Answer:
Approach:
- Introduce the answer by highlighting why the Indian Constitution is called a borrowed document.
- In the body of the answer, discuss in detail the reasons for the same.
- In the second part of the body, highlight why such a perception is a myth.
- Conclude the answer by giving a quote or stating a fact in support of your argument.
|
Answer:
In a constitutional democracy such as India, the Constitution serves as the highest legal authority. Because many significant elements of the Indian Constitution were drawn from other sources, some critics believe it to be a borrowed document. such as:
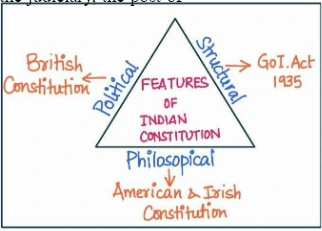
- Structural Elements – The GOI Act of 1935 is Quoted in several structural elements of our constitution, including the federal system, the judiciary, the post of governor, etc.
- Legislative Parts of the Constitution, such as the cabinet system, rule of law, and parliamentary form of government, have all been adopted from the British Westminster system.
- The Philosophical Part of the Constitution: The American and Irish constitutions served as the inspiration for several laws, such as the Fundamental Rights and the Directive Principles of State Policies (DPSPs).
- French Constitution– The ideals of liberty, equality and fraternity are inspired by the French Constitution.
- South African Constitution-The details of the Constitutional Amendment have been borrowed from the South African Constitution.
As a result, critics referred to it as a “bag of borrowings” or “hotch-potch Constitution.” But such allegations are only a myth:
- Overlapping Principles: In all democratic constitutions around the world, there are some fundamental elements that are shared. Also, the Indian constitution was drafted in the late 1940s, by which time the majority of constitutional ideas had already been adopted by many other nations.
- Modification in Indian Context: The Constituent Assembly adjusted the clauses in accordance with Indian requirements and aspirations rather than slavishly copying them. Eg. “complete separation of state from religion” is the concept of secularism in the West. However, in India it is “the state treats all religions equally”.
- Social Inclusion: The Indian Constitution has tried to encompass the needs of minorities and the backward sections of society. E.g., special provisions for Scheduled and Tribal areas in the constitution.
- Organic Document: The Indian Constitution is a living document that has the ability to evolve with the changing times and thus remains relevant and sensitive to contemporary developments. Eg., Right to privacy, Panchayati Raj system, etc.
The Indian Constitution’s creativity can be seen in the way it arranges and changes several fundamental ideas in accordance with Indian ambitions. As Dr B.R. Ambedkar said, “All constitutions, in their main provisions, must look similar. Variations have been made to remove the faults and accommodate the needs of the country.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


Latest Comments