Exploring the intricacies of India's onion market, from production dynamics and onion price rise to government interventions and global trade connections. Understand the factors driving fluctuating onion prices and the measures implemented to stabilize the market, alongside insights into the crop's growth conditions and economic significance.

Let’s Understand the Concerns over onion scarcity prompt the Indian government to implement export restrictions and bolster buffer stocks, as shortage is expected to continue until the new kharif harvest in December.
Look at the Insights into India’s onion production, including its diverse varieties, climatic preferences, and significant export volumes, particularly to neighboring countries and Southeast Asia.
Understand the Onion prices surge due to increased demand during festivities and crop losses from both excessive and insufficient rainfall across India
Strategic measures including export taxes, buffer stocks, anti-hoarding efforts, subsidized selling, price monitoring, and imports are adopted to stabilize onion prices in the domestic market.
Onions are central to India’s food culture as well as the rural economy. The price range of onion must be such that it gives profitable returns to the cultivator and affordability to the end consumers.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
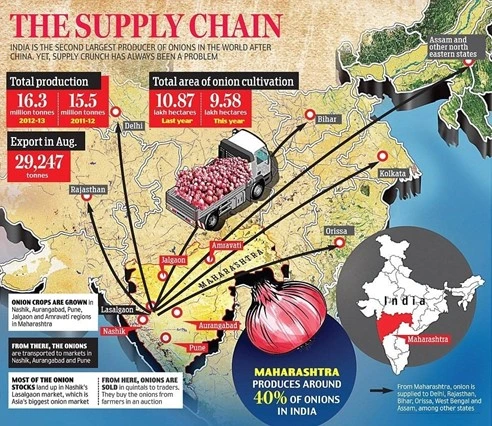
The Onion price rise is due to decrease in onion supply in the markets. The shortage of onion is a result of stock being destroyed due to recent rains.
The government has notified the minimum export price (MEP) of USD 800 per Metric Ton (MT) for the export of onions. In addition, the government has also procured an additional 2 lakh tonnes of onion for the buffer. Onions from buffers have been disposed of continuously since August in major consumption centres all over the country.
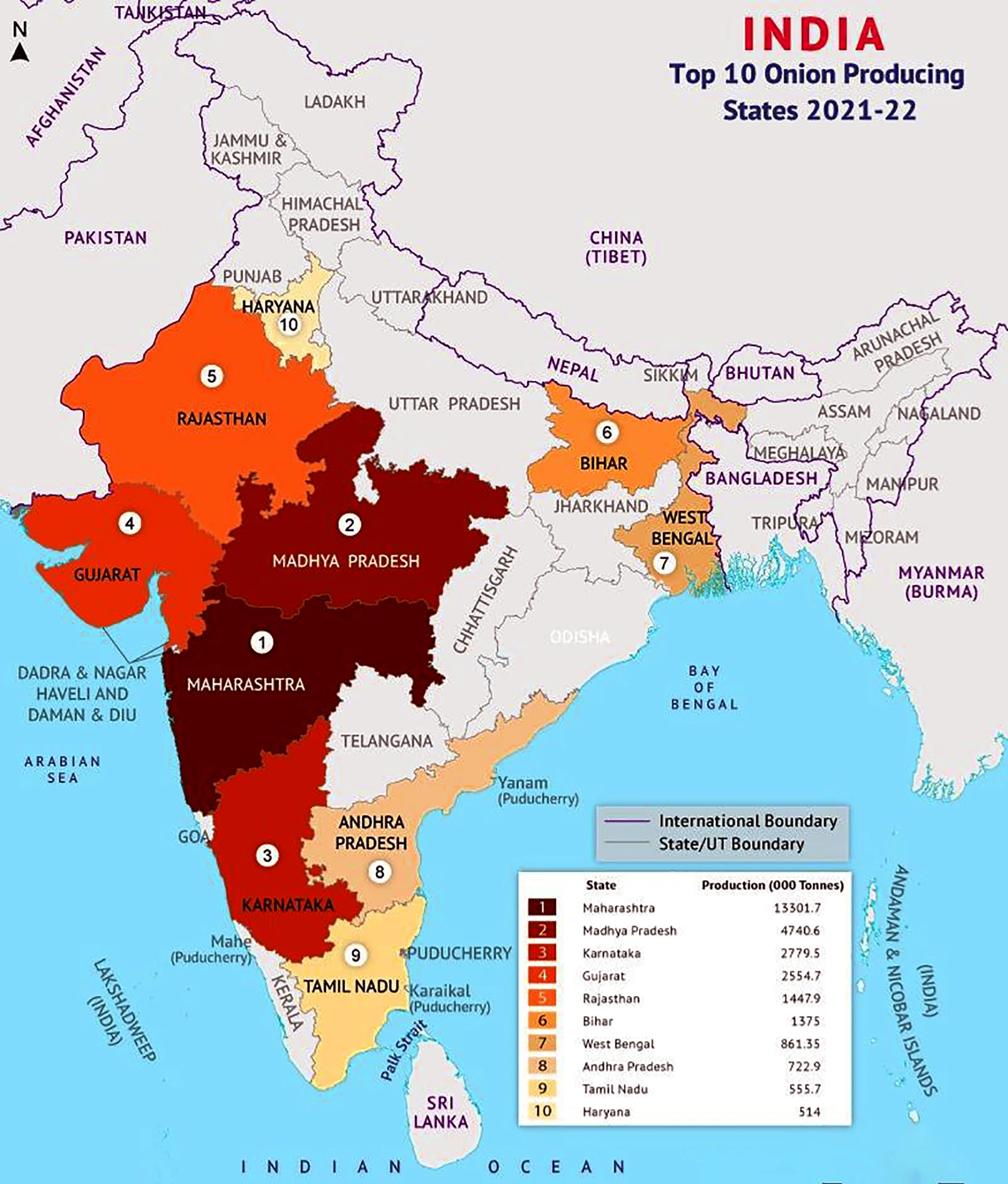
Maharashtra, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana and Telangana are the largest onion producing states in the country.
Agrifound Dark Red, Agrifound Light Red, NHRDF Red, Agrifound White, Agrifound Rose and Agrifound Red, Pusa Ratnar, Pusa Red, and Pusa White Round. Tana F1, Arad-H, Suprex, Granex 55, HA 60 and Granex 429 are varieties of yellow onion which are suitable for export.
Onion is a temperate crop but can be grown under climatic conditions such as temperate, tropical and subtropical climate. They cannot tolerate extreme conditions. Areas with low (< 650 mm) or heavy rainfall (>750 mm) are not suitable for onion production. It needs an optimal temperature of 13-24˚C for vegetative phase and 16-25˚C for bulb development.
India’s biggest onion export destinations include Bangladesh, Malaysia, United Arab Emirates, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Indonesia.

<div class="new-fform">
</div>