Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: Over-The-Top (OTT) Communication Services, OTT Platforms, OTT Regulation, OTT Platforms, and Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI).
Relevancy for Mains: Over-The-Top (OTT) Communication Services, its comparison with Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) and its associated challenges and needed measures. |
What are Over-The-Top or OTT Platforms?
- It refers to the audio and video hosting and streaming services that have evolved from content hosting platforms to creators and distributors of various types of content.
- Examples: Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, Hulu, HBO Max, and many others.
- Current Regulation in India: As of now, there are no specific laws or rules for OTT regulation in India.
Why is OTT regulation important?
- Regulation and Charges: Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) argue that OTTs should be subject to regulation and fees as they heavily rely on the existing telecom infrastructure developed by TSPs.
- Revenue Erosion: TSPs claim that OTT communication services have resulted in a decline in their revenue streams by the shifting of consumer behavior towards OTT.
- Regulatory Parity: TRAI contends that telecom operators and OTT platforms, like WhatsApp, provide similar services but are subject to different regulatory requirements.
- Licensing Requirements: OTT communication service providers offer voice calls, messaging, and video call services without holding licenses unlike Telecom operators.
- Legal Framework: Telecom service providers in India are governed by various laws, including the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885, the Wireless Telegraphy Act, 1933, and the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, 1997, which do not currently apply to the OTT services.
- Financial Contribution: OTT services don’t make any financial contributions for expansion of telecom services, while telecom operators are obligated to contribute to the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) for promotion of telecom services in underserved areas.
- National Security and Public Order: For proper OTT regulation, OTT platforms should be subject to lawful interception and monitoring by security agencies to prevent the dissemination of misinformation, incitement of violence, or facilitation of criminal activities.
ALSO READ: INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
What are the challenges for OTT regulation in India?
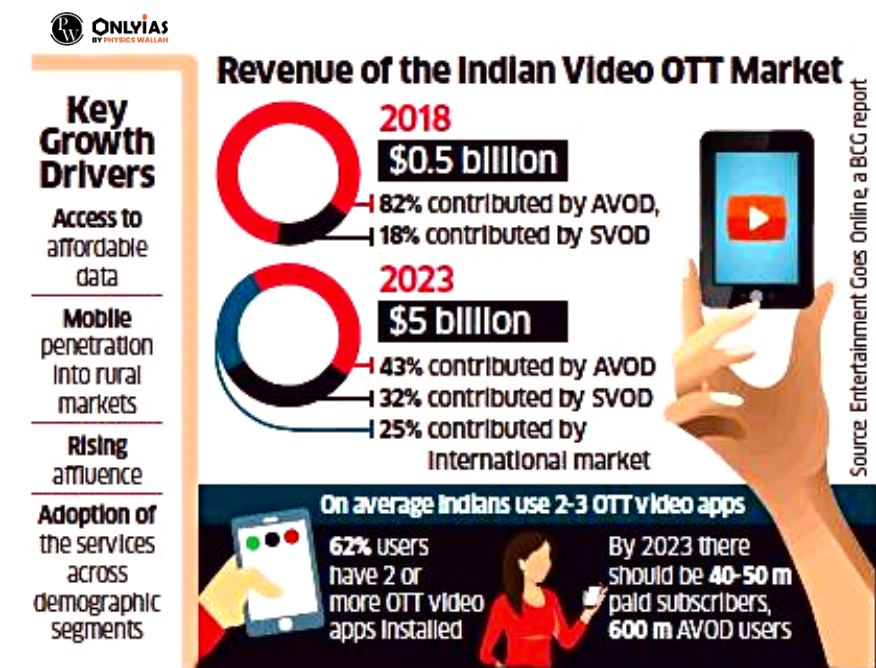
- Volume and Accessibility: India’s OTT viewership stands at 43 million people and is projected to rise up to 50 million by the end of 2023.
- Media Freedom Concerns: OTT Regulation efforts have faced backlash due to concerns over media freedom, with critics fearing it could stifle free speech and expression.
- Differences from Traditional Media: OTTs differ significantly from conventional media, covering more liberalized and diverse themes, challenging conventional censorship paradigms.
- Foreign Content and Enforcement: Regulating content from foreign countries poses enforcement challenges, leading to concerns about piracy.
- Increasing Legal Challenges: Producers of web series and films face legal challenges and petitions for content removal, adding to the complexity of regulation as observed in web series Tandav, whose producers are charged with offenses under the IPC,6 and the IT Act.
What are the solutions for the OTT regulation?
- Need of a Hybrid Governance Model which involves establishment of an independent self-regulatory body, appeal mechanism, involvement of a quasi-judicial body and to ensure speedy resolution.
- Need for an impartial OTT regulation body to oversee content on OTT platforms.
- Strict implementation of Legislation like Draft Indian Telecommunication Bill, 2022 which proposes to expand the definition of “telecommunication services” to encompass OTT communication services.
- This expansion would mean to apply licensing conditions over OTTs platforms and need to hold a Unified Access Service License (UASL).
Conclusion
The ongoing debate around the OTT regulations in India highlighted that we need a fair system. It also calls for strict enforcement of new laws, like the Draft Indian Telecommunication Bill, 2022, which suggests putting rules on OTT services to make sure they follow the same conditions as traditional telecom services.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
In India, which of the following reviews the independent regulators in sectors like telecommunications, insurance, electricity, etc.? (2019)
- Ad Hoc Committee set up by the Parliament.
- Parliamentary Department Related Standing Committee.
- Finance Commission.
- Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission NITI Aayog
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2
- 1, 3 and 4
- 3, 4 and 5
- 2 and 5
Ans: D |
![]() 7 Oct 2023
7 Oct 2023


