![]() 3 Mar 2025
3 Mar 2025

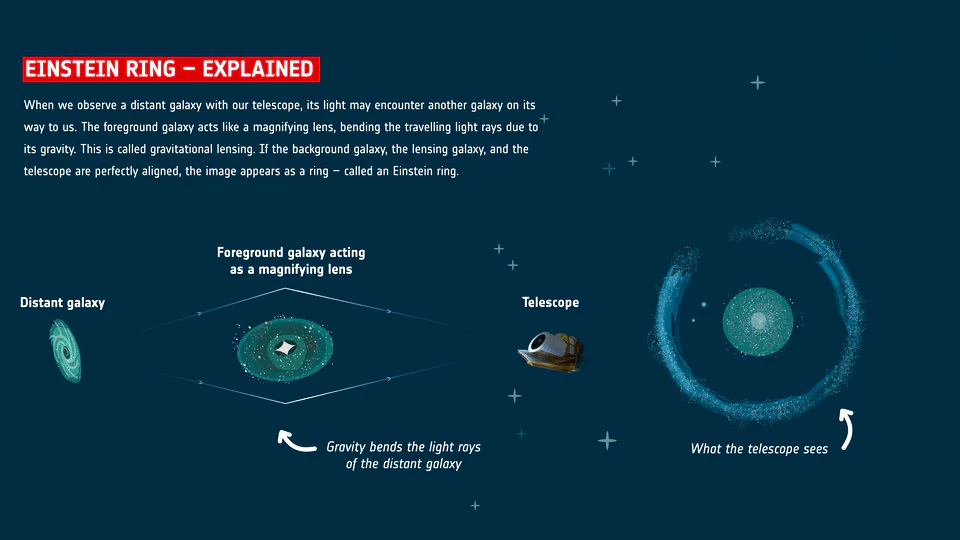
The Euclid Space Telescope has made an exciting discovery—a new Einstein ring in the nearby galaxy NGC 6505, located 590 million light-years from Earth.

| Key Features of the Euclid Telescope | |
| Feature | Details |
| Orbit | Sun-Earth Lagrange Point 2 (L2), approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth in the opposite direction of the Sun. |
| Instruments | Visible Imaging Camera (VIS) & Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) |
| Resolution | High-resolution images covering large sky areas |
| Mission Duration | 6 years (extendable) |
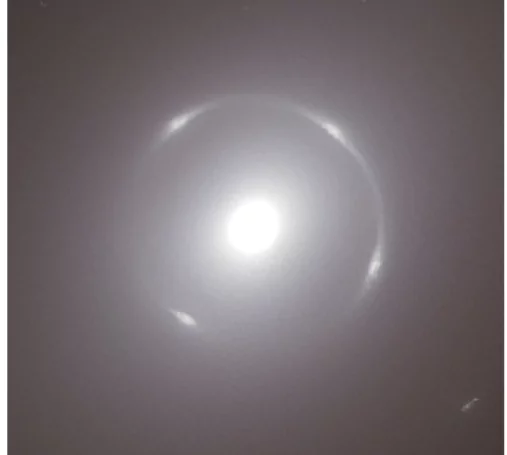
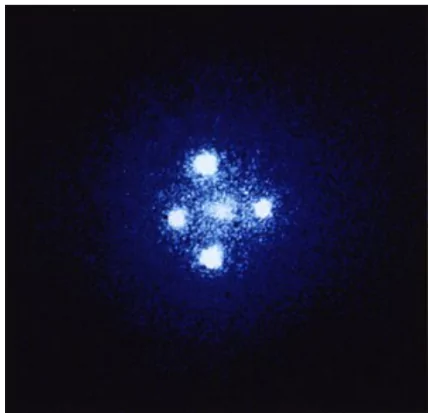


Einstein Cross
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>