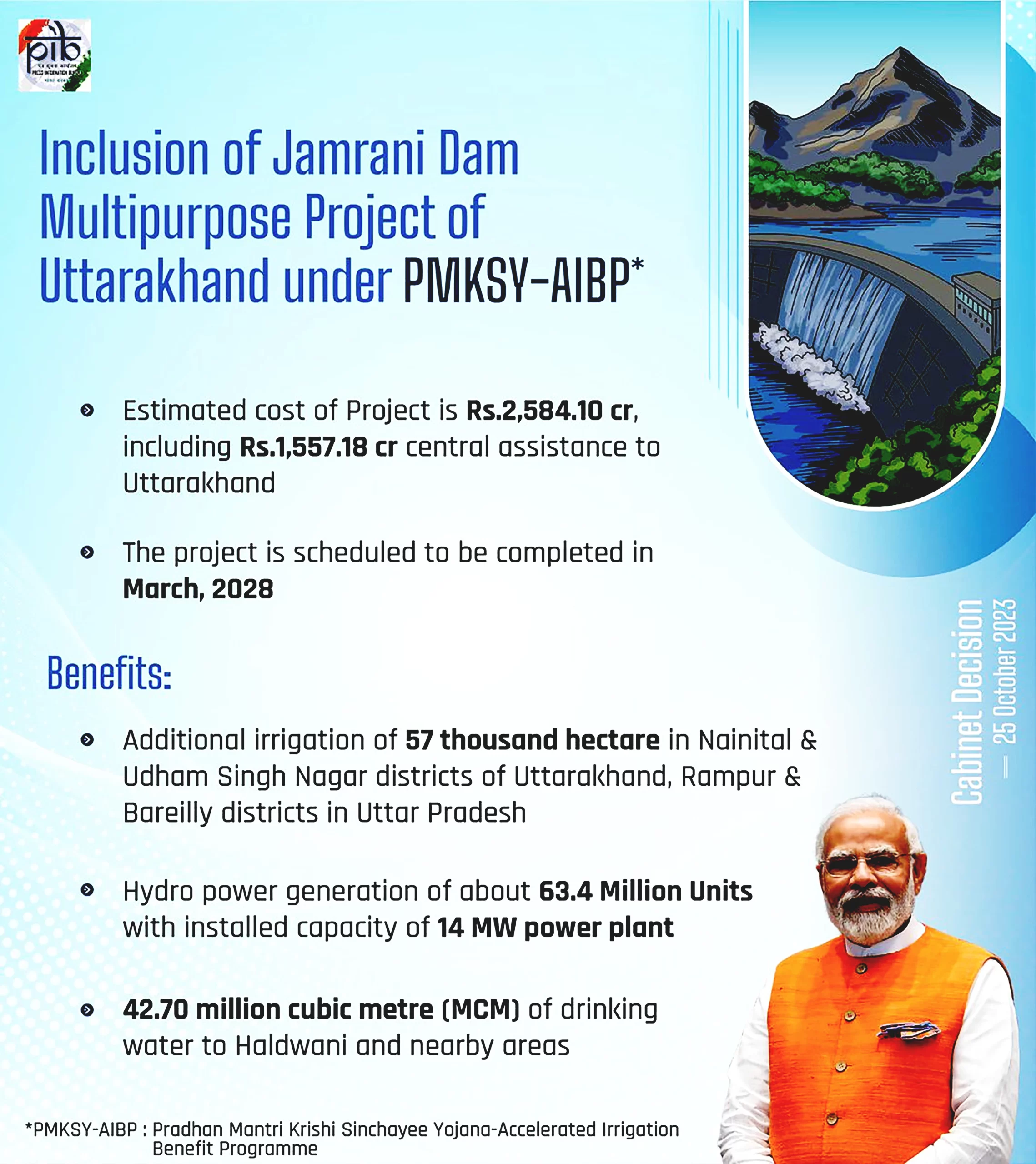
Context: Recently, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approved the inclusion of Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project of Uttarakhand under Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP).

