Context
In the past, we have seen that there is interdependence between humans, animals, and the environment has been made increasingly evident with the emergence of pandemics such as COVID-19.
| Relevance For Prelims: Health, Role Of Government In Health, Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC), ‘National One Health Mission’.
Relevance For Mains: National One Health Mission – Key Features |
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Key Features of National One Health Mission
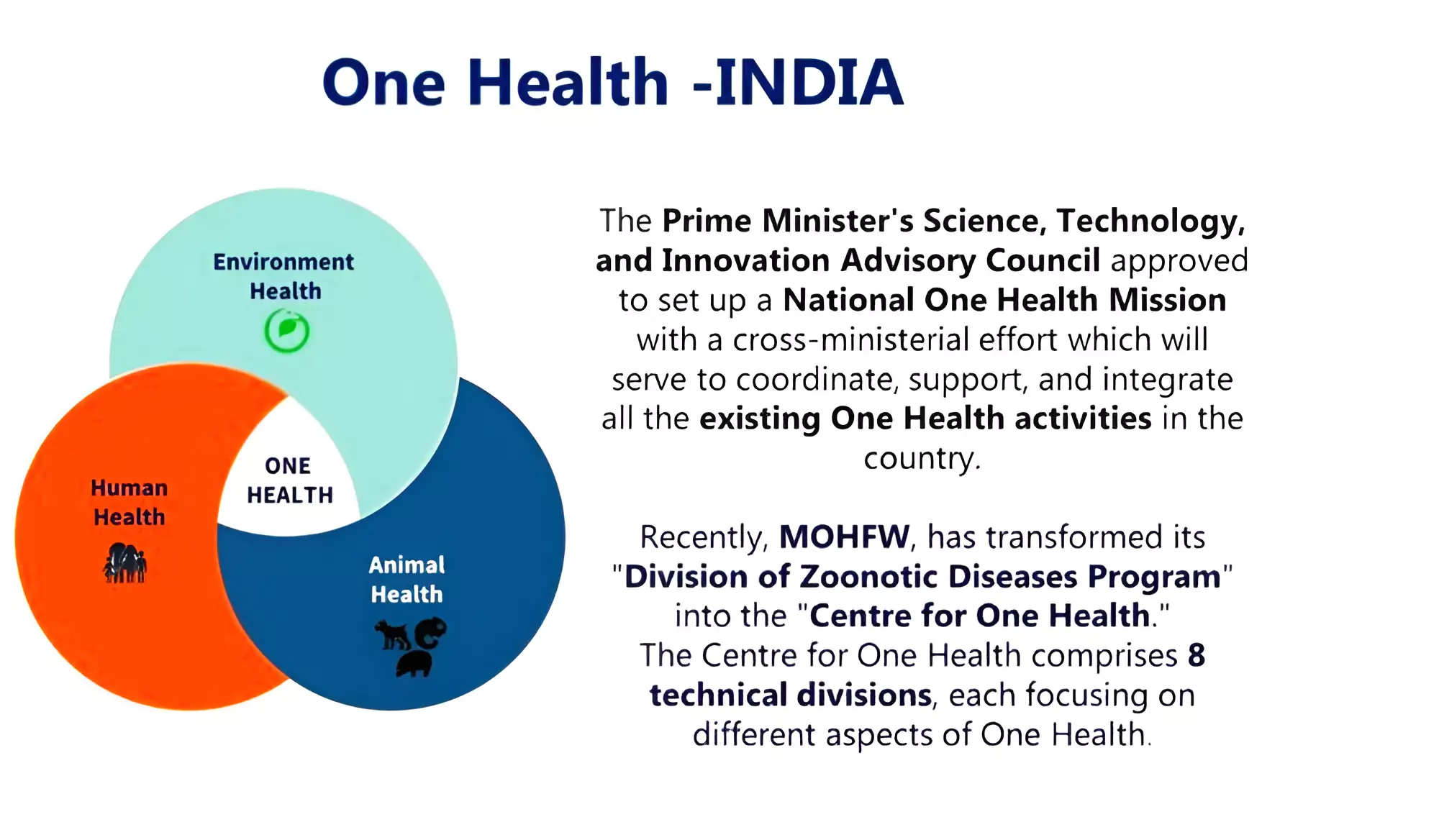
- Founding of National One Health Mission: In July 2022, the Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC) endorsed the setting up of the ‘National One Health Mission’.
- Inter-Sectoral Collaboration: The purpose of the mission is to organize, support, and integrate all existing One Health projects in the country, including the Ministries of Health and Family Welfare, Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairy, Environment, and Science and Technology.
- Integrated Disease Surveillance: The mission executes integrated disease surveillance in the human, animal, and environmental sectors to combat communicable diseases, including zoonotic diseases, as well as improve overall pandemic preparedness and disease control.
- For Example: Other diseases such as canine distemper affect wild animals and their conservation.
- Coordinated Approach: Only a coordinated approach will ensure that we are better prepared for diseases that can cause the next pandemic such as avian influenza or Nipah.
- Integrating all Stakeholders: It is not just government departments but also our academic centers and the private sector that will be the critical stakeholders in making this a reality.
- Establishment of Laboratories: Under the mission, a national network of high-risk pathogen (Biosafety level or BSL 3 and BSL 4) laboratories has been created.
- Convergence among Laboratories: Bringing such laboratories that are managed by different departments together will serve to address the disease outbreak response better regardless of human, animal and environmental sectors.
- Better Resource Utilization: There will be better resource utilization of expensive but much-needed infrastructure but also good linking from across sectors better to tackle diseases
- such as Nipah that involve bats, pigs, and humans, for example.
- Enhancing Coordination Capacity: Under the mission, efforts are being made to apply artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning and disease modeling to address these issues and coordinate capacity building in epidemiology across sectors.
- Genomic Surveillance: Emerging approaches such as genomic surveillance from wastewater showed promise during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- This will be expanded to other sentinels such as places where animals (livestock or wildlife) congregate for a broader set of diseases to be taken up.
- Global Agenda of One Health: One Health’ is a global topic. During India’s presidency of the G-20, this approach was highlighted and widely endorsed by all the members.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
One Health’ requires close engagement of not just different governmental agencies but also non-governmental organizations, academia, the private sector and also citizens.
Also Read: ADB Report On Health Emergency Preparedness
| Prelims PYQ (2020):
Consider the following pairs International agreement/set-up Subject
1. Alma-Ata Declaration – Healthcare of the people
2. Hague Convention – Biological and chemical weapons
3. Talanoa Dialogue – Global climate change
4. Under2 Coalition – Child rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c) |
![]() 11 Apr 2024
11 Apr 2024


