The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) informed that the upper stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle C-37 (PSLV C-37 mission) re-entered the Earth’s atmosphere on October 6.
About PSLV-C37 Mission
- Launched on February 15, 2017 with Cartosat-2D as the main payload along with another 103 satellites,
- INS-1A, INS- 1B, Al-Farabi 1, BGUSAT, DIDO-2, Nayif 1, PEASS, 88 Flock-3p satellites, and 8 Lemur-2 satellites.
- 104 satellites: Highest number of satellites launched in a single flight so far
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Orbital Decay and Re-entry
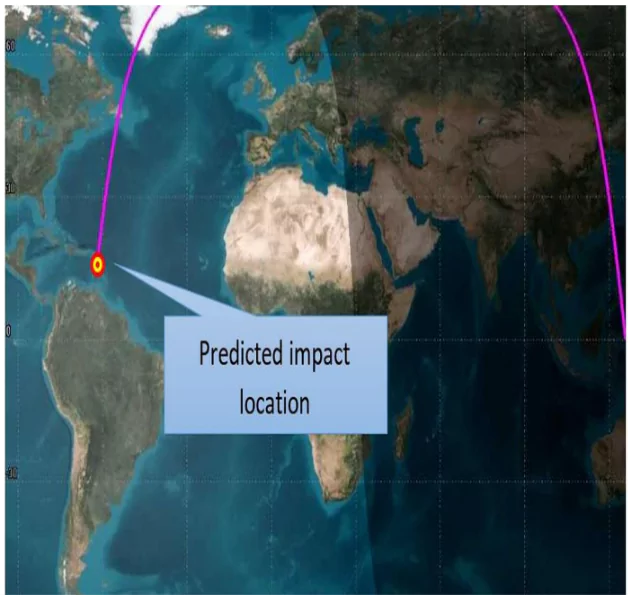
- After injecting satellites into orbit, the PS4 upper stage was left in a 470×494 km orbit.
- Due to atmospheric drag, the orbit decayed, leading to re-entry.
- Re-entry occurred in the North Atlantic Ocean, as predicted by both ISRO and US Space Command (USSPACECOM).
Compliance with International Guidelines
- The re-entry was compliant with the Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) guidelines, which recommend limiting post-mission orbital life of defunct objects in Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) to 25 years.
- ISRO reduced the residual orbital lifetime to 8 years through a passivation sequence.
Future Debris Mitigation Initiatives
- ISRO is working to reduce the post-mission orbital lifetime of PSLV upper stages to less than 5 years using engine restarts.
- Controlled re-entry is planned for future PSLV missions.
- ISRO aims to achieve the “Debris Free Space Mission” (DFSM) by 2030 as part of its commitment to space sustainability.
About Debris-Free Space Missions (DFSM)

- The Debris-Free Space Missions (DFSM) is an initiative by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to make all Indian space missions debris-free by 2030.
- The initiative aims to ensure the sustainability of space by reducing the amount of space debris and preventing future collisions.
- The DFSM initiative includes:
- Avoiding debris generation: This includes avoiding debris during the operational life of satellites and launch vehicles, as well as during post-mission disposal.
- Avoiding on-orbit collisions: This includes using failure mode studies, redundant systems, and mission design with high reliability.
- Guidelines for space actors:
- This includes guidelines for all Indian space actors, both governmental and non-governmental,
- It is on how to select clean orbits, budget fuel for post-mission disposals, and control trajectories during atmospheric re-entry.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Re-entry missions of ISRO
- LVM3-M3
- The LVM3-M3 rocket body was disposed of through natural orbital decay within two years of orbital injection.
- This complied with international guidelines and India’s Debris Free Space Missions (DFSM) initiative.
- Crew Module Atmospheric Re-entry Experiment (CARE)
- Launched on December 18, 2014, CARE was an experimental test vehicle for ISRO’s future orbital vehicle, Gaganyaan.
![]() 9 Oct 2024
9 Oct 2024