Jamrani Dam Project: Overview, Benefits, and Cost
Dams in India: Scale, Age, and Safety Concern
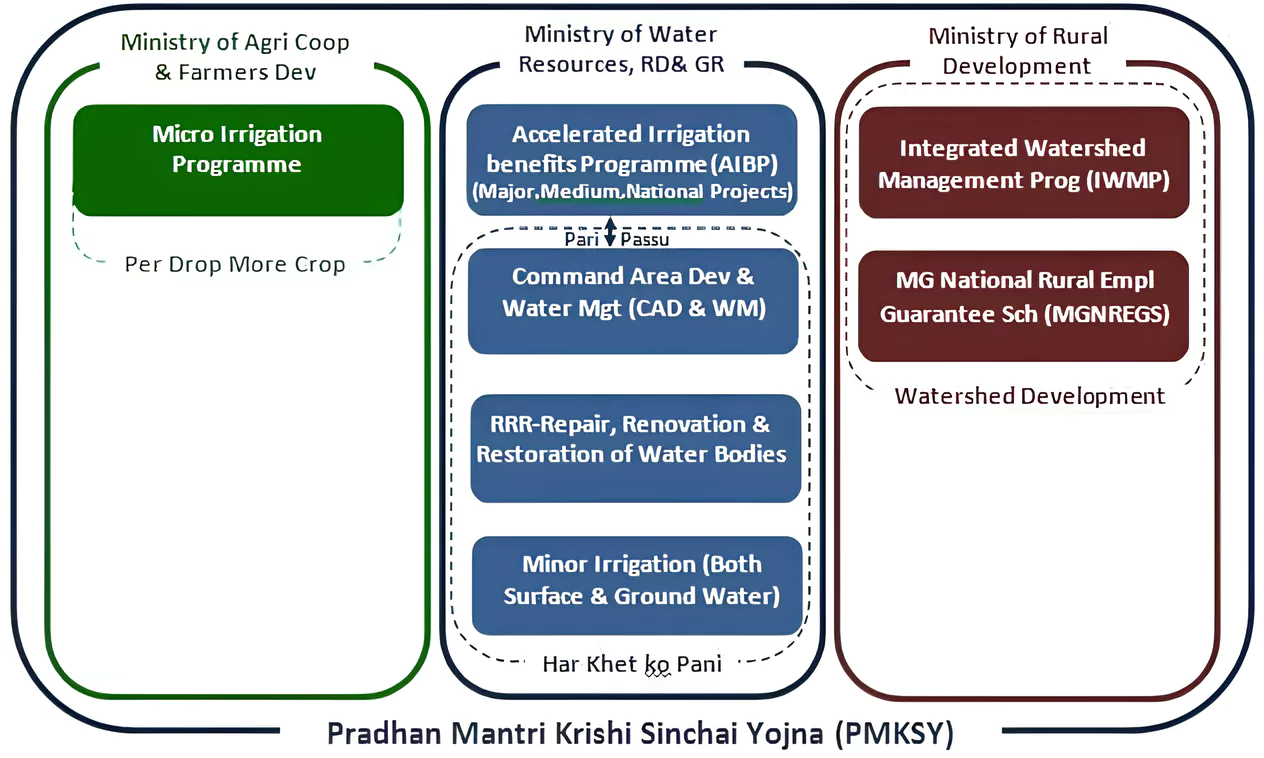
PMKSY-AIBP: Enhancing Agricultural Water Access and Efficiency
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Accelerated Irrigation Benefit programme (AIBP) Har Khet ko Paani Per Drop more crop
Geotagging of assets Approval of dam projects under PMKSY-AIBP Special focus on micro-irrigation
The recent amendment ‘Dam Safety Act 2021’ governs the detailed procedure for ensuring dam safety in India
Implementation is through the State Irrigation Plan (SIP) and District Irrigation Plan (DIP).

<div class="new-fform">
</div>