Context:
Recently, the Foreign Ministers of India and the Philippines met at the fifth meeting of the Philippines-India Joint Commission on Bilateral Cooperation in New Delhi and outlined the path for a strengthened bilateral partnership between both countries in the 21st century.
South China Sea:
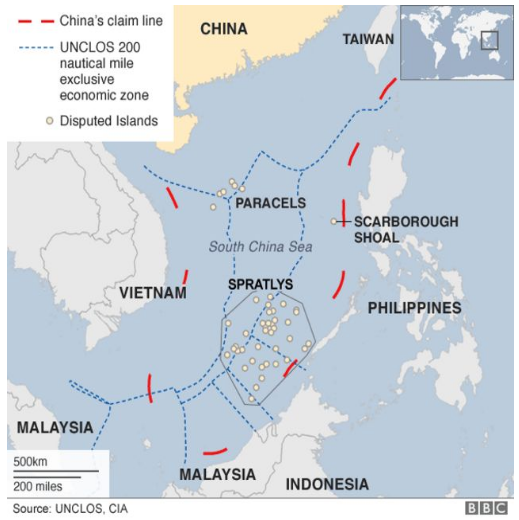
Image Source: BBC
Location:
- It is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean.
- A marginal sea is partially covered by land and connected to a larger ocean or sea.
- The South China Sea is connected by Taiwan Strait with the East China Sea and by Luzon Strait with the Philippine Sea.
South China Sea Dispute:
- Claiming Members of the Islands located in the South China Sea:
- The Paracel Islands: China, Taiwan and Vietnam.
- The Spratly Islands: China, Taiwan, Vietnam, Brunei and Philippines.
- The Scarborough Shoal: Philippines, China and Taiwan.
- China’s Assertion: China claims almost the entirety of the resource-rich sea, and
- China’s claim to the sea is based both on the Law of the Sea Convention and its so-called nine-dash line, which extends for 2,000 Km from the Chinese mainland, encompassing over half of the sea.
Case in Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA):
- The Philippines had submitted a case of arbitration to the Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA) in 2013 to settle disputes with China.
- Despite China’s formal withdrawal from the arbitration, the proceedings continued as scheduled under UNCLOS guidelines.
- The UNCLOS’ Annex VII stipulates: “The absence of a party or the failure of a party to present its case shall not be a bar to the proceedings.” The PCA finally released the Award on July 12, 2016.
- Judgment by the PCA:
- Final Decision: The PCA unanimously favored the Philippines and its decision is “final and binding” in accordance with UNCLOS Article 296 and Article 11 of Annex VII.
- Unfounded Nine-dash Line: It further stated that any prior claims to resources situated inside the “nine-dash line” were unfounded.
- Environment Degradation: China has inflicted irreparable harm to the maritime environment and destroyed evidence of the natural condition of features in the South China Sea.
- Violation of Sovereignty: China has violated the sovereign rights of the Philippines in its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) by:
- interfering with Philippines’ fishing and petroleum exploration
- constructing artificial islands
- failing to stop Chinese fishermen from fishing in the zone
- China had no legal basis for asserting historic rights to resources located within the sea areas under the Tribunal’s jurisdiction.
- Construction Activities & Military Installations: However, the Tribunal did not rule that construction activities on the disputed islands by China was unlawful and there is nothing in the decision which would make it unlawful for China to construct military installations on the islands it occupies, with the exception of Mischief Reef.
Why did China refuse to take part in the case?
- China has argued that the tribunal does not have jurisdiction, because it involves sovereignty issues, which are outside the tribunal’s legal purview.
India’s Stand:
- While India reiterated its consistent position on adhering to international law, but departed from its earlier positions by call to respect the 2016 Arbitral Award on the South China Sea.
- India has maintained that it is not a party to the South China Sea dispute.
- However, as per Act East Policy, India has started internationalizing disputes in the Indo-Pacific region to oppose China’s threatening tactics in the South China Sea.
- India has also deployed its navy with Vietnam in the South China Sea for protection of sea lanes of communication (SLOC), denying China any space for assertion.
- India’s membership as a Quad member is also to counter China’s tactics.
Significance of the South China Sea:
- Strategic Location: The South China Sea is a crucial maritime gateway and junction for shipping between the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- Any confrontation will be a danger to regional and global security.
- Geopolitical Importance: According to the United Nations Conference on Trade And Development (UNCTAD) one-third of the global shipping passes through it, carrying trillions of trade which makes it a significant geopolitical water body.
- Natural Resources: The sea is believed to have abundant natural resources, including fisheries and potential oil and gas reserves.
- More than half of the world’s fishing vessels are in the South China Sea, and millions of people depend on these waters for their food and livelihoods
Areas of Cooperation between India and Philippines:
- Defense: Open the resident defense attaché office in Manila (Philippines Capital), regular official-level interaction among defense agencies, consideration of India’s offer for concessional Line of Credit to meet Philippines’ defense requirements.
- Maritime Security: Expansion of training and joint exercises on maritime security and disaster responses, information exchange, and commencing a maritime dialogue.
- Boosting cooperation between the Coast Guards of the two countries
- Acquisition of naval assets by Manila under a concessional line of credit from Delhi
- The agreement on regional and multilateral issues, particularly on maritime highways such as the South China Sea.
- Cyber Security: Both share cooperation in anti-terrorism measures, intelligence exchange, cyber security, Artificial Intelligence and space cooperation.
Conclusion:
- Free and stable marine commons are crucial to global trade and economy and all nations have to work in collaboration for a prosperous and conductive environment.
- Despite the fact that the PCA declared its decision, the reality on the ground has not altered.
- It could only be solved through a political framework, which can only be created through dialogue and here the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) can play an important role, which requires greater understanding among members.
| Additional Information:
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), 1982:
- Also known as the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty
- Its classified maritime zones:
- Internal Water – Bays, Ports, Inlets, Rivers, and lakes
- Territorial Sea – Up to 12 nautical miles
- Contiguous Zone – Up to 24 nautical miles
- Exclusive Economic Zone – Up to 200 nautical miles
- High Seas – The common heritage of all
Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA):
- Established: By the Convention for the Pacific Settlement of International Disputes, concluded at The Hague in 1899
- The convention was revised in the second Hague Peace Conference in 1907
- Headquarter: The Hague, Netherland
- Settles Disputes: Between member states, International organizations or private parties, like territorial and maritime disputes, sovereignty, human rights, International investments and regional trade etc.
- Rulings: Binding in nature. However, it has no powers to enforce its rulings.
- It is the first permanent intergovernmental organization to provide arbitration.
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN):
- A regional organization: Established in 1967, by Bangkok Declaration, to promote political and social stability among the Asia-Pacific’s post-colonial states with the motto of “One Vision, One Identity, One Community.
- Secretariat – Jakarta, Indonesia
- Members: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar and Cambodia
|
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 13 Jul 2023
13 Jul 2023

