Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: IPRD 2023, South China Sea Dispute and Permanent Court of Arbitration.
Relevancy for Mains: the South China Sea, its associated challenges, and steps that need to be taken. |
The South China Sea Dispute and the Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA):
- The Philippines had submitted a case of arbitration to the PCA in order to settle South China Sea disputes.
- Despite China’s formal withdrawal from the arbitration, the proceedings continued as the UNCLOS’ Annex VII stipulates that the absence of a party or the failure of a party to present its case shall not be a bar to the proceedings.
- Release of Award: On July 12, 2016, in accordance with UNCLOS Article 296 and Article 11 of Annex VII, the PCA denied China’s assertion in the South China Sea.
- The Tribunal also found that “China has violated the Sovereign rights of the Philippines in its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) by:
- interfering with Philippines’ fishing and petroleum exploration.
- constructing artificial islands.
- failing to stop Chinese fishermen from fishing in the zone.
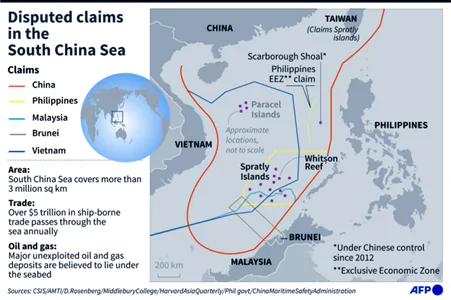
Strategic Importance of South China Sea (SCS)
- Global Shipping Lane: More than $3 trillion in trade passing through its waters annually.
- Fishing Ground: It is home to rich fishing grounds that provide for the livelihoods of millions.
- Energy Reserves: It has proved oil and gas reserves.
- Energy Routes: Significant energy routes for East Asian countries to transport oil and natural gas.
Also Read: Indo-Pacific Region
Strategic Importance of the South China Sea (SCS) for India
- Economic Significance:
- Sea Lanes of Communication (SLOCs): Nearly 55% of India’s trade transits through it.
- Energy Resources: India seeks to explore the vast reserves of oil and natural gas.
- Maritime Connectivity: The SCS is a key link in India’s Act East Policy.
- Security Significance:
-
- Freedom of Navigation: India is a staunch supporter of freedom of navigation.
- Countering China’s Expansionism: India seeks to balance it by strengthening its own maritime capabilities and deepening its ties with regional partners.
- Protecting Indian Ocean Interests: Maintaining a stable and rules-based order in the South China Sea is crucial for safeguarding India’s interests in the Indian Ocean region.
- Geopolitical Significance:
-
- Emerging as a Regional Power: With a vested interest in shaping the Indo-Pacific order.
- Strengthening Alliances: With the US, Japan, Australia, and ASEAN countries.
- Promoting a Rules-Based Order: For the prevalence of international law and norms.
Other Recent Developments in the Region
- 10-Dash Line: China recently published a new standard map for 2023, often referred to as the 10-dash line,’ which extends its territorial claims far beyond its recognized EEZ.
- Building Artificial Islands: China continues the world’s largest island-building campaign, in complete disregard of international law.
- Gray Zone Activities: These are a form of slow-intensity conflict that China has increasingly employed over the last year to assert its territorial claims in the SCS.
Concerns with China’s Expansion
- Fishing ban: China arbitrarily imposed a ban since 1999.
- Legal actions: Article 22 of the Coast Guard Law, 2021 of China enables the China Coast Guard to use weapons that infringe on China’s sovereign rights and jurisdiction at sea.
Way Forward
- Need of diplomatic engagement and dialogues
- Participation in negotiations for a legally binding, comprehensive, and effective Code of Conduct.
- Maritime Cooperation by the Southeast Asian nations with SCS claims.
- Defence Cooperation to counter China’s aggressiveness.
- Economic Cooperation to explore the possibility of negotiating free trade agreements. Indo-Pacific Economic Framework would be key in this regard.
- Humanitarian Aid and relief packages will help in building mutual trust and friendship.
- Science and Technology have the potential to mutually benefit concerning countries.
Conclusion:
The South China Sea dispute, highlighted at the IPRD 2023, underscores the precarious situation, urging diplomatic solutions for stability and adherence to international law in the region.
| Prelims Question (2022)
Which one of the following statements best reflects the issue with the Senkaku Islands, sometimes mentioned in the news?
(a) It is generally believed that they are artificial islands made by a country around the South China Sea.
(b) China and Japan engage in maritime disputes over these islands in the East China Sea.
(c) A permanent American military base has been set up there to help Taiwan to increase its defence capabilities.
(d) Through International Court of Justice declared them as no man’s land, some South-East Asian countries claim them.
Ans: (b) |
![]() 21 Nov 2023
21 Nov 2023


