India’s agro based industries play an important role in its economic landscape, with sectors like textiles, jute, and sugar standing as pillars of industrial growth. The evolution of these industries dates back to the 19th century, marking significant milestones in India’s industrial journey. From the first textile mill in Kolkata to the emergence of sugar factories in Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh, these industries have shaped regional economies and contributed to national prosperity.
Overview of India’s Agro-based Industries and Textile Sector
1. Textile Industry
- Origin and Status: Cotton textiles were handmade through spinning and weaving; power-looms emerged in the 18th century.
- The first textile mill in the country was established at Fort Gloster near Kolkata in 1818;
- The first successful modern textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854;
- Ahmedabad is often referred to as the ‘Manchester of India’.
- Spinning vs. Weaving: Spinning centralized in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu;
- Weaving is decentralized to incorporate traditional skills.
- Cotton Textile
- Integral to agriculture: It is closely linked with agriculture.
- Employing farmers, workers, and artisans in various stages of production.
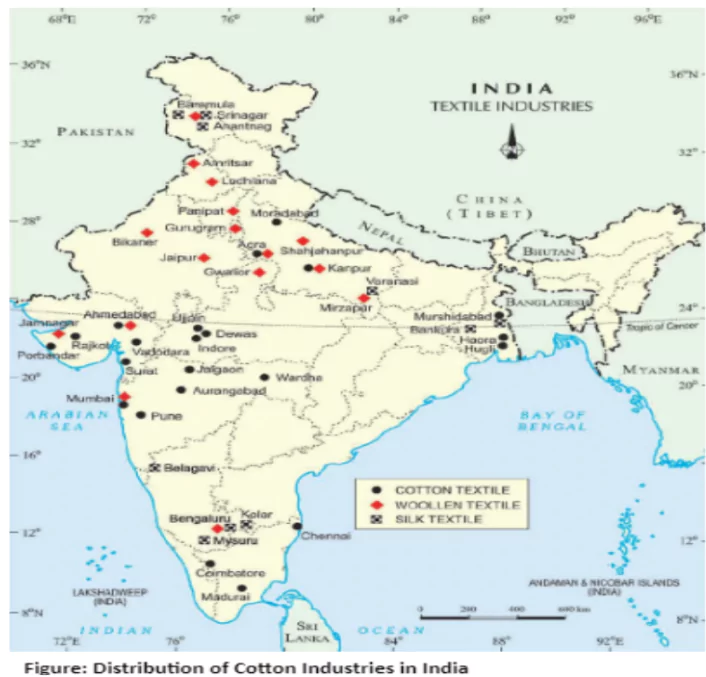 Spinning vs. Weaving: While spinning remains centralized in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu, weaving is highly decentralized to incorporate traditional skills and designs in fabrics like cotton, silk, zari, and embroidery.
Spinning vs. Weaving: While spinning remains centralized in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu, weaving is highly decentralized to incorporate traditional skills and designs in fabrics like cotton, silk, zari, and embroidery.
- However, weaving often produces low-quality fabric due to insufficient use of high-quality yarn.
- Factors: Uninterrupted supply of raw cotton from large cotton growing areas of west India benefited the industry in centres like Ahmedabad (Manchester of India), Nagpur, Surat, Indore and Coimbatore
- Major Centres: Ahmedabad, Bhiwandi, Kanpur, Coimbatore, Solapur, Kolhapur, Nagpur, Indore and Ujjain; Tamil Nadu has the largest number of mills and most of them produce yarn rather than cloth.
- At 18% of the global total, India is the world’s largest producer of cotton.
- Socio Economic Impact: Integral to agriculture,
- Export and Import Dynamics:
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Significance of the Textile Industry
- Contribution to Industrial Production, Employment, and Foreign Exchange Earnings
- GDP Contribution and Self-reliance in the Value Chain
- Cotton Textiles
- Global Trade
- Export of Yarn and Importers India exports yarn to Japan and cotton goods to various countries, but imports fabric due to a mismatch between yarn production and fabric utilization.
- Challenges and Prospects
- Fragmented Production: Weaving, knitting, and processing units face challenges in utilizing high-quality yarn, primarily due to fragmented small-scale production focused on the local market.
- This imbalance results in cotton yarn exports while garment manufacturers import fabric.
- Import Dependency: Despite increased production of good quality long-staple cotton, import dependence persists.
- Other Challenges: Erratic power supply, outdated machinery (especially in weaving and processing sectors), low labour productivity, and competition from the synthetic fibre industry.
Jute Textiles
- Origin and Status: India is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods and stands in second place as an exporter after Bangladesh.
- Most of the mills are located in West Bengal, mainly along the banks of the Hugli River, in a narrow belt.
- The British set up the first jute industry in India in 1855 near Hooghly river near Kolkata.
- Major Producer: West Bengal alone accounts for over 90% of India’s jute production.
