![]() 30 Nov 2023
30 Nov 2023
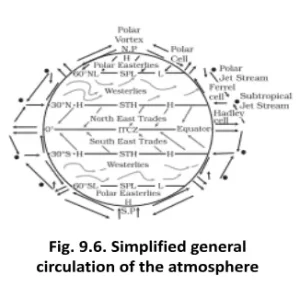
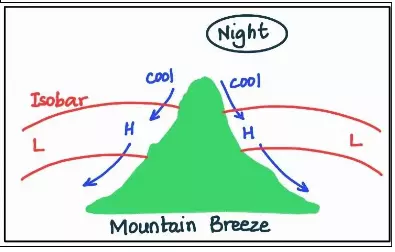
The Earth’s atmosphere is a complex and dynamic system governed by a delicate balance of forces and intricate circulation patterns. One key element in this atmospheric symphony is the geostrophic wind—a wind that flows parallel to straight isobars when the pressure gradient force and the Coriolis force are in perfect equilibrium. This geostrophic wind forms the foundation for broader atmospheric circulation patterns, influencing everything from surface winds to the creation of clouds and precipitation.
These circulation patterns and the rising and descending of air are fundamental components of the Earth’s atmospheric dynamics.
Warming and cooling of the Pacific Ocean is most important in terms of general atmospheric circulation. The warm water of the central Pacific Ocean slowly drifts towards South American coast and replaces the cool Peruvian current. Such appearance of warm water off the coast of Peru is known as the El Nino. The El Nino event is closely associated with the pressure changes in the Central Pacific and Australia. This change in pressure condition over Pacific is known as the southern oscillation. The combined phenomenon of southem oscillation and El. Nino is known as ENSO. In the years when the ENSO is strong, large-scale variations in weather occur over the world. The arid west coast of South America receives heavy rainfall, drought occurs in Australia and sometimes in India and floods in China. This phenomenon is closely monitored and is used for long range forecasting in major parts of the world.
The atmosphere is a complex and integrated web of circulations, surface and upper tropospheric winds. Whatever changes occur in the system at one place affects the other parts of it. Find out the mechanism through which such changes are transmitted to other parts of the atmosphere? Can you establish the link between Indian monsoon and global air circulation based on the same lines?
<div class="new-fform">
</div>