Answer:
|
How to approach the question
- Introduction:
- Write about the Indian federal polity.
- Body
- Highlight the mechanism for central control over state governments.
- Conclusion
|
Introduction
In order for a federal system to function effectively, it is crucial to have a high level of harmony and cooperation between the central and state governments. The Constitution of India includes detailed provisions that facilitate cooperation between the center and states. These provisions primarily serve as methods of control exercised by the Union over the states, ensuring coordination and effective functioning of the federal system.
Mechanisms for central control over state governments in India:
- Legislative Jurisdiction: The Constitution clearly defines the territorial extent of legislation, outlining the authority of the center and the states in their respective territories.
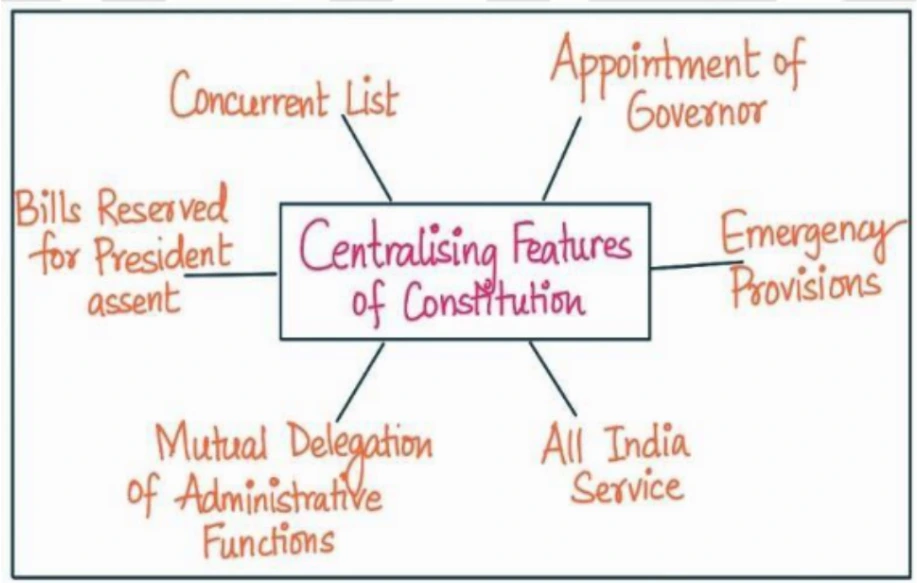
- 7th Schedule: It categorizes subjects into the Union List, State List, and the residuary list, effectively delineating the legislative powers of each level of government.
- Parliament’s Control: Provisions such as Article 249 enable the Rajya Sabha to pass resolutions, granting Parliament the authority to legislate on specific subjects of the state list in the national interest.
- Emergency Provisions: During a national emergency or President’s rule (as per Articles 352 and 356), Parliament gains the power to legislate on matters within the state list.
- Consent-based Legislation: Parliament can pass laws for multiple states with their consent (Article 252) and enact legislation to give effect to international laws (Article 253).
Some other Methods of Control:
- Reserved Bills and Presidential Sanction: The Governor can reserve certain bills for the President’s consideration, and prior sanction of the President is required for introducing specific bills in state legislatures.
- Article 365: It empowers the Center to issue directives to the state administration when there is non- compliance with constitutional provisions or inadequate performance by the state government.
- Mutual Delegation of Administrative Functions: Center and states can mutually delegate administrative functions to foster cooperation and efficient governance.
- All India Services: As per Article 312, the provision of All India Services ensures administrative continuity and promotes cooperation between the center and the states.
- NITI Aayog Initiatives: Recent initiatives by NITI Aayog aim to promote cooperative federalism and enhance coordination between the center and states.
Overall, these measures illustrate the various mechanisms available to the Union for exercising control over the states, ensuring cooperation and effective functioning within the federal system. These provisions are essential for the successful functioning of a federation and create the groundwork for effective cooperation and coordination between the central and state governments.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


Latest Comments