India’s reliance on kerosene-based lamps as a secondary lighting source leads to release of 12.5 gigagrams (Gg) per year of a potent climate pollutant called black carbon.
Black Carbon Emissions in India
- India releases 12.5 gigagrams (Gg) of black carbon annually due to kerosene-based lighting.
- This accounts for 10% of total residential black carbon emissions (from cooking, heating, and lighting).
- Rural Dependency on Kerosene Lamps:
- 30% of rural households use kerosene lighting during power cuts.
- The figure reaches as high as 70% in eastern regions of India.
- Regional Emission Contributions:
- Eastern India contributes 60% (7.5 Gg) of black carbon emissions from secondary lighting sources.
- Bihar alone emits over 3 Gg per year from kerosene lighting.
- Impact of Festivals (Diwali):
- Sesame oil lamps during Diwali contribute significant emissions (additional 3 Gg of black carbon in 2 days).
- Emissions from Diwali lamps in top states (Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Bihar).
- Switching to wax-based lamps could reduce emissions by 90%.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Key Government Initiatives to Reduce Black Carbon Emissions in India
- Saubhagya Scheme: Helped reduce kerosene consumption by expanding access to electricity.
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana: LPG connections to women of Below Poverty Line families, helped to reduce Black carbon emission.
- SATAT Scheme: Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT), has been launched to set up 5000 Compressed Biogas (CBG) production plants and make CBG available in the market for use.
- FAME Scheme: Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) phase-2 scheme
- National Clean Air Programme: Under the Programme, the government has revised its target to achieve a 40% reduction in particulate matter concentrations in the cities covered by the initiative by 2026, exceeding the previous goal of a 20-30% reduction by 2024.
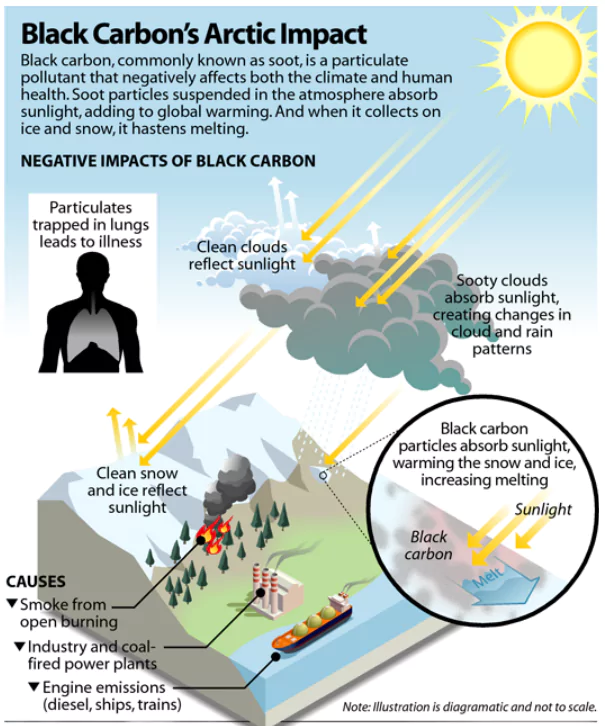
About Black Carbon
- Black carbon is a short-lived climate pollutant, less than a week, but is highly potent.
- It contributes to global warming and air pollution.
- Sources: Black carbon is emitted from a variety of sources, including: Vehicles, Non-road mobile machinery, Ships, Coal or wood burning stoves, Forest fires, Agricultural waste burning.
- Though kerosene has a lower burn rate than biomass, the emissions factors of the former are higher than the latter.
Impacts of Black Carbon
- Climate change
- Black carbon is a major contributor to climate change, absorbing solar radiation and releasing heat into the atmosphere.
- It’s the second most important contributor to global warming, after carbon dioxide.
- Global warming potential: Black carbon’s 20-year potential is 700-4,000 times that of CO2
- Black carbon emissions can also accelerate the melting of snow and ice, which can increase the impacts of global warming in the Arctic.
- Air pollution
- Black carbon is a component of particulate matter (PM), which is the most harmful air pollutant to health.
- Black carbon particles are very fine and can enter the bloodstream and reach other organs.
- PM2.5, a type of fine particulate matter, can cause damage to the lungs, heart, and brain.
![]() 9 Oct 2024
9 Oct 2024
