India has achieved an outstanding outcome in the Mutual Evaluation conducted during 2023-24 by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
- The Currency Swap Facility will be available to all SAARC member countries, subject to their signing the bilateral swap agreements.
About FATF
FATF is an intergovernmental organization established in 1989 out of a G-7 meeting of developed nations in Paris.
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Secretariat: Located at the OECD headquarters in Paris, it supports the substantive work of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) membership and global network.
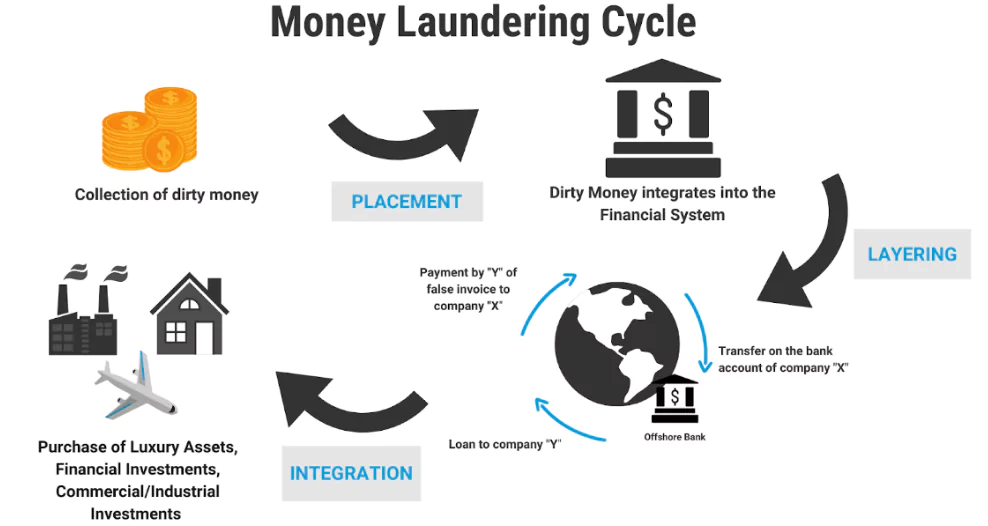
- Evolution of Mandate: Originally formed to combat money laundering, it expanded its mandate after the 9/11 attacks to include efforts against terrorist financing.
- Later, efforts to counter the financing of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) were added in 2012.
- Weapons of mass destruction (WMD) are weapons that can cause massive destruction and loss of human life on a large scale.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Grey and Black Lists
- Grey List: Includes countries considered safe havens for supporting terror funding and money laundering, serving as a warning.
- Black List: Comprises Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs) supporting such activities.
- As of now, Iran, North Korea, and Myanmar are on the blacklist.
|
- Sessions and Decision-Making:Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Plenary is the decision-making body, meeting three times per year to discuss Mutual Evaluation Reports (MERs) of countries.
- Countries with major deficiencies in their Anti-Money Laundering/Combating the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) regimes are listed under “jurisdictions under increased monitoring” (grey list) or “high-risk jurisdictions” (black list).
- Membership: Currently, a 39-member body representing major financial centers globally.
- Includes two regional organizations: the European Commission and the Gulf Cooperation Council.
- India’s Association: India joined as an observer in 2006 and became a full member in 2010.
-
- Additionally, India is part of its regional partners, the Asia Pacific Group (APG) and the Eurasian Group (EAG).
- Observers: Indonesia is the sole observer country of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
- Organizations with observer status include the Asian Development Bank (ADB), International Monetary Fund (IMF), Interpol, and the World Bank, among others.
Mutual Evaluation Report
- It is an assessment of a country’s measures to combat money laundering and the financing of terrorism and proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
- Evaluation Team: The reports are peer reviews, where members from different countries assess another country.
- Without prejudice: The mutual evaluation report is without prejudice to the status or justification that led to the designation of an entity as a terrorist or terrorist group or organisation.
- Mutual Evaluations have two main components
- Effectiveness
- Technical compliance
|
FATF has recognised the efforts made by India on
- Mitigation: Mitigating the risks arising from ML/TF, including the laundering of proceeds from corruption, fraud, and organised crime.
- Transition to Digital: Effective measures implemented by India to transition from a cash-based to a digital economy to reduce ML/TF risks.
- Implementation of the JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile) Trinity, along with stringent regulations on cash transactions
- It has led to a significant increase in financial inclusion and digital transactions
- These measures have made transactions more traceable, thereby mitigating ML/TF risks and enhancing financial inclusion.
Significance & Impact of India’s performance on the FATF Mutual Evaluation
It holds significant advantages for a country’s growing economy:
- Stability: It demonstrates the overall stability and integrity of the financial system.
- Access to global financial markets: Good ratings will lead to better access to global financial markets and institutions and increase investor confidence.
- UPI: It will also help in the global expansion of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), India’s fast payment system.
- Shows country’s commitment to International standards: This recognition from the FATF is a testament to the rigorous and effective measures implemented by India over the last 10 years to safeguard its financial system from ML/TF threats.
- It underscores the country’s commitment to international standards and its proactive stance in the global fight against financial crimes.
- Benchmark for Regional Countries: This sets a benchmark for countries in our region to effectively implement international standards on terrorist financing.
- Capacity Enhancement: India’s excellent rating will enhance the capacity of our country to lead the global effort on countering cross border terror financing and money laundering.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Conclusion
India remains committed to further strengthening its AML/CFT framework and continuing its collaboration with international partners to combat financial crimes.
- The nation will build on this success to ensure a secure and transparent financial environment for all.
![]() 29 Jun 2024
29 Jun 2024
