Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Introduce the Rajya Sabha as the upper house of the Indian Parliament and briefly mention its transformation from being perceived as a ‘useless stepney tyre’ to an essential supporting organ in the legislative process over the past few decades.
Body
- Discuss the factors and areas in which the transformation of the Rajya Sabha is visible.
- Elaborate on each factor, explaining how it has contributed to the transformation of the Rajya Sabha into a more essential and effective institution within the Indian legislative process.
Conclusion
- Write a relevant conclusion.
|
Introduction:
The Rajya Sabha, the upper house of India’s Parliament, has undergone a remarkable transformation in recent decades. Once dismissed as a ‘useless stepney tyre,’ it has evolved into an indispensable supporting organ, playing a vital role in the legislative process and safeguarding the principles of Indian democracy.
Body:
This transformation can be attributed to various factors and is visible in several areas, as discussed below:
- Checks and Balances: The Rajya Sabha serves as an essential check on the actions and policies of the Lok Sabha (lower house) and the executive. By scrutinizing bills and legislation, the Rajya Sabha ensures that the government’s decisions are well-considered, and minority voices are not suppressed.
- For instance, In 2015, the Rajya Sabha blocked the controversial Land Acquisition Bill proposed by the Lok Sabha and the executive. The bill was widely criticized for being anti-farmer and for not providing adequate compensation to those whose lands were acquired.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
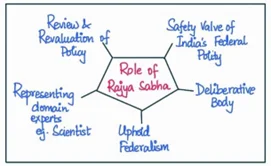
- Representation of States: Rajya Sabha’s members are elected by the members of the State Legislative Assemblies, ensuring that each state has equal representation irrespective of its population size. This balanced representation allows the Rajya Sabha to uphold federalism and protect the interests of the states in the legislative process.
- A notable example is the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Bill, passed in 2016. This bill impacted all states, and the Rajya Sabha, with its balanced representation, played a vital role in considering the interests of all states before passing the bill.
- Special Powers: The Rajya Sabha has specific powers not shared by the Lok Sabha, such as the ability to initiate the process of creating an All India Service. This enables the upper house to contribute to the establishment of crucial administrative structures that serve the nation.
- For example, in 1951, the Rajya Sabha initiated the creation of the All India Services, leading to the establishment of services like the Indian Administrative Service, Indian Police Service, and Indian Forest Service that have been instrumental in India’s administration.
- Review and Reconsideration: The Rajya Sabha has the power to review and reconsider bills passed by the Lok Sabha. This mechanism allows for a more thorough examination of the legislation and helps prevent hasty decisions or potential loopholes in the law.
- For instance, The Triple Talaq Bill, initially passed by the Lok Sabha in 2017, was sent back by the Rajya Sabha for review. This allowed for further scrutiny, and changes were made to address concerns of potential misuse before it was passed.
- Role in Constitutional Amendments: The Rajya Sabha plays a crucial role in the amendment of the Constitution. Constitutional amendments require the approval of both houses of Parliament, which grants the Rajya Sabha the power to influence and shape India’s constitutional framework.
- For example, The 123rd Constitutional Amendment Bill, which granted constitutional status to the National Commission for Backward Classes, was passed by the Rajya Sabha in 2018. This amendment aimed to ensure more effective protection of socially and educationally backward classes.
- Deliberation and Debate: The Rajya Sabha provides a forum for informed debate and deliberation on key policy issues, often featuring experts and experienced politicians who may not have a direct electoral mandate. This allows for a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the issues at hand, leading to better-informed decisions.
- For instance, during the debate on the Citizenship Amendment Act in 2019, the Rajya Sabha provided a platform for extensive debate, enabling a detailed examination of the potential implications of the act.
- Stability and Continuity: Unlike the Lok Sabha, the Rajya Sabha is a permanent house, with one-third of its members retiring every two years. This ensures stability and continuity in the legislative process, as members can carry forward their expertise and knowledge over a longer period.
- For example, the staggered terms of the Rajya Sabha members ensured continuity during the COVID-19 crisis. Despite the general elections and changes in the Lok Sabha, the Rajya Sabha could carry on its legislative duties without disruption.
Conclusion:
The Rajya Sabha has been instrumental in upholding federalism, but there is potential for further improvement to enhance its effectiveness and relevance. Key areas to address include increasing transparency in the nomination process, engaging with civil society, and collaborating more closely with the Lok Sabha.
