India is a vast subcontinent and experiences a diverse range of climatic variations influenced by the distinctive monsoon climate patterns. With changing seasons, habits and attire change, reflecting the profound impact of weather on our daily lives. In India, summer requires light attire, and winter requires woolen. These variations arise from the ever-fluctuating elements of weather, such as temperature, pressure, and wind direction.
Central to this part is the monsoon climate, characterised by its unique seasonal reversal of wind, which bestows India with its hot and humid monsoonal climate, a characteristic shared with other regions of south and southeast Asia.
|
|---|
Climate: Factors and Influences Shaping Long-term Weather Conditions
|
POINTS TO PONDER The Monsoon Winds, In their genesis, have a North Eastern pattern. However, after crossing the Equator, a sudden change in the direction i.e. South-West winds are witnessed which brings a significant amount of rainfall in the Indian Subcontinent. Can you find out the reason for this change in direction of the winds? |
|---|
Geographical factors and their impact on India’s Monsoon Climate
|
POINTS TO PONDER Surface winds and upper tropospheric winds have their own distinctions. They do affect each other but are not necessarily mirror images. Can you find out the reason and factors which affect upper tropospheric circulations and distinguish it with surface winds in the Indian context? |
|---|
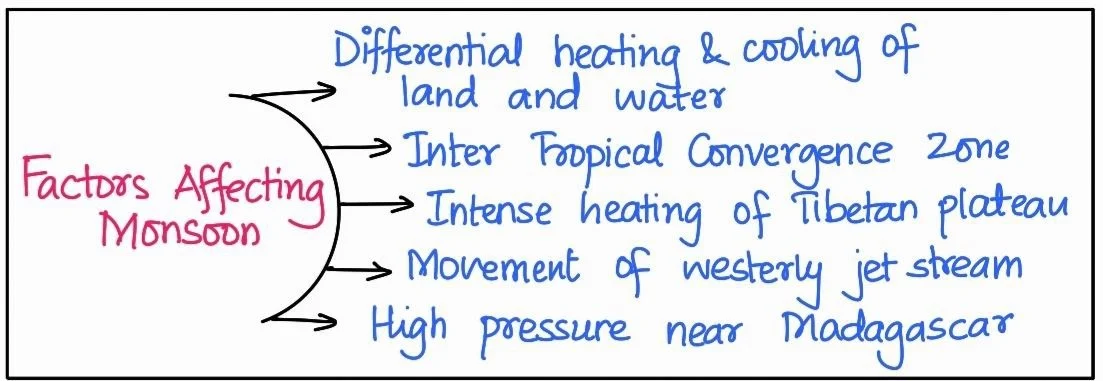
Factors Related to Air Pressure and Wind in India’s Monsoon climate:
Winter Weather Mechanisms and Monsoon Climate Impact in India
|
Western Cyclonic Disturbance and Tropical Cyclones
|
|---|
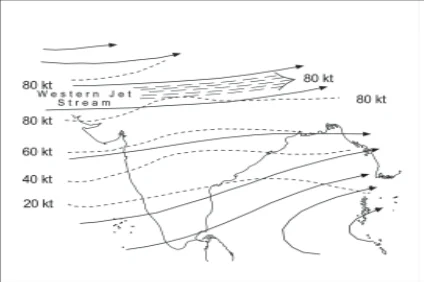
Direction of Winds in India in Winter at the Height of 9-13 km
Monsoon: India’s Seasonal Wind Phenomenon and Monsoon Climate
It refers to a climate characterised by seasonal reversals of the wind system.
