Context
All the contesting candidates have promised the implementation of Article 244(A) of the Constitution to create an autonomous ‘state within a state’ in Assam’s tribal-majority Diphu Lok Sabha constituency.
About Diphu Lok Sabha Constituency
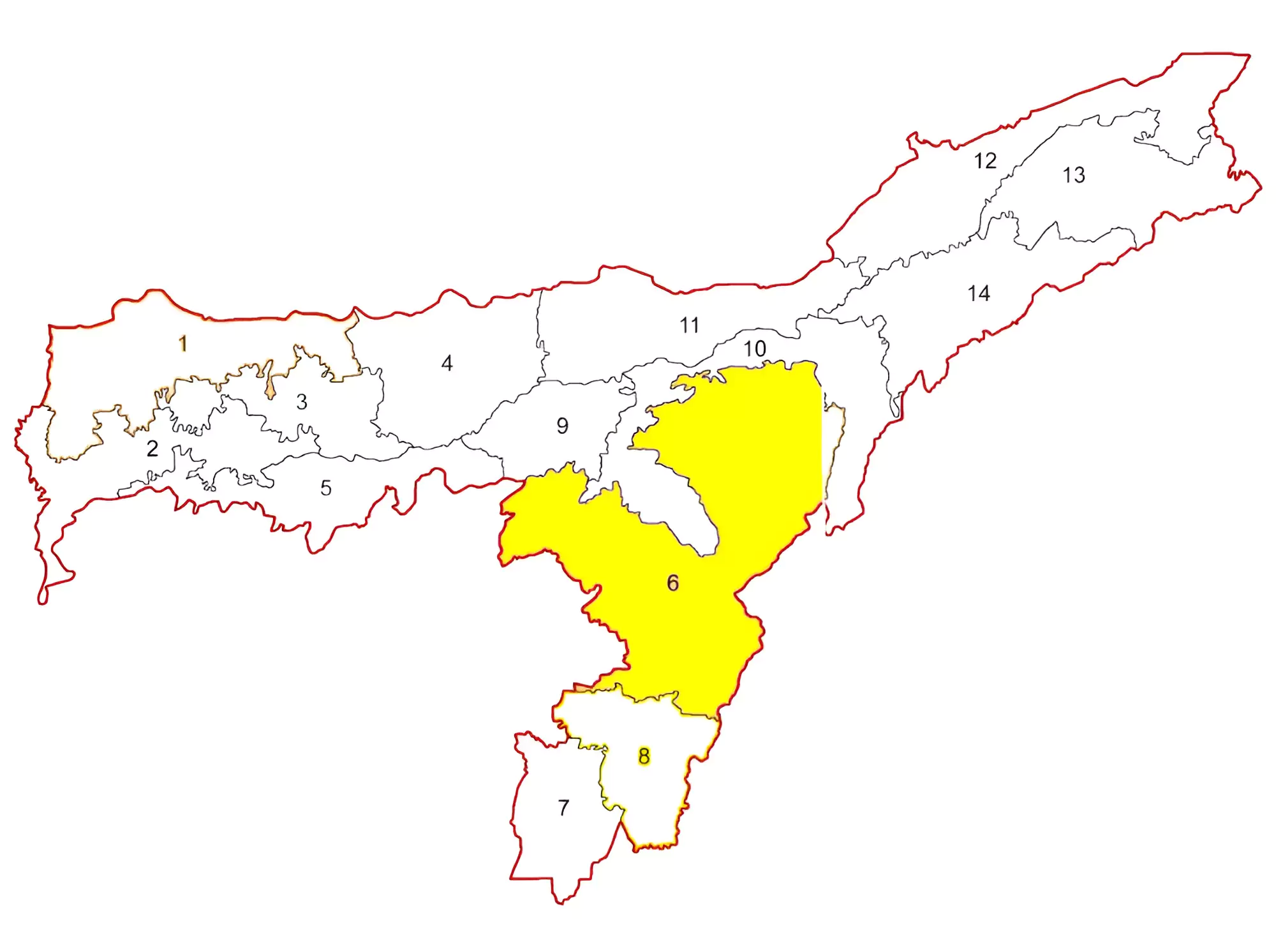
Diphu is the most sparsely populated constituency of Assam’s 14 Lok Sabha constituencies, with a voter count of just 8.9 lakh.
