Recently, the Election Commission notified “Rajya Sabha Elections 2024” to 56 Rajya Sabha seats that will be held on February 27.

Recently, the Election Commission notified Rajya Sabha Elections to 56 Rajya Sabha seats that will be held on February 27.
The members of the Rajya Sabha are elected by the elected members of the state legislative assemblies and the union territory legislative councils, and not by the people directly. Rajya Sabha reflects the federal nature of the Indian polity, and safeguards the interests and rights of the states and union territories in the Parliament


The Rajya Sabha, or the Council of States, is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of India. It represents the interests of the states and union territories of India, and acts as a check and balance on the power of the Lok Sabha, or the House of the People, which is the lower house of the Parliament.
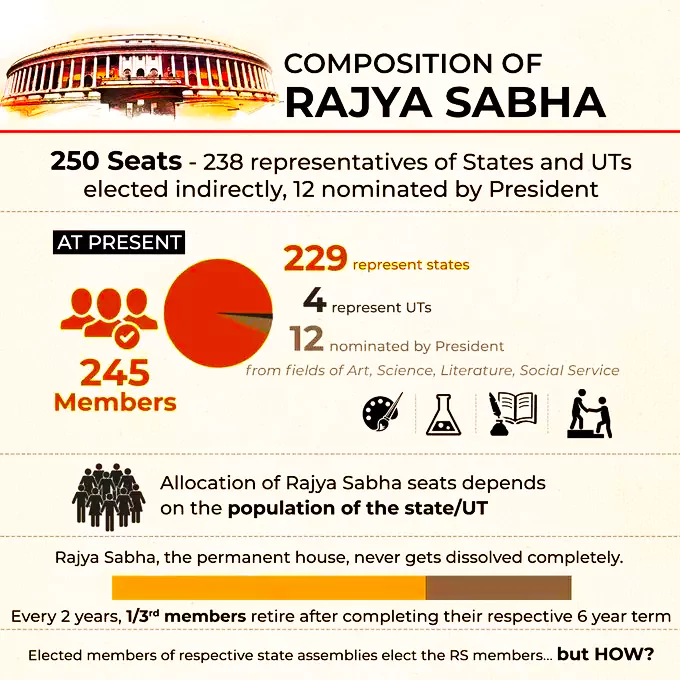
The Rajya Sabha is a representative of the states and union territories of India, and not of the people directly. The Rajya Sabha is a permanent and continuous house, and not subject to dissolution. The Rajya Sabha does not have a fixed tenure, and can only be prorogued by the president. The Rajya Sabha does not depend on the confidence of the Lok Sabha or the government, and cannot be dissolved by the president on the advice of the prime minister.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Elected by state assembly and union territory council members through single transferable vote.
Majority mark stands at 123 out of the total 245 members.
Proposed by either 10 state assembly members or 10% of the party's strength in the assembly.
Single Transferable Vote (STV) system allows voters to rank candidates; voting via open ballot.
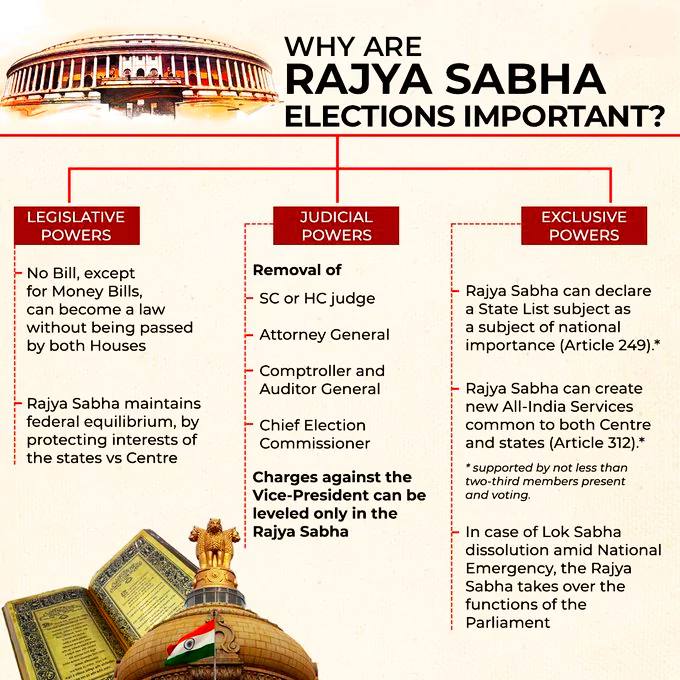
Rajya Sabha can pass resolutions on state list subjects, create all-India services, and approve emergencies.

<div class="new-fform">
</div>