The sailors who came to India in historic times were among the first to notice the phenomenon of the monsoon.
|
POINTS TO PONDER Monsoon Winds play a deterministic role in the Indian climate system. However, the Monsoon weather system is not confined only to the Indian Subcontinent. Find out the other parts of the world where they have a role to play. Also, assess the impact they have in such regions. |
|---|
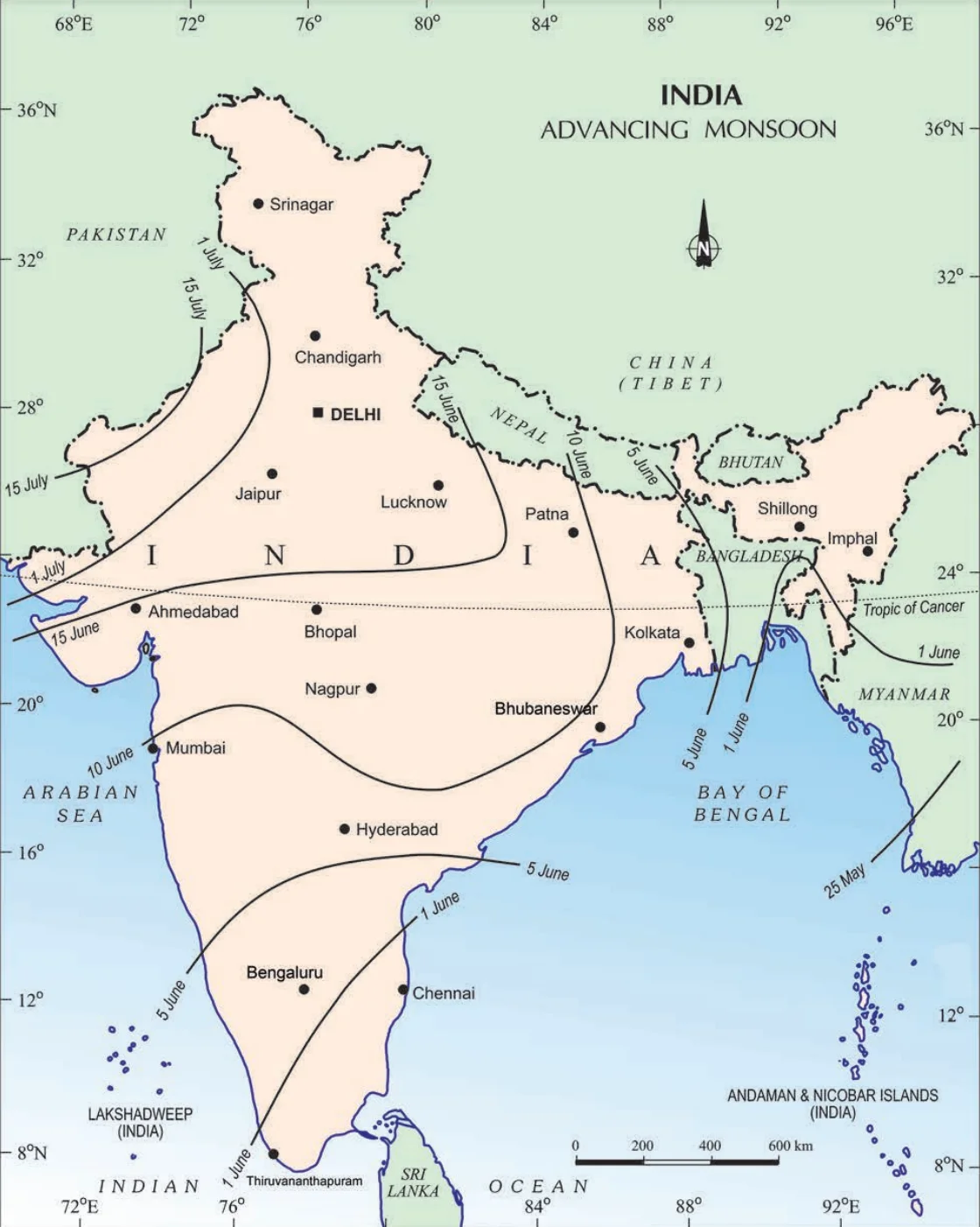
India: Normal Dates of Onset of the Southwest Monsoon

| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>