Context
Wildlife authorities in Himachal Pradesh have started surveys as part of a census aimed at estimating the population of blue sheep (also known as bharal) and the Himalayan ibex constituting the primary prey of the iconic snow leopard.
Blue sheep and Himalayan ibex Census
- Field Survey: Field staff from the National Conservation Foundation and Wildlife Division, Spiti, will survey the challenging terrain of the district which borders Chinese-controlled Tibet for the next 15 days.
- The surveying is being done through the double-observer survey technique.
- Ban on Hunting Wild Animals: There is a complete ban on hunting all types of wild animals including blue sheep and Himalayan ibex in Lahaul & Spiti.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Snow Leopards
- Scientific Name: Panthera uncia
- Indicator Species: Due to their position as the top predator in the food web, they act as an indicator of the health of the mountain ecosystem in which they live.
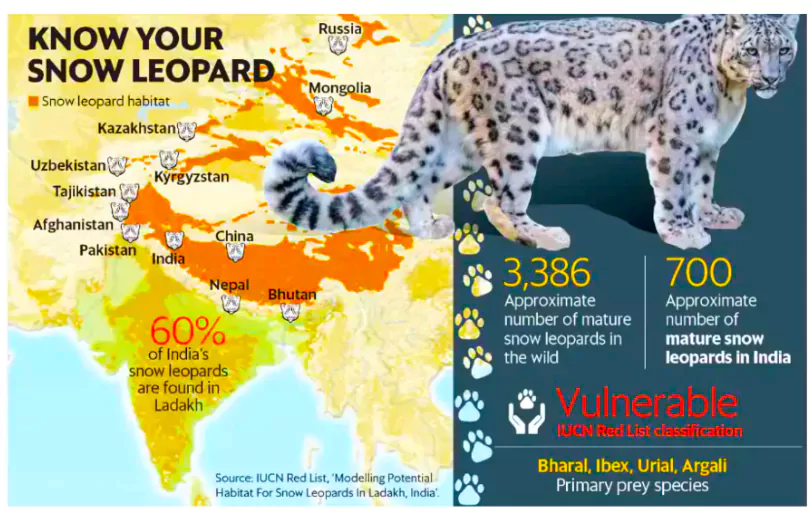 Habitat: Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent
Habitat: Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent- Geographical Distribution of Snow Leopards: Afghanistan, Bhutan, China, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Mongolia, Nepal, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- Geographical Distribution of Snow Leopard In India: Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Uttarakhand, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, and Himachal Pradesh.
- Hemis National Park (Ladakh) has a good presence of Snow Leopard and is also known as the Snow Leopard Capital of the world.
What Are Indicator Species?
- About: An indicator species is one whose existence signals the presence of a group of other species, but its absence shows the absence of the entire group.
- Features: Microbes and plants can both function as indicator species.
- These species often interact with their surroundings, which makes them very sensitive to any changes.
- Examples of Indicator Species: Lichens, Spotted owls, Mayflies, and Salmons
|
- Threats: Habitat destruction, invasive species, climate change, and pollution, which collectively exert an unprecedented impact on their survival.
- Protection Status:
- Global Conservation Measures:
- Project Snow Leopard (PSL): It was launched in 2009 to promote an inclusive and participatory approach to conserving snow leopards and their habitat.
- Snow Leopard is on the list of 21 critically endangered species for the recovery program of the Ministry of Environment Forest & Climate Change.
- SECURE Himalaya: Global Environment Facility (GEF)-United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) funded the project on the conservation of high-altitude biodiversity and reducing the dependency of local communities on the natural ecosystem.
- HimalSanrakshak: Launched in 2020 as a community volunteer programme, to protect snow leopards.
- Global Snow Leopard and Ecosystem Protection (GSLEP) Programme: GSLEP was created in 2013 through the Bishkek Declaration (2013) as an intergovernmental alliance for the conservation of the snow leopard.
