Energy, the driving force behind all natural processes, exists in various forms, such as kinetic, potential, and thermal. It is essential for sustaining life and fueling technological advancements, energy undergoes transformations but adheres to the law of conservation.
Example: An object of mass 15 kg is moving with a uniform velocity of 4 m s–1. What is the kinetic energy possessed by the object?
Solution:
Mass of the object, m = 15 kg, velocity of the object, v = 4 m s–1.
From Eq. (10.5),
Ek = ½ mv2
= ½ × 15kg × 4ms–1 × 4ms–1
= 120 J
The kinetic energy of the object is 120 J.
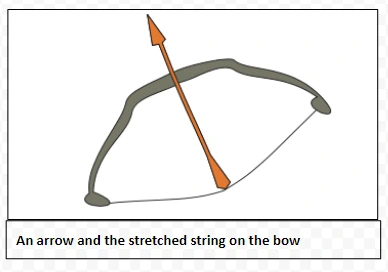
W = mg × h = mgh
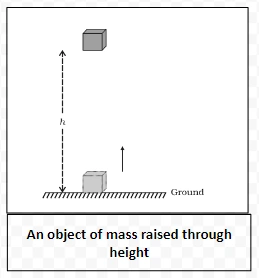
Example: Find the energy possessed by an object of mass 10 kg when it is at a height of 6 m above the ground. Given, g = 9.8 m s–2.
Solution: Mass of the object, m = 10 kg, displacement (height), h = 6 m, and acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m s–2. From Eq. (10.6),
Potential energy = mgh
= 10kg × 9.8ms–2 × 6m = 588 J.
The potential energy is 588 J.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>