Context:
- This article is based on an Editorial “Stubble fires witness spike in Punjab; 63% rise since 2022” which was published in the Hindu. As the the key Kharif season crop (paddy) harvest gains pace in Punjab, the perennial problem of stubble burning is also rising.
- In Punjab, the ban and action against people burning crop residue are regulated under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Stubble Burning in Punjab, Crop Residue Management Guidelines and innovative farm technologies.
Relevancy for Mains: Crop Burning, its associated concerns, measures taken by the government to control it, measures needed to be taken further – 15-Point Winter Action Plan. |
What is the concept of stubble burning?
- A Practice of removing agricultural waste from the field by setting on fire the straw stubble (parali) that is left on the land after harvesting of grains like paddy, wheat etc.
- Region: Mainly in the Indo-Gangetic plains of Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh.
- A Crime: Burning crop residue is a crime under Section 188 of the IPC and under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act.
ALSO READ: CLIMATE CHANGE & MITIGATION STRATEGIES
What are the problems related to stubble burning?
- Air Pollution: Each year, air pollution levels rise due to stubble burning and the Air Quality Index (AQI) reaches a ‘severe’ and ‘hazardous’ level.
- Heat Penetration: Stubble burning generates heat that penetrates the soil, causing an increase in soil erosion, loss of useful microbes and moisture, leading to soil degradation and its fertility.
- Lack of Political Will: As farmers are an important political constituency, the state government adopted a soft approach.
- Lack of Viable Alternatives: Although farmer outfits in Punjab are against the burning of stubble, they would continue it without a viable alternative or financial incentive.
- Harmful Health Impacts: Stubble burning emits toxic pollutants in the atmosphere containing harmful gases like Carbon Monoxide (CO), methane (CH4), carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and volatile organic compounds (VOC).
- Global Warming: Pollution and greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) lead to global warming. These are also responsible for the haze in Delhi and the melting of Himalayan glaciers.
ALSO READ: POLLUTION AND ITS EFFECTS ON HEALTH
What is the solution for stubble burning issue? – Way Forward
- Need to subsidize innovative farm technologies like happy seeder, rotavator, baler, paddy straw chopper, etc. are costly but they could help farmers to manage crop residues effectively.
- It’s time to use new and improved seed varieties like Pusa Basmati-1509 and PR-126, which mature quickly and also improve the quality of the soil. Using Bio-Waste Decomposers which increase the Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR).
- Sustainable farm management practices, which could not only manage the crop residues but also help control Green House Gases emissions.
- Educating and Empowering the Stakeholders is important for better utilization of agricultural waste for financial and environmental gains.
- Need to adopt best practices of other state governments like:
- The Punjab government instructed brick kiln owners to replace at least 20 percent of coal with paddy straw pellets for fuel.
- In Chhattisgarh Gauthans Model, the paddy growers donate the crop residues in thousands of Gauthans (cattle shed premises for conservation and augmenting livestock) where it is used as fodder.
How is the government taking action to tackle the problems associated with stubble burning?
- National Policy for Management of Crop Residues for control of burning of crop residue by promotion of in-situ management (incorporation in soil, mulching) of crop residue.
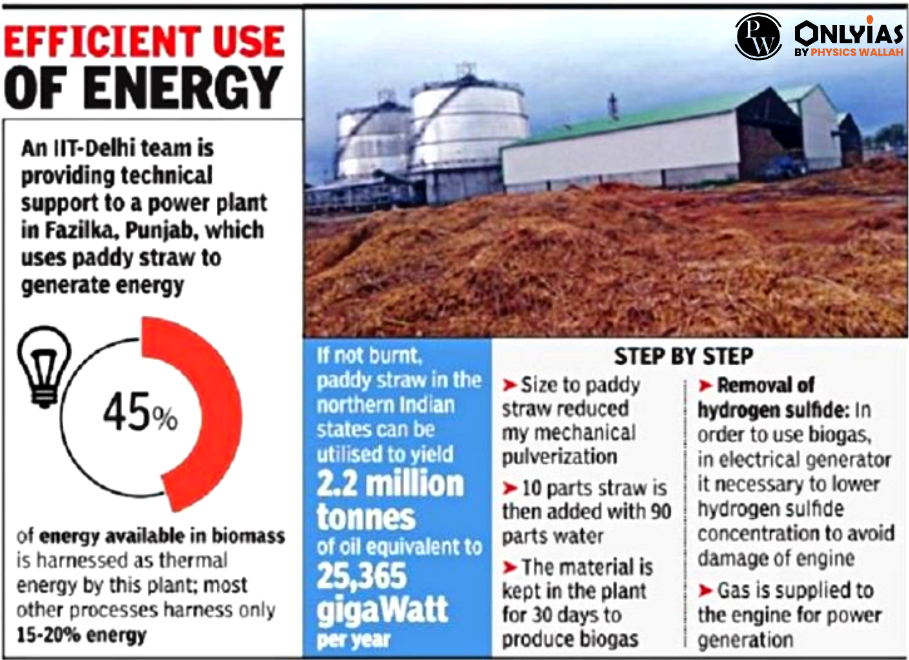
- Waste to Energy Programme under the National Bioenergy Programme for the generation of biogas, bioCNG, power, and syngas from urban, industrial and agricultural residues.
- Crop Residue Management Guidelines for efficient ex-situ management of paddy straw.
Conclusion
Addressing the challenge of stubble burning requires a collaborative effort, emphasizing innovative technologies, government initiatives, and sustainable farming practices.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
What is/are the advantage/ advantages of zero tillage in agriculture?
- Sowing of wheat is possible without burning the residue of previous crop.
- Without the need for a nursery of rice saplings, direct planting of paddy seeds in the wet soil is possible.
- Carbon sequestration in the soil is possible.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Ans: D |
![]() 9 Oct 2023
9 Oct 2023


