Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Introduce the Panchayat system as an integral part of India’s local government, focusing on grassroots democracy, decentralization, and inclusive development.
Body
- Discuss the importance of the Panchayat system in India, addressing aspects such as decentralization, grassroots democracy, socio-economic development, and social justice.
- Explore alternative financing sources for Panchayats apart from government grants, including local taxes, user charges, public-private partnerships, corporate social responsibility funds, and community contributions. Provide examples for each source.
Conclusion
- Write a relevant conclusion.
|
Introduction:
The Panchayat system is a crucial part of India’s local government, aimed at promoting grassroots democracy, decentralization, and inclusive development. Panchayats play a significant role in empowering communities and fostering socio-economic progress at the local level.
Body:
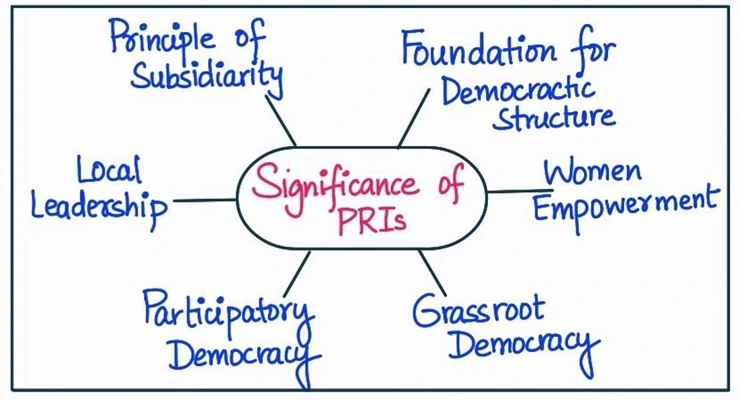
Importance of the Panchayat system in India:
- Decentralization: Panchayats promote decentralization by transferring powers and responsibilities to local bodies, ensuring better decision-making and effective implementation of development projects.
- Grassroots Democracy: Panchayats facilitate the active participation of citizens in decision-making processes, ensuring that their needs and preferences are considered in policy formulation and implementation.
- Socio-economic Development: Panchayats are responsible for the implementation of various government schemes and projects, contributing to local development in areas like education, health, sanitation, and infrastructure.
- Social Justice: Panchayats help promote social justice by ensuring the representation of marginalized groups, such as women, Scheduled Castes, and Scheduled Tribes, in local governance.
Alternative financing sources for Panchayats:
- Local Taxes: Panchayats can generate revenue through the collection of local taxes, such as property tax, market fees, and professional tax.
- User Charges: Panchayats can levy user charges for the services they provide, such as water supply, waste management, and community halls.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Panchayats can collaborate with private entities to finance and implement development projects. For example, the Punsari village in Gujarat partnered with private companies to set up solar-powered streetlights and Wi-Fi facilities.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) funds: Panchayats can seek CSR funds from companies to support development projects. For instance, some Panchayats in Rajasthan have utilized CSR funds from local industries to improve school infrastructure.
- Community contributions and crowdfunding: Panchayats can mobilize resources from the local community, NGOs, and through crowdfunding platforms to support development initiatives. The Hiwre Bazar village in Maharashtra successfully raised funds from the community to implement water conservation projects.
Conclusion:
The Panchayat system serves as the backbone of India’s local governance, empowering communities and driving grassroots democracy, decentralization, and socio-economic development. To maximize their impact, Panchayats must not only rely on government grants but also proactively explore diverse financing sources such as local taxes, user charges, public-private partnerships, CSR funds, and community contributions.
