Urban settlements, unlike rural areas, are typically larger and more densely populated. They serve as centers for a diverse range of economic, administrative, and non-agricultural activities. Cities play a crucial role in connecting with surrounding rural regions, facilitating the exchange of goods and services directly or through intermediary market towns. This interconnectedness fosters both direct and indirect links between villages and cities and among different urban centres themselves.
Urbanisation in India: Evolution and Classification
Evolution of Indian Towns
- Ancient Towns: Towns have been part of India’s history for over 2000 years,
- Example: Varanasi and Prayag emerged as ancient centres of religion and culture.
- Medieval Towns: During the medieval period, certain places developed as fortified hubs for kingdoms and principalities.
- Example: Towns like Delhi and Jaipur
- Modern Towns: European powers like the British established trading ports such as Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata, later expanding administrative and industrial centers.
- Post-Independence Urban Development: Post-independence, A large number of towns emerged as administrative headquarters
- For example: towns like Chandigarh and Durgapur emerged as administrative and industrial hubs,
- Satellite Towns: Ghaziabad grew around major cities like Delhi.
- Today, with increased investment, numerous medium and small towns have sprouted across the country.
Growth of Urbanisation In India
- The level of urbanisation is measured in terms of percentage of urban population to total population.
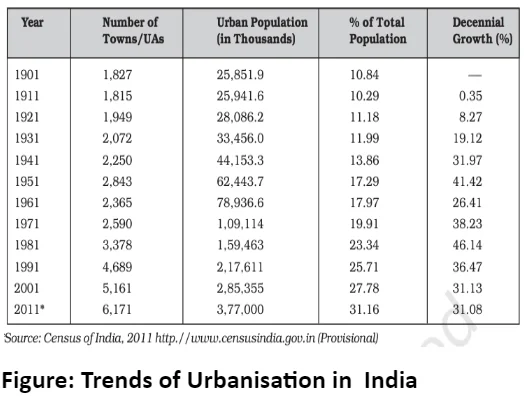
- 31 out of every 100 people live in Indian cities, which is less compared to richer countries.
- During the 20th century, urban population in India has gone up eleven times.
- However, recently, the rate at which cities are growing has started to slow down.
Definition of Urban Areas
- The definition of urban areas was refined in 2011, according to which urban areas are composed of two types of administrative units – Statutory towns and Census towns.
- Statutory Towns: All administrative units that have been defined by statute as urban, like Municipal Corporation, Municipality, Cantonment Board, Notified Town Area Committee, Town Panchayat, Nagar Palikas etc.
- Census Towns: Administrative units satisfying the following three criteria simultaneously:
- A minimum population of 5000;
- At least 75 percent of the male working population engaged in the non-agricultural sector;
- A density of population of at least 400 persons per square km.
Types of Urban Settlements
A. Based on Function
- Functional Classification of Towns: Besides being central or nodal points, many towns and cities have specific roles.
- Some are known for particular activities, products, or services they specialize in.
- However, each town typically fulfills multiple functions.
- Based on their primary or specialized functions, Indian cities and towns can be broadly categorized as follows:
| Functional Classification |
Characteristics |
Examples |
| Administrative Towns |
Serve As Administrative Headquarters. |
Chandigarh, New Delhi, Bhopal |
| Industrial Towns |
Driven By Industrial Activities. |
Mumbai, Salem, Coimbatore |
| Transport Cities |
Primarily Engaged In Export And Import Activities |
Kandla, Kochchi, Agra |
| Commercial Towns |
Specialize In Trade And Commerce. |
Kolkata, Saharanpur, Satna |
| Mining Towns |
Developed In Mineral-Rich Areas. |
Raniganj, Jharia, Digboi |
| Garrison Cantonment Towns |
Emerged As Garrison Towns. |
Ambala, Jalandhar, Mhow |
| Educational Towns |
Started As Educational Centers. |
Roorki, Varanasi, Aligarh |
| Religious and Cultural Towns |
Came To Prominence Due To Their Religious/Cultural Significance. |
Varanasi, Mathura, Amritsar |
| Tourist Towns |
Emerged As Tourist Destinations. |
Nainital, Mussoorie, Shimla |
B. Based on Population
-
- Based on population, urban settlements can be classified into the following categories.
- City: A city is typically considered a large urban area, but there are no precise criteria to distinguish it from a smaller town.
- It’s a concentrated settlement with diverse functions and usually features a central business district.
- Metropolitan City: Metropolitan Cities are those cities that have a Population in between one million to five million.
-
- The number of metropolitan cities increased from 12 in 1981 to 53 in 2011.
- Megacity: A megacity is a very large city, and it can be a single metropolitan area.
- Population: More than 5 million population are in metropolitan cities.
- Megacities: Cities with a population of 5 million and above.
- Megalopolis: When a large city sprawls and brings into its fold smaller adjacent towns and cities.
- Population: more than 5 million.
- Conurbation: It is formed by the coalescence of urban settlements that were separated by open space in the past.
- The coalescence usually occurs through ribbon development along the main inter-urban transport routes.
Conclusion
Urbanisation in India reflects a dynamic process of growth and transformation, characterized by the emergence of diverse urban settlements catering to various functions and needs. As the country continues to urbanise, understanding the nuances of different urban typologies becomes essential for effective planning and sustainable development.