- Community profile: Karbi (third largest tribe in Assam), Dimasa, Hmar, Kuki, Rengma Naga, Zeme Naga, Bodo, Garo, Assamese, Bengali, Bihari, Gorkha, etc.
- It is reserved for Scheduled Tribes (STs), and covers six legislative Assembly segments in three tribal-majority hill districts of Assam ie. Karbi Anglong, West Karbi Anglong, and Dima Hasao.
- These areas come under two autonomous councils: the Karbi Anglong Autonomous Council (KAAC) and the North Cachar Hills Autonomous Council.
Background on the Demand For Autonomy in Assam
- Movement for separate Hill state: It started with the movement in the hill areas of undivided Assam, beginning in the 1950s, seeking a separate hill state which resulted in the creation of the full-fledged state of Meghalaya in 1972.
- The leaders of the Karbi Anglong region opted to remain with Assam because of the promise extended through Article 244(A).
- Formation of an organization: The Autonomous State Demand Committee (ASDC) was formed to press for the region’s autonomy.
- It signed a Memorandum of Settlement with the state and central governments in 1995 for enhancing the powers of the two autonomous councils in the region by increasing the number of departments under their charge to 30 from 10.
- Armed Insurgency: The demand for implementation of Article 244(A) also took the form of an armed insurgency, with the autonomy for the region remaining unmet.
- Several peace accords have been signed with the militant groups, including with the Karbi and Dimasa over the years by both the central and state government.
- Peace Accord: In 2021, a peace settlement was reached with five militant groups in Karbi Anglong (Karbi People’s Liberation Tigers, People’s Democratic Council of Karbi Longri, Karbi Longri NC Hills Liberation Front, Kuki Liberation Front, and United People’s Liberation Army ) under which greater autonomy and a special development package of Rs 1,000 crore over five years were promised.
- In 2023 an agreement was signed with the Dimasa National Liberation Army along the same lines.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Article 244(A) of the Constitution
- Added to The Constitution with the constitution Twenty-second Amendment Act, 1969.
- It enables the Parliament to pass an Act, to form within the State of Assam an autonomous State comprising (whether wholly or in part) all or any of the tribal areas specified in Part I of the table appended to paragraph 20 of the Sixth Schedule
- This autonomous state would have its own Legislature or Council of Ministers or both
- Any such law may in particular suggest:
- Subject matters: Specify the matters on which the Legislature of the autonomous State shall have power to make laws, whether to the exclusion of the Legislature of the State of Assam or otherwise
- Define the matters with respect to which the executive power of the autonomous State shall extend.
- Tax devolution: Provide that any tax levied by the State of Assam shall be assigned to the autonomous State in so far as the proceeds thereof are attributable to the autonomous State
|
Sixth Schedule
This Schedule contains provisions regarding the administration of tribal areas in the states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
- Provisions:
- Creation of Autonomous District and Regional Councils (ADCs and ARCs): These are elected bodies with the power to administrate tribal areas.
- Membership: Every autonomous district consists of a district council consisting of 30 members (four nominated by the governor and the other 26 elected on the basis of adult franchise). Each autonomous region also has a separate regional council.
- Term of office: The elected members hold office for a term of five years and nominated members hold office as per governor’s pleasure.
- Power of Governor:
- Reorganization: He is empowered to organize and reorganize the autonomous districts by increasing or decreasing their areas or changing their names or defining their boundaries and so on.
- Administration: The governor can appoint a commission to examine and report on any matter relating to the administration of the autonomous districts or regions.
- He may dissolve a district or regional council based on the recommendation of the commission.
- Power and Functions:
- Legislative Power: They can make laws on subjects such as forest management, agriculture, administration of villages and towns, inheritance, marriage, divorce and social customs.
- Judicial powers: In cases where the offenses are punishable with death or more than five years of imprisonment, the Governor of the state can confer upon the ADCs and ARCs the power to try them under the country’s criminal and civil laws.
- Creation of village councils: The ADCs and ARCs may also constitute village councils or courts to decide disputes between parties from Scheduled Tribes, and appoint officers to oversee the administration of the enacted laws.
- Administrative Powers: They are empowered to collect land revenue, impose taxes, regulate money lending and trading, collect royalties from licences or leases for the extraction of minerals in their areas, and establish public facilities such as schools, markets, and roads.
Also Read: ULFA Signs Landmark Peace Pact With Centre & Assam
![]() 27 Apr 2024
27 Apr 2024

