Answer:
|
How to approach this question?
- Introduction
- Body
- Describe the characteristics of ITCZ.
- Explain the relation of ITCZ to global atmospheric circulation.
- Conclusion
- Conclude on the basis of the above points.
|
Introduction
The ITCZ is a low-pressure belt near the equator (between 5 degrees N and 5 degrees S latitudes) where trade winds from both hemispheres converge, causing upward movement of warm, moist air, resulting in clouds, frequent rainfall, and thunderstorms.
Characteristics of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ):
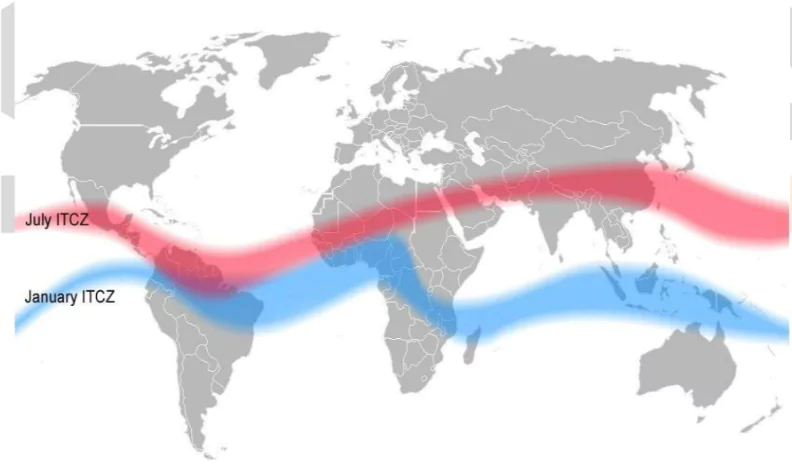
- Convergence of Trade Winds: It is the convergence zone where the trade winds from the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere meet and ascend due to the Earth’s rotation and Coriolis effect.
- Low-Pressure Area: The ITCZ is characterized by low atmospheric pressure, which results from the rising warm and moist air.
- Frequent Precipitation: The convergence of moist air creates a region of abundant rainfall and thunderstorms, making it one of the wettest areas on Earth.
- Seasonal Movement: The ITCZ shifts its position northward during the Northern Hemisphere’s summer and southward during the Southern Hemisphere’s summer, following the apparent movement of the Sun. This seasonal movement influences the wet and dry seasons in tropical regions.
Body
Relation to the Global Atmospheric Circulation:
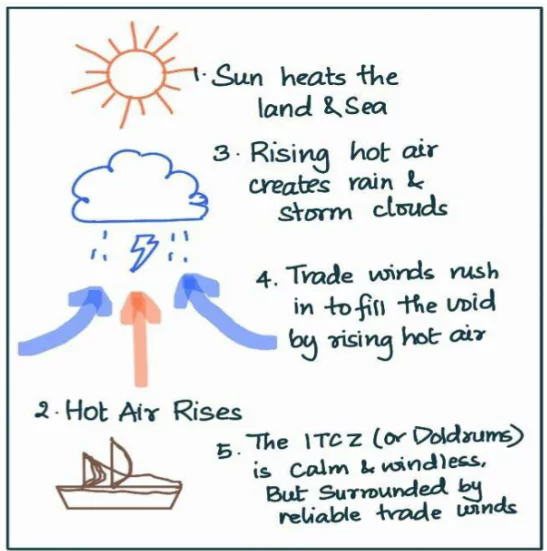
- Hadley Cell Circulation: The ITCZ is part of the Hadley cell, where warm air rises near the equator, creating low pressure in the ITCZ. This air moves poleward at higher altitudes, forming high-pressure subtropical highs.
- Trade Winds: The convergence of air in the ITCZ generates trade winds that blow from east to west in the tropics, influencing ocean currents and tropical weather patterns.
- Monsoons: The seasonal movement of the ITCZ leads to shifting monsoons, bringing heavy rainfall as it moves northward during Northern Hemisphere summer and southward during Southern Hemisphere summer.
- Rainfall Distribution: The ITCZ is associated with abundant rainfall and intense convection, serving as a primary source of precipitation in the tropics and influencing global rainfall patterns.
- Climatic Zones: The ITCZ defines distinct climatic zones, with tropical climates near the equator experiencing high temperatures and high precipitation. Its movement affects the boundary between tropical and subtropical regions, impacting climate and vegetation patterns.
Conclusion
The ITCZ is an integral part of the global atmospheric circulation, specifically the Hadley cell. It influences the movement of air masses, formation of trade winds, and distribution of rainfall on a global scale. ITCZ and global atmospheric circulation together contribute to the weather patterns, climate variations, and ecosystem dynamics in different parts of the world.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.



Latest Comments