
Context:
The inclusion of the African Union into the G20 Grouping as its 21st member has given a new voice to the global south, providing an opportunity in ensuring global critical mineral security.
More on News:The global shift toward low-carbon economies and ambitious net-zero emission targets has driven the race for critical minerals.
- According to the International Energy Agency, the energy sector has played a pivotal role in tripling the overall demand for lithium from 2017 to 2022, with cobalt witnessing a 70% jump in demand and nickel seeing a 40% rise.
- India has recently identified 30 critical minerals, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, graphite, tin and copper.
- It was done on the basis of a report on critical minerals prepared by an expert team constituted by the Ministry of Mines.
- That report analysed 11 groups of minerals under categories such as metallic, nonmetallic, precious stones and metals, and strategic minerals.
About African union (AU):
- AU is a continental body which consists of the 55 member states (including Niger) that make up the countries of the African Continent.
- It was officially launched in 2002 as a successor to the Organisation of African Unity.
- It aims to promote unity, cooperation and development among African nations.
SWOT Analysis of Role of Africa in Solving World’s Critical Mineral Challenge
Strengths:
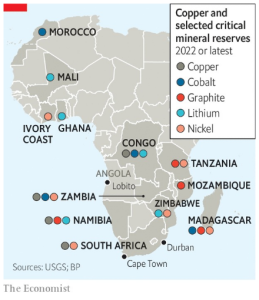
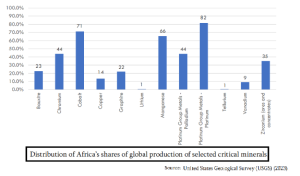
- Resources Availability: It has approximately 30% of the world’s reserves, including about 85% of manganese, 80% of platinum and chromium, 47% of cobalt, 21% of graphite, and 6% of copper.
- Global Supply: Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) with its cobalt reserves and Zimbabwe’s lithium deposits play pivotal roles in the global supply chain.
- India:
- India- AU Relations: India has good relations with AU and it played a key role in addition to AU in G20 as member.
- Economic Cooperation: India has invested in various sectors and it imports a variety of goods from Africa, including raw materials and minerals.
- For instance, as per a report by Bloomberg, India has provided credit to 42 African countries, totaling about $12 billion, with 38% of this credit extended in the last decade.
- For World at Large:
- Abundant Reserves: These reserves can potentially meet a significant portion of global demand for these essential resources.
- Diverse Mineral Resources: AU has diverse mineral resources, providing a broad spectrum of critical minerals that are vital for different industries, including electronics, energy storage, aerospace, and automotive.
- Reducing Supply Chain Dependence: AU offers an opportunity to reduce the world’s dependence on a single source, such as China, for critical mineral requirements.
Opportunities Available:
- For African Union:
- Economic Development: Export of critical minerals can boost the economies of African countries, creating jobs and generating revenue.
- Value Addition: Investing in processing and refining capabilities within Africa would create a more significant economic impact and reduce reliance on external markets.
- For India:
- Access to Critical Minerals: India can explore partnerships with African nations to access these resources for its domestic industries.
- Investment in Mining Operations: India is encouraging its domestic industries to invest in mining operations and infrastructure development in African countries.
- This could involve joint ventures, public-private partnerships, or direct investments in mining projects.
- Technology Transfer: India can collaborate with African nations to transfer knowledge and expertise in mining, processing, and sustainable resource management.
- For World at Large:
- Diversification of Trade: With a significant demand for critical minerals, establishing trade partnerships with African countries can secure a stable supply of critical resources.
Associated Weaknesses:
- AU’s Weaknesses:
- Africa’s Resource Curse: It has hindered the development of domestic industries, leading to economic stagnation and political instability.
- For example, the DRC provides only 19% of its population with electricity.
- High Indebtedness: It is holding back public spending on energy projects, while private investors are reluctant to invest because of the prevalence of fragile states.
- India:
- Competition with Other Countries: Including China, the United States, and European nations, which have already established a presence in Africa’s critical mineral sector and have more extensive financial resources.
- World:
- Resource Nationalism: Some African nations may adopt resource nationalist policies, seeking a larger share of mining profits or greater control over their resources.
- Security Concerns: Including risks associated with civil conflicts, terrorism, and theft of mineral resources.
Threats:
- China taking the lead: Beijing has pursued a decades-long strategy to secure a reliable supply of critical minerals through its Belt and Road Initiative and other efforts.
- For instance, Zimbabwe has seen over $1 billion in Chinese investments in lithium projects, surpassing Western nations.
- Environmental Degradation: Mining operations can lead to extensive environmental degradation, including deforestation, soil erosion, and habitat destruction.
- For example, Open-pit mining can have a profound impact on local ecosystems.
- Habitat Disruption: Critical mineral mining can disrupt natural habitats and migration routes for wildlife, leading to habitat loss and potentially threatening endangered species.
- Waste Management: The disposal of mining waste, including tailings and slag, can pose significant environmental risks if not properly managed.
Way Forward:
- Promoting Regional Cooperation. In order to maximize the benefits of these resources, developing common standards for mining and processing and sharing information on investment opportunities can help the world to tap the resource potential.
- Asia-Africa Growth Corridor (AAGC): The idea of AAGC emerged in the joint declaration issued by India and Japan in 2016, it can be utilized to overcome challenges posed by lack of infrastructural development.
- Value Addition and Local Processing: Encourage investments in mineral processing and refining facilities within African countries to add value to raw materials before export.
- For instance, African countries are now investing in developing processing and refining facilities.
- Diversification of Trade Partners: Forge partnerships with a diverse range of countries to reduce dependency on a single market and enhance resource security.
- For example, India is also engaging with other critical mineral exporters like sArgentina, Australia, China, and Mongolia for critical minerals.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Align mineral resource development, emphasizing poverty reduction, gender equality, and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion:
Collaborative efforts among African countries, India, and the international community can create a win-win situation, promoting economic development, technological advancement, and sustainability for all stakeholders.
News Source: Mint
![]() 12 Sep 2023
12 Sep 2023


