Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Briefly introduce the concept of the Citizens’ Charter in India.
Body
- Discuss the limitations of the Citizens’ Charter in India.
- Present measures for greater effectiveness of the Citizens’ Charter.
- Provide examples alongside each limitation and measure.
Conclusion
- Write a relevant conclusion.
|
Introduction:
The Citizens’ Charter, introduced in India in 1997, is a tool designed to improve the quality of public services, enhance transparency, and ensure accountability. While it holds potential as an instrument for organizational transparency and accountability, there are certain limitations that hinder its effectiveness.
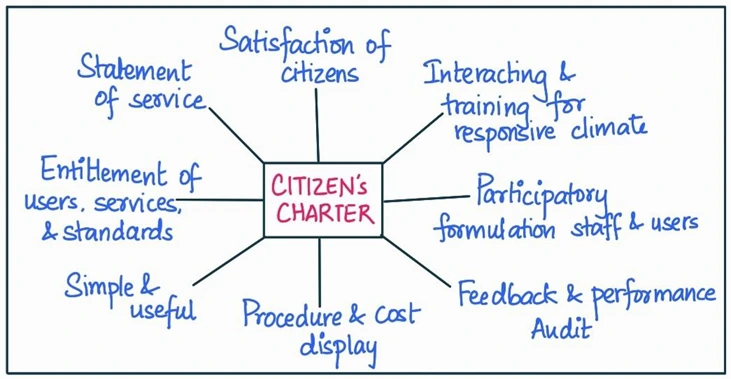
Body:
Limitations of the Citizens’ Charter in India and measures for greater effectiveness:
- Lack of Awareness: For instance, The Passport Seva Kendras have seen improved service delivery since the introduction of the Citizens’ Charter, but many citizens are still unaware of the commitments and grievance redressal mechanisms outlined in the charter.
- Measure: Conduct awareness campaigns and use various communication channels to inform citizens about the Citizens’ Charter and its purpose.
- Bureaucratic Resistance: For instance, the Indian Railways’ Citizens’ Charter has faced challenges in implementation due to bureaucratic resistance, leading to delays and a lack of adherence to the commitments made.
- Measure: Foster a culture of accountability within the bureaucracy and provide incentives for the successful implementation of the Citizens’ Charter.
- Inadequate Monitoring and Evaluation: For instance, the Municipal Corporation of Delhi’s Citizens’ Charter does not have a strong monitoring and evaluation system, limiting its effectiveness in driving service improvements.
- Measure: Establish a strong monitoring and evaluation mechanism to assess the performance of public services against the commitments made in the Citizens’ Charter, and use the findings to drive continuous improvement.
- Generic Charters: For instance, The Citizens’ Charter of the Department of Posts is often criticized for being too generic and not providing specific service standards or time-bound commitments.
- Measure: Ensure that the Citizens’ Charter contains specific, measurable, and time-bound commitments to enhance its effectiveness as an accountability tool.
- Limited Participation: For instance, the Citizens’ Charter of the National Health Mission has faced criticism for not involving local communities and healthcare providers in its preparation and implementation.
- Measure: Involve citizens and civil society organizations in the preparation, implementation, and monitoring of the Citizens’ Charter to ensure its relevance and effectiveness.
Conclusion:
By addressing these challenges, India can unlock the full potential of the Citizens’ Charter, ultimately leading to better governance and a more empowered citizenry.
