![]() 2 Oct 2023
2 Oct 2023

| Relevancy for Prelims: FICCI CASCADE report, UJJAWALA, Illicit Trade, associated International Conventions and the Golden Triangle & the Golden Crescent, Import-Export, NIRVIK Scheme
Relevancy for Mains: Linkages of Organized Crime with Terrorism, Drug Menace in India, Role of FICCI in tracking the illegal trade. |
|---|
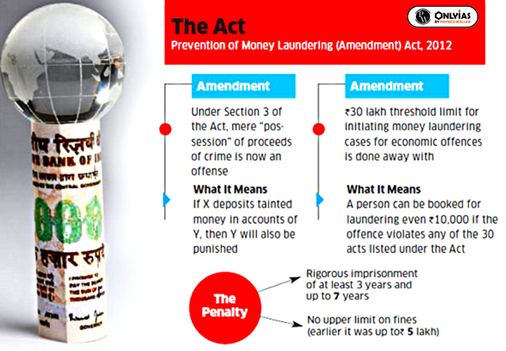
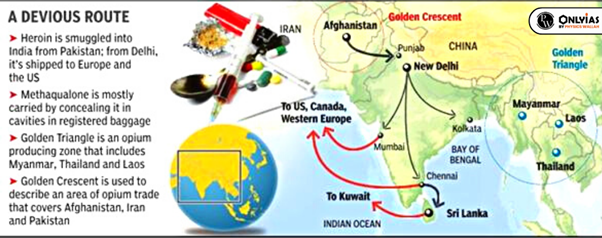
International Conventions to which India is a Signatory:
|
|---|
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question:
Consider the following statements: (2019)
Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2, 3 and 4 only (c) 2 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 Answer – D |
|---|

<div class="new-fform">
</div>