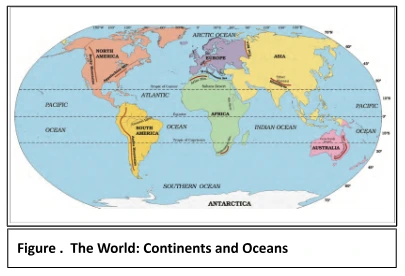
Earth, a celestial body in the vast expanse of the universe, is a dynamic and interconnected system. The four major domains of the earth are Lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. Beneath our feet lies a dynamic world, with molten magma churning at its core, giving rise to phenomena such as earthquakes and volcanoes. Above, the gaseous envelope of the atmosphere serves as our protective shield, while the lithosphere, our solid ground, cradles lakes, rivers, and vast landscapes. The hydrosphere, covering over 70% of the Earth, teems with life and plays a crucial role in regulating our climate. Binding all these domains is the biosphere, a testament to Earth’s unparalleled capacity to support life.
The Earth, unique in its ability to support life, possesses key elements: Land, Water, and Air.
Fascinating Earth Facts:
|
The gaseous layer enveloping the Earth contains essential gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. The atmosphere acts as a shield, providing the air essential for life and safeguarding us from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays.

The biosphere, a confluence of land, water, and air, is the unique realm where life thrives. Within it exist myriads of organisms, ranging from minuscule microbes to colossal mammals.
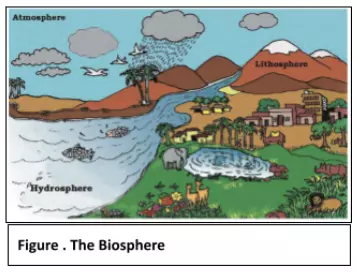
After comprehending the vast expanse and varied components of our planet’s exterior, it’s intriguing to delve beneath the surface. The hidden depths below offer insights into the Earth’s constitution, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of its interior dynamics.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>