- Factors favoring this location: Proximity to jute-producing areas, Cheap water transport, and a network of railways, roadways, and waterways.
- Abundant Water Resources: aid in processing raw jute,
- Labour: Availability of cheap labor from West Bengal and neighboring states is advantageous.
- Other Facilities: Kolkata, serving as a major urban centre, offers essential banking, insurance, and port facilities for jute goods export.
- Employment: The jute industry directly employed 3.7 lakh workers in 2010-11, along with supporting approximately 40 lakh small and marginal farmers engaged in jute and mesta cultivation.
- Challenges:
- Competition with other jute-producing nations such as Bangladesh, Brazil, the Philippines, Egypt, and Thailand.
- Competition in the global market from Synthetic alternatives.
- Rise in Internal Demand: However, internal demand has risen due to government policies mandating the use of jute packaging, necessitating diversification of products to stimulate further demand.
- The National Jute Policy of 2005: was enacted to enhance productivity, improve quality, ensure fair prices for jute farmers, and increase yield per hectare.
- Jute Packaging Material Act 1987: 100% of food grains and 20% of sugar must be packed in jute bags.
- Key export markets: include the USA, Canada, Russia, the United Arab Republic, the UK, and Australia.
- Expanding Horizons: The growing global concern for environmentally friendly, biodegradable materials presents new opportunities for jute products.
2. Sugar Industry
- Sugar Production: India is the largest producer of both sugarcane and cane sugar. Sugar industry is a seasonal industry.
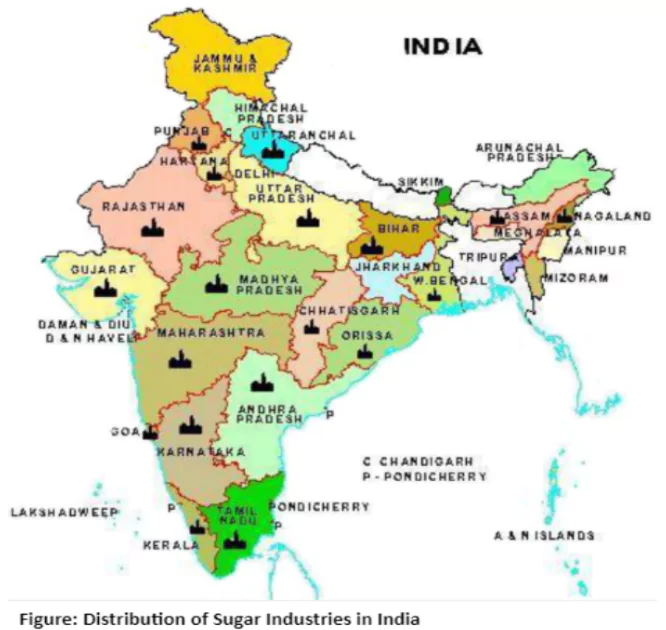 Ideal Mill Location: Sugarcane is a weight-losing crop; Sugar factories hence, are located within the cane producing regions.
Ideal Mill Location: Sugarcane is a weight-losing crop; Sugar factories hence, are located within the cane producing regions. - Distribution of Mills: Maharashtra has emerged as a leading sugar producer in the country.
- In UP, the sugar factories are concentrated in two belts – the Ganga-Yamuna doab and the Terai region.
- Tamil Nadu: Coimbatore, Vellore, Tiruvannamalai, Villupuram and Tiruchchirappalli districts.
- Karnataka: Belagavi, Ballari, Mandya, Shivamogga, Vijayapura and Chitradurga.
- The other States which produce sugar are Bihar, Punjab, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat.
- Cooperative Sector: The industry’s seasonal nature makes it suitable for the cooperative sector due to its periodic operations.
- Shift to Southern and Western States: In recent years, the mills have shifted in the southern and western states, especially in Maharashtra because the cane produced here has a higher sucrose content.
- Challenges: Seasonal industry nature, outdated production methods, transport delays in cane delivery, and the need to maximize bagasse utilization pose major challenges.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
- India’s agro based industries stand as important pillars of economic growth, providing employment opportunities, driving industrial production, and contributing to foreign exchange earnings.
- The growing global demand for environmentally friendly materials presents new opportunities for these industries to thrive and innovate, despite facing challenges such as competition from synthetic alternatives and outdated production methods.
 Spinning vs. Weaving: While spinning remains centralized in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu, weaving is highly decentralized to incorporate traditional skills and designs in fabrics like cotton, silk, zari, and embroidery.
Spinning vs. Weaving: While spinning remains centralized in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu, weaving is highly decentralized to incorporate traditional skills and designs in fabrics like cotton, silk, zari, and embroidery.
 Ideal Mill Location: Sugarcane is a weight-losing crop; Sugar factories hence, are located within the cane producing regions.
Ideal Mill Location: Sugarcane is a weight-losing crop; Sugar factories hence, are located within the cane producing regions.