Answer:
|
How to approach the question
- Introduction
- Write briefly about the conquest of Bengal.
- Body
- Write the significance of the conquest of Bengal for the British rule in India.
- Write the economic, administrative, and political impacts of the conquest of Bengal.
- Conclusion
- Give appropriate conclusion in this regard
|
Introduction
The British completed the conquest of Bengal after the Battle of Plassey in 1757 by defeating the Nawab of Bengal, Siraj ud-Daulah and the Battle of Buxar, 1764 where they triumphed over a combined force of the Nawab of Awadh, the Mughal Emperor, and the Nawab of Bengal.
Body
Significance of the conquest of Bengal for the British rule in India:
- Economic Wealth: Bengal was known as the “Richest province in the world” at the time of its conquest. It became a valuable source of revenue and wealth for the British on account of its flourishing textile industry.
 Treaty of Allahabad (1765): After the Battle of Buxar, it granted them the Diwani rights, which allowed them to collect taxes and administer the region of Bengal.
Treaty of Allahabad (1765): After the Battle of Buxar, it granted them the Diwani rights, which allowed them to collect taxes and administer the region of Bengal.- Expanding British Influence: British implemented their administrative system and governance models in Bengal serving as a blueprint for their rule in other parts of India. It provided a strong foothold for the British East India Company acting as a stepping stone for further territorial acquisitions in other parts of India.
- Commercial Dominance: The British used their control over Bengal’s trade and its prosperous industries such as silk, cotton, indigo etc to promote their own commercial interests to bolster their own economy.
- Cultural influence: English became the language of administration and education, leading to a gradual erosion of traditional Bengali culture and the emergence of an anglicized elite.
- Military dominance: They established military cantonments and recruited Indian soldiers, who played a crucial role in maintaining British control across India.
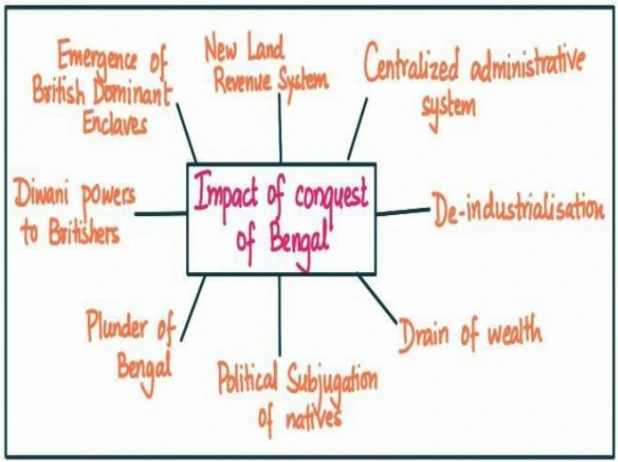
Economic, Administrative and Political impact of the conquest of Bengal
- Administrative and Political impacts:
- Dual government: It led to administrative breakdown in Bengal and proved to be disastrous for the people.
- Political subjugation: It marked the beginning of British political dominance in India. The conquest of Bengal served as a precedent for the British to employ similar tactics and strategies in their further expansion and consolidation of power in India.
- Administrative centralization: The British introduced a centralized administrative system, with the appointment of British officials and the imposition of English law, undermining traditional systems of governance.
- Rebellion and resistance: The most notable example is the Sanyasi revolt and Fakir uprising.
- Demographic shifts: With an influx of British officials, traders, and settlers led to the emergence of British-dominated enclaves.
- Economic impact:
- Plunder of Bengal: The company and its officials misused their position and carried out what is called “Plunder of Bengal”.
- Deindustrialization: For example, the British levied heavy taxes on local industries such as textiles and agriculture, causing a decline in indigenous economic activities.
- Drain of wealth: Bengal’s wealth was systematically drained by the British through extortionate taxes, forced cultivation of cash crops, and the export of raw materials.
- Land revenue system: They introduced the Permanent Settlement in Bengal in 1793, which led to the concentration of land in the hands of a few wealthy landlords.
Conclusion
The conquest of Bengal had far-reaching implications on British rule in India. It consolidated economic control, expanded British dominion, centralized political power, weakened Indian rulers and shaped the course of Indian history.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
 Treaty of Allahabad (1765): After the Battle of Buxar, it granted them the Diwani rights, which allowed them to collect taxes and administer the region of Bengal.
Treaty of Allahabad (1765): After the Battle of Buxar, it granted them the Diwani rights, which allowed them to collect taxes and administer the region of Bengal.
Latest Comments