the backdrop of estimated fall in sugar production in 2023-24 marketing year (October-September).
- Under Directive of Sugar (Control) Order, 1966: As per clause 4 and 5 of this order, the government has allowed use of ‘B-molasses’ for ethanol production in 2023-24.
- Curbing Price Rises: This move is expected to release 1.8-2 million tonne (MT) of sugar in the domestic market which would help curb rise in prices amidst reports of fall in Sugar production.
Know about Sugarcane Production In India here.
About Ethanol
- Also Called As: Ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol.
- Characteristic: An organic chemical, volatile, flammable, colorless with a characteristic odor.
- Production: It is naturally produced by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration.
- Importance: It is used as an antiseptic & disinfectant, as a chemical solvent and is a fuel source.
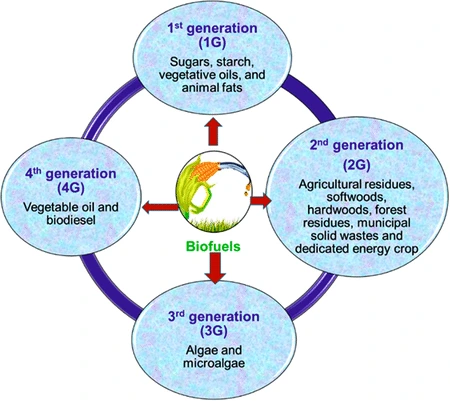
What is Ethanol Blending?
- Energy Efficient Blending: It means blending of ethanol with other relevant fuels to make them more energy efficient. Ethanol can be mixed with gasoline to form different blends.
- Ethanol is produced from plants that use the sun energy, and hence is a renewable fuel.
- Significance of Ethanol Blending: It allows the engine to more completely combust the fuel, resulting in fewer emissions and thereby reducing the occurrence of environmental pollution.
Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP): Aim, Targets and Current Status
- Launched in: The Ethanol Blending Programme was launched in January 2003.
- Aim: The programme sought to promote the use of alternative and environment friendly fuels and to reduce import dependency for energy requirements.
- Used Source: Sugarcane and its by-products like B molasses are the major source of ethanol production in India. Other sources for producing ethanol are corn, rice, and barley.
- Current Ethanol Blending Target: The Indian government has pledged to meet a 20% ethanol blending target by 2025-26.
- This target is referred to as E20 (20% ethanol blending with petrol) by 2025.
- Current Status: In 2022-23 ethanol supply year (November-October), the government achieved 12 per cent blending of ethanol with petrol.
- The target for the current year is 15% for which 690 liters of ethanol would be required.
- Significance: India has met the initial target of 10 per cent ethanol blending in mid-2022, ahead of the targeted timelines of November 2022.
Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP): Advantages
- Reduction in Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) Emissions by 44 to 52% compared to gasoline.
- Reducing Import Dependency by E20 implementation by 2025.
- High Opportunity as by 2050, there will be 3.5-5x biofuels growth due to net zero targets.
- Expectation of High Growth in Ethanol Market (grow at a CAGR of 5.1% by 2032).
Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP): Concerns and Challenges
- Water Scarcity: Currently, ethanol is produced from only sugarcane in India. It would increase the acreage under sugarcane for ethanol production that requires high usage of water.
- Impact on Other Crops: Rise in sugarcane production could potentially put pressure on other food crops and their future availability and prices.
- Priority to Food-based Feedstocks: The ethanol blending target of India primarily focuses on food-based feedstocks which is against the 2018 National Policy on Biofuels.
- Logistics Issues: Currently, the mode of transportation used is road which is expensive and also requires burning fuel in order to carry fuel, which releases GHGs into the atmosphere.
- Inefficient Subsidy Mechanism: FCI is currently purchasing broken rice for PDS, but is supplying it to distilleries at half the price and can impact the rural poor and expose them to hunger risk.
Learn more about the Ethanol Blending Programme Challenges: Food Security vs. Biofuel Goals, here.
Roadmap for India’s Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP)
- Compensatory Increase in Price of Ethanol to ensure sufficient cash flow for sugar mills.
- Priority to Food Crops over Fuel to counter the associated climate change.
- Need to Use Biofuels from Waste to bring both strong climate and air quality benefits.
- Time to Departure from Water Intensive Crops to avoid the issue of water crisis.
Conclusion:
We need to be careful with the Ethanol Blending Programme targets because using human food for biofuels may affect people’s right to enough food, while the existing production and usage of biodiesel do not satisfy demands for environmental sustainability. It’s important to find a balanced approach.
| Prelims Question (2020)
According to India’s National Policy on Biofuels, which of the following can be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels?
1. Cassava
2. Damaged wheat grains
3. Groundnut seeds
4. Horse grams
5. Rotten potatoes
6. Sugar beet
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 5 and 6 only
(b) 1, 3, 4 and 6 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Ans: (a) |
![]() 13 Dec 2023
13 Dec 2023


