Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Write about the diversity of natural vegetation of India briefly
Body
- Factors Responsible for Diversity of Natural Vegetation in India
- Significance of Wildlife Sanctuaries in Rain Forest Regions of India
Conclusion
- Give appropriate conclusion in this regard
|
Introduction
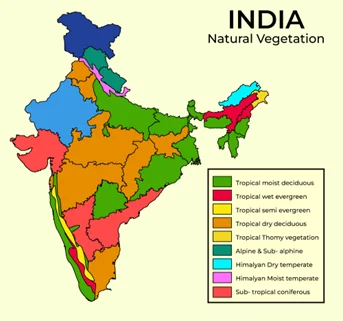
Natural vegetation in India spans a wide spectrum of plant cover that flourishes organically within its diverse ecological regions. This botanical diversity includes tropical evergreen rainforests, monsoon forests, dry deciduous forests, mountain forests, tidal mangrove forests, and resilient semi-desert and desert vegetation. To safeguard these natural treasures, India has implemented various measures, including the establishment of national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
Body
Factors Responsible for Diversity of Natural Vegetation in India:
- Geographical Extent: India’s vast geographical extent, from the Himalayas in the north to the coastal regions in the south, contributes to a wide range of climatic zones and altitudes, fostering diverse vegetation. For example, the alpine meadows of the Himalayas are vastly different from the tropical rainforests of the Western Ghats.
- Temperature: Varying temperatures across India contribute to vegetation diversity. The arid conditions of the Thar Desert favor the growth of resilient succulents, such as cacti and agaves. In contrast, the cool and moist environment of the Western Ghats supports lush tropical rainforests with a wide variety of tree species, ferns, and orchids flourishing.
- Rainfall Patterns: Varying rainfall patterns across India determine the distribution of vegetation types. For instance, the lush, dense forests of the Western Ghats, with annual rainfall exceeding 250 cm, contrast with the thorny scrub vegetation in Rajasthan’s arid Thar Desert, which receives less than 25 cm of annual rainfall.
- River Systems: Major river systems like the Ganges and Brahmaputra have created fertile alluvial plains that support diverse vegetation. For example, the alluvial plains of the Ganges and Brahmaputra support extensive wetland ecosystems with diverse plant species.
- Altitude: India’s diverse altitudes result in a range of temperature and rainfall conditions, which, in turn, give rise to unique vegetation zones. For instance, the Himalayan region exhibits a clear delineation of vegetation types, including tropical forests in lower elevations, subtropical forests at mid-altitudes, temperate forests in higher reaches, and alpine vegetation in the lofty heights above.
- Soil Diversity: India’s diverse soils, such as the fertile alluvial soils of the Indo-Gangetic plains and the laterite soils of Kerala, support a wide array of plant species adapted to specific soil conditions.
Significance of Wildlife Sanctuaries in Rain Forest Regions of India:
- Biodiversity Conservation: Wildlife Sanctuaries within rainforest regions function as vital protected habitats for a wide range of species. The Periyar Wildlife Sanctuary in Kerala stands as a prominent example, which ensures the preservation of the habitats of tigers, Asian elephants, and numerous endemic bird species.
- Preserving Genetic Diversity: Rainforest sanctuaries protect not only species but also the genetic diversity within them. This genetic pool can be crucial for breeding programs and future ecological adaptations.
- Tourism and Sustainable Livelihoods: Many wildlife sanctuaries in rainforest regions promote eco-tourism, generating income for local communities and fostering a sense of responsibility for rainforest conservation. Manas Wildlife Sanctuary serves as an example.
- Ecological Balance: Wildlife sanctuaries in rainforest regions play a pivotal role in maintaining ecological balance, crucial for processes like carbon sequestration, oxygen production, and climate regulation, ensuring the overall health and stability of these vital ecosystems.
- Preservation of Traditional Knowledge: Many rainforest sanctuaries like Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, encompass regions inhabited by indigenous communities, enabling the integration of their traditional knowledge and sustainable practices into conservation efforts.
- Research and Education: Rainforest sanctuaries provide opportunities for research and scientific study of unique ecosystems. They also serve as educational platforms, raising awareness about rainforest conservation and the importance of biodiversity. The Agumbe Rainforest Research Station in Karnataka serves as a prime example.
Conclusion
The diversity of India’s natural vegetation arises from numerous factors. However, this diversity is currently threatened by deforestation, habitat destruction, climate change, and unsustainable agricultural practices. While initiatives like the establishment of wildlife sanctuaries have yielded positive results, ongoing and concerted efforts are essential to pave the way for the preservation of this valuable natural heritage.
