Earth’s geomagnetic field is like a giant invisible force field surrounding our planet. It’s created by the movement of molten iron and nickel in the Earth’s outer core. This field acts like a giant magnet, with a north and south pole, which helps protect us from harmful solar radiation and guides compass needles. It’s crucial for our survival and has been essential for navigation for centuries.
Earth’s Dynamic Geomagnetic Field: Magnetosphere, Core and Lithosphere
- Geomagnetism: It is the study of Earth’s magnetic field, which surrounds our planet in the form of the magnetosphere.
- Geomagnetism relies on instruments to measure the Earth’s magnetic field, which emanates from sources such as the outer core, magnetized rocks in the lithosphere, and electric currents in the magnetosphere.
- Even though it’s challenging to separate them, they all give us valuable information about Earth’s interior and space environment.
- Geomagnetism helps us understand the magnetic forces shaping our planet.
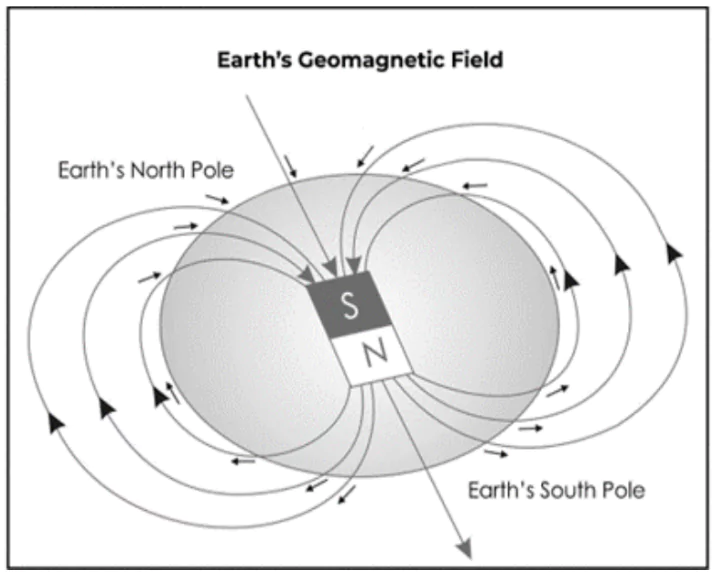 Earth’s magnetic field: It is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11 degrees with respect to Earth’s rotational axis as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the centre of the Earth.
Earth’s magnetic field: It is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11 degrees with respect to Earth’s rotational axis as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the centre of the Earth.
- The geomagnetic field is dynamic and it changes across geological time scales.
- The study of this magnetic field and its variations gives us a better understanding of the metallic core of the Earth.
- Causes of Geomagnetic Field :
- Origins: The magnetic field of the Earth is generated by the motion of molten iron alloys in the Earth’s liquid outer core.
- Convection Currents in Earth’s Core: Differences in temperature, pressure, and composition within the core cause convection currents in the molten metal.
- Dynamo Effect: This flow of liquid iron generates electric currents, which in turn produce magnetic fields. Which is known as the Dynamo Effect.
Geomagnetic Reversal and Intensity Variations
- Cyclical Changes: A geomagnetic reversal is a change in a planet’s magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged. This happens in a cycle of a few hundred thousand years.
- Intensity: The intensity of the geomagnetic field is greatest near the poles and weaker near the Equator.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Geomagnetic Poles
- Meaning: The Geomagnetic poles are the intersections of the Earth’s surface and the axis of a bar magnet hypothetically placed at the centre of the Earth.
- Dipole Model: If the Earth’s magnetic field were a perfect dipole, the field lines would be vertical to the surface at the Geomagnetic Poles, and they would coincide with the North and South magnetic poles.
- However, the approximation is imperfect, and so the Magnetic and Geomagnetic Poles lie some distance apart.
Significance Of Geomagnetic Field
- Shielding Against Solar Winds: This field acts as a shield that blocks the solar winds emanating from the sun, consisting of energetically charged particles that can severely damage life on the planet.
- Auroras: Some particles manage to enter our planet, being directed by the magnetic field towards the poles, and excite the molecules of nitrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere. These excited molecules produce light, seen as Auroras.
- These are mostly seen around the poles because of the highest intensity of the geomagnetic field there.
- Northern Hemisphere: Aurora Borealis
- Southern Hemisphere: Aurora Australis.
- Navigation: Helps in navigation by using the compass.
- Magneto-Perception: Some animals can use this magnetic field to navigate while migrating over long distances.
- Palaeomagnetism: The study of palaeomagnetism provides us with information about the past record of geomagnetism and the age of rocks on the surface of the planet.
- It also helped in developing the theories of Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics.
- Magnetosphere: The geomagnetic field is the cause of the formation of the magnetosphere around the Earth. A region of space influenced by a celestial body’s magnetic field.
- Function: Traps charged particles from solar winds and channels them into plasma.
- Spread: It extends up to 60,000 km on the side facing the Sun and to a greater extent on the opposite side.
- Its boundary is known as Magnetopause, outside which is a turbulent magnetic region known as magneto-sheath.
- Van Allen Radiation: It contains the Van Allen radiation belts, which contain high energy charged particles.
- Lower Belt: It contains electrons and protons extending from 1000 to 5000 km above the Earth’s equator.
- Upper Belt: It has mainly electrons extending from 15000 to 25000 km above the equator.
- Magnetic Storm: When the strong gusts of solar wind collide with the magnetosphere of the Earth, resulting in rapid magnetic field variation, this is known as magnetic storm.
- Impact: This results in the generation of electric currents in near earth space, which can harm our artificial satellites (eg. GPS) and long-range radio communication.
- Position: Magnetic storms are known as Ring Currents and they are mostly concentrated over the equator.
Conclusion
Earth’s geomagnetic field, generated by the movement of molten iron alloys in the outer core, shields us from harmful solar winds, guides navigation through compasses, and provides valuable insights into the planet’s past and core composition through paleomagnetic studies.
 Earth’s magnetic field: It is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11 degrees with respect to Earth’s rotational axis as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the centre of the Earth.
Earth’s magnetic field: It is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11 degrees with respect to Earth’s rotational axis as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the centre of the Earth.