![]() 20 Dec 2023
20 Dec 2023
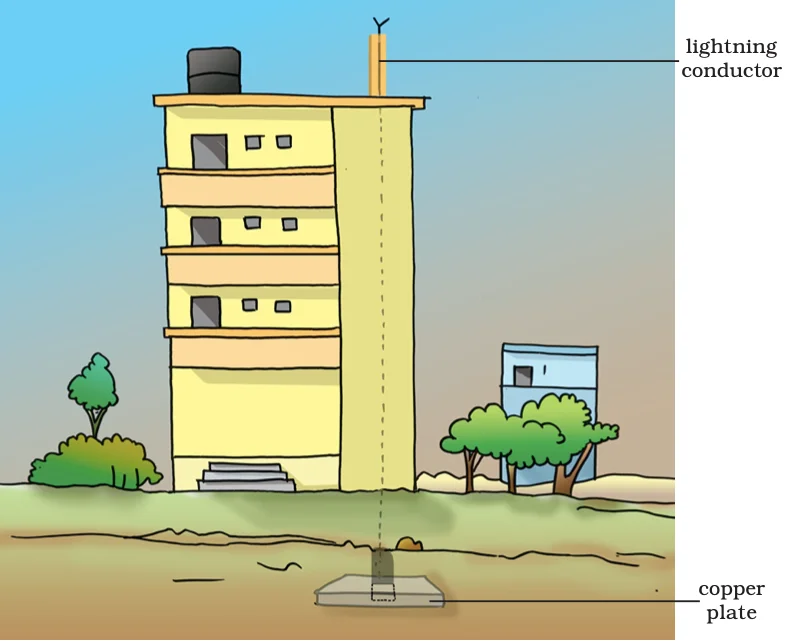
Lightning: Nature’s Electric Display and Safety Measures
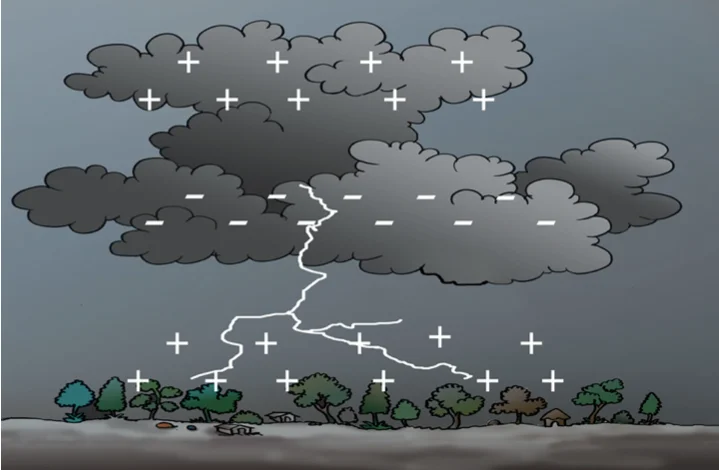
Lightning is a natural atmospheric discharge of electricity that occurs during thunderstorms. While captivating, it poses safety risks, and its study helps in understanding atmospheric phenomena and implementing measures to protect lives and property from the associated hazards.
Understand Lightning:
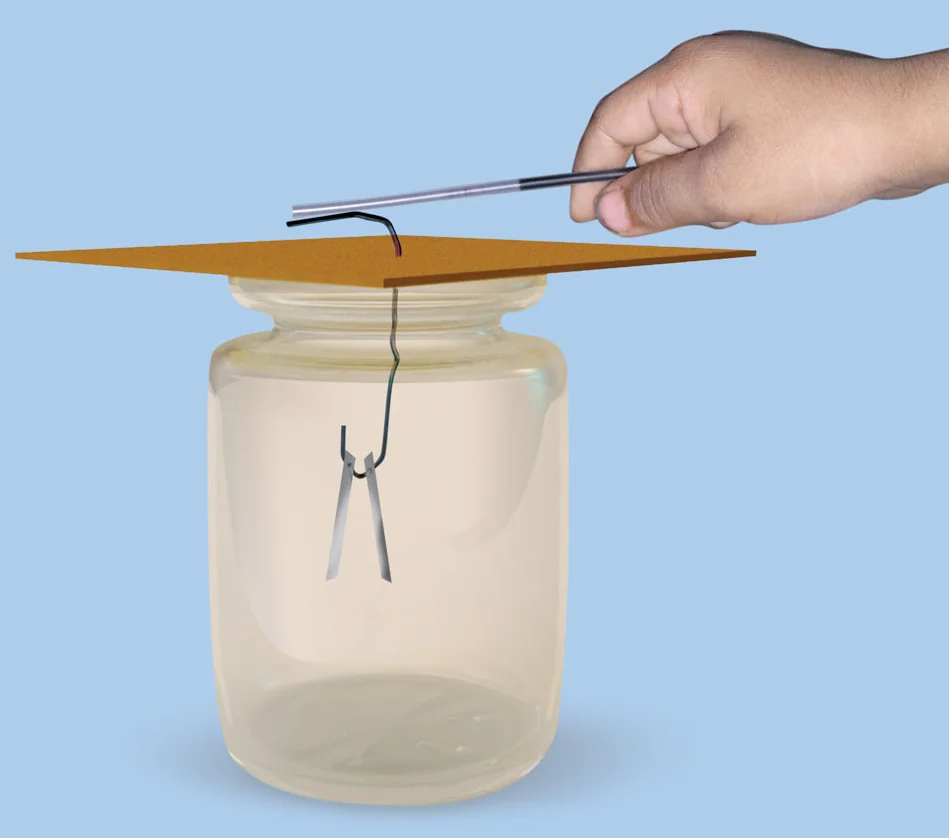
Electroscope


Outdoors:
Indoors:
<div class="new-fform">
</div>