![]() 30 Nov 2023
30 Nov 2023
This chapter pivots towards a distinct inquiry, how does a firm determine the quantity to produce? The exploration of this question is far from simple or uncontested, hinging on a critical, although somewhat unreasonable, assumption that a firm in Perfect Competition is a ruthless profit maximizer.
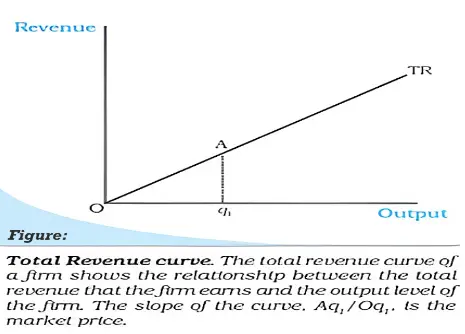
Under this premise, a firm’s production and sales in the Perfect Competition market are tailored to the pinnacle of profit maximisation. It’s also posited that whatever a firm produces in Perfect Competition is sold in the market, allowing for the terms ‘output’ and ‘quantity sold’ to be used interchangeably.
TR = p × q.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>