Coal mining involves extracting coal from either underground mines or open-pit mines, which is then used for various purposes such as energy production and industrial processes. You can find a comprehensive list of coal mines in India categorized by states, major coal fields, and different types of coal.

Coal Mines in India: In India, there are significant reserves of coal, amounting to about 319 billion tonnes. This makes India one of the largest coal producers globally. The main areas where coal is found are in the eastern and central parts of the country. The type of coal commonly found in India is mainly bituminous and sub-bituminous.
There are two main categories of coal reserves in India – Gondwana coal and Tertiary coal. Gondwana coal is one of the oldest and most important coal reserves in the world. It’s located in central India. On the other hand, Tertiary coal, which is relatively younger, is mostly found in the northeastern part of India. Both types of coal are used for various purposes, including generating power and supporting industries. Among the Gondwana coal, there are three different categories based on the carbon content – anthracite, bituminous, and sub-bituminous. These categories determine the quality and usability of the coal for different applications.
In India, there are several places where coal is mined from the ground. These areas are called coal mines. Some of the well-known coal mines in India include:
< p style="text-align: justify;">
| List of Coal Mines in India | |
|---|---|
| Coal Mine | States |
| Jharia Coalfield
Bokaro Coalfield Jayanti Coalfield Godda Coalfield Giridih (Karbhari Coal Field) Ramgarh Coalfield Karanpura Coalfield Daltonganj Coalfield |
Jharkhand |
| Korba Coalfield
Hasdeo Arand Coalfield Mand-Raigarh Coalfield |
Chhattisgarh |
| Singareni Collieries Company Limited
Kantapalli Coalfield Kothagudem Coalfield |
Andhra Pradesh / Telangana |
| Neyveli Lignite Coalfield | Tamil Nadu |
| Jharsuguda Coalfield
Rampia Coalfield Talcher Coalfield Ib Valley Coalfield |
Odisha
|
| Ledo Coalfield
Makum Coalfield Najira Coalfield Janji Coalfield Lakhimpur Coalfield Ledo Coalfield |
Assam |
| Darrangiri (Garo hills)
Maolong and Langrin Coalfields (Khasi & Jaintia Hills) Cherrapunji Coalfield Liotryngew Coalfield |
Meghalaya |
| Singrauli Coalfield
Satpura Coalfield Sohagpur Coalfield Johila Coalfield Umaria Coalfield Satpura Coalfield |
Madhya Pradesh |
| Pench-Kanhan Coalfield
Wardha Valley Coalfield |
Maharashtra |
There are different types of coal that come from the ground, and they are categorized based on how they were formed and their properties. Here are the main types:
These different types of coal have varying qualities and are used for different purposes, like producing energy, making products, and heating.
Some of the biggest places where coal is mined in India are known as the largest coal mines. These mines produce a lot of coal to be used for various things. Here are a couple of them:
These coal mines are important because they provide a lot of coal that’s used for making electricity, industries, and other things we use every day. Remember, there are more big coal mines in India, but these are a couple of examples.
The oldest places in India where coal has been mined for a long time are known as the oldest coal mines. These mines have been around for a while. Here are a couple of them:
These coal mines have been in operation for a long time and have contributed to the country’s energy and industrial needs for many years. Keep in mind that there are other old coal mines in India too, but these are a couple of examples.
An illustration displaying the geographical arrangement of coal reserves across India is depicted on a coal mines map. You can view an example of such a map here.
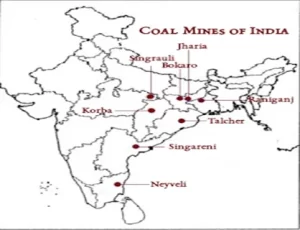
Coal mining in India encounters various difficulties and obstacles that affect the industry’s operations and outcomes. Some of the key challenges include:
Understanding coal mines in India is important for the UPSC exam because they play a crucial role in the nation’s energy sector, impacting economic growth and development. UPSC candidates need a solid grasp of India’s energy landscape, challenges, and strategies to tackle them. Moreover, coal mining links to societal, environmental, and economic concerns, making UPSC questions about these challenges common.
| Related Links | |
|---|---|
| Space Centres | High Courts in India |
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Coal mines are important because coal is a primary source of energy for electricity generation, industrial processes, and more. It significantly impacts India's energy security and economic growth.
The largest coal mine in India is the Jharia Coalfield, located in the state of Jharkhand. Jharia Coalfield is one of the oldest and most productive coal mining areas in India, known for its significant coal reserves and production capacity.
Here are five major coal mines in India: Jharia Coalfield: Located in Jharkhand, it's one of the largest and oldest coalfields in India. Singrauli Coalfield: Situated in Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, it's another significant coal mining area. Talcher Coalfield: Located in Odisha, this coalfield is known for its substantial coal reserves. Raniganj Coalfield: Situated in West Bengal, it's one of the oldest coal mining areas in India. Korba Coalfield: Located in Chhattisgarh, it's known for its coal production and is a key contributor to India's energy needs.
The first coal mine in India is generally considered to be the Raniganj Coalfield, located in West Bengal.
Burning coal releases greenhouse gases, contributing to global climate change. Efforts are being made to reduce coal consumption and transition to cleaner alternatives.

<div class="new-fform">
</div>