Context:
Recently, the United Nations Secretary-General reiterated about the consequences of the climate catastrophe that has challenged the globe. He said the earth had passed from a warming phase into an “era of global boiling”.
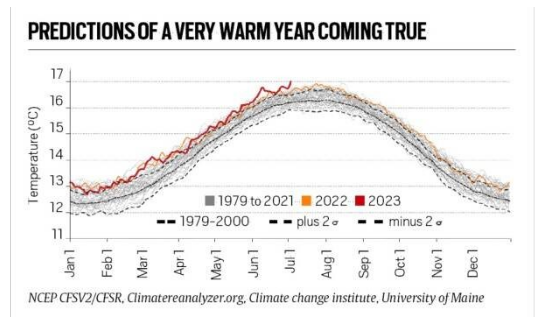
Evidences of Climate Catastrophe:
- Record High Temperature: This July is set to be the hottest month in the last 12,000 years.
- Average July temperature so far has been 16.95° Celsius, 0.2° C warmer than in July 2019, a record in the 174-year observational data of the European Union.
- Unprecedented Condition: Scientists from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the European Commission’s Copernicus Climate Change Service described it as rather remarkable and unprecedented.
Probable Reasons of this Hottest July:
- Transitioning from La Niña to El Niño Conditions: With ocean temperatures on the rise and the Central Equatorial Pacific Ocean transitioning from La Niña conditions (where average sea surface temperatures are below normal) to El Niño conditions (the opposite), it was widely expected that temperatures would be warmer than that in the last three years.
- El Niño:
- It is the warming of the ocean surface, or above-average sea surface temperatures (SST), in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It results with lower than normal monsoon rainfall in India.
- La Niña:
- It is the cooling of the ocean surface, or below-average SSTs, in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It results with higher than normal monsoon rainfall in India.
- Anthropogenic Reasons: Human-induced by burning of fossil fuels and other anthropogenic activities.
Impacts of this High Mercury:
- Temperature in northwest China touching 52° C
- Wildfires in Greece
- The baking heat in the United States’ Southwest
- The extraordinarily high rains in north and western India
- It is due to the warm air increasing atmospheric capacity to hold moisture resulting in short torrential bursts, causing floods and devastation.
- A risk to increase in the frequency of Heat waves
- Risk to livelihood and food security
- Habitation loss especially in coastal areas
- It accelerates the melting of glaciers and the water level of the ocean rises
Way Forward:
- World’s largest economies should be more ambitious with emission cuts.
- Every nation needs to take on a greater share of greenhouse gas mitigation responsibilities.
- There is a need to advance net zero commitments of countries from 2070 to earlier.
- There is an urgent need to shift from use of non-renewable energies to renewable energies.
| Additional Information:
Net-Zero Target:
- It is referred to as carbon neutrality.
- It is a state in which a country’s emissions are compensated by the absorption and removal of greenhouse gases from the atmosphere.
- Absorption of the emissions can be increased by creating more carbon sinks such as forests.
- While the removal of gases from the atmosphere requires futuristic technologies such as carbon capture and storage.
- More than 70 countries have promised to become Net Zero by the middle of the century i.e., by 2050.
- India has promised to cut its emissions to net zero by 2070.
|
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 29 Jul 2023
29 Jul 2023