- Associated Nations: Afghanistan, Bhutan, China, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Nepal, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
- Secretariat: Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan
Himalayan Ibex
- Local name: Tangrol
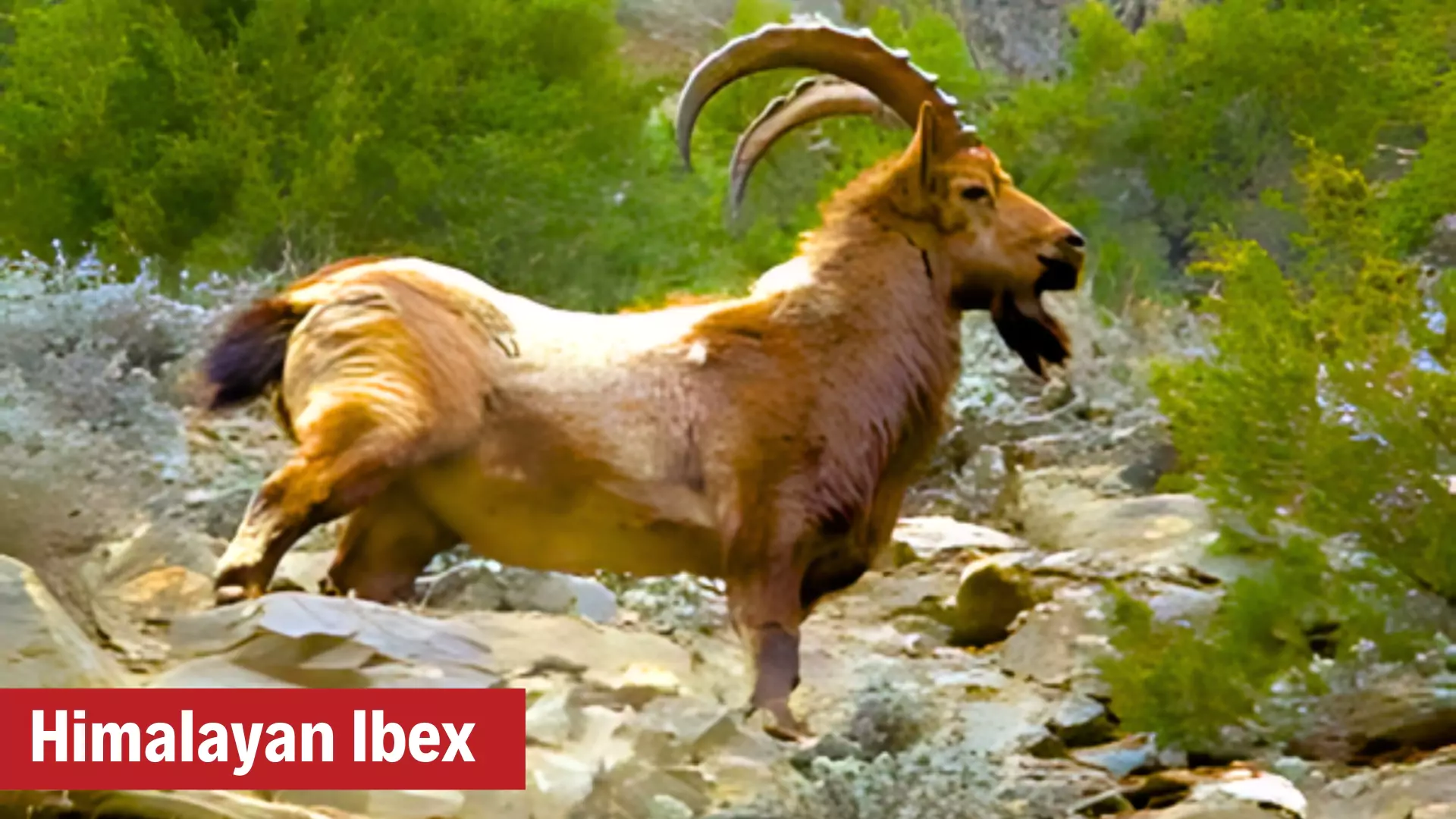 IUCN Indian status: Least Concern/Uncommon
IUCN Indian status: Least Concern/Uncommon- Characteristic:
- It is recognized by its contoured horns and beards, which are the primary reason for their poaching.
- Male Himalayan ibexes have longer, more heavily ridged, and curved horns than females, and their horns are also larger in size.
- Behavior: The Ibex does not always migrate to lower heights in winter and mostly stays at fairly high altitude using wind blown ridges.
- Distribution: Trans Himalayas region of Ladakh and the Greater Himalayas and Pir Panjals of Jammu & Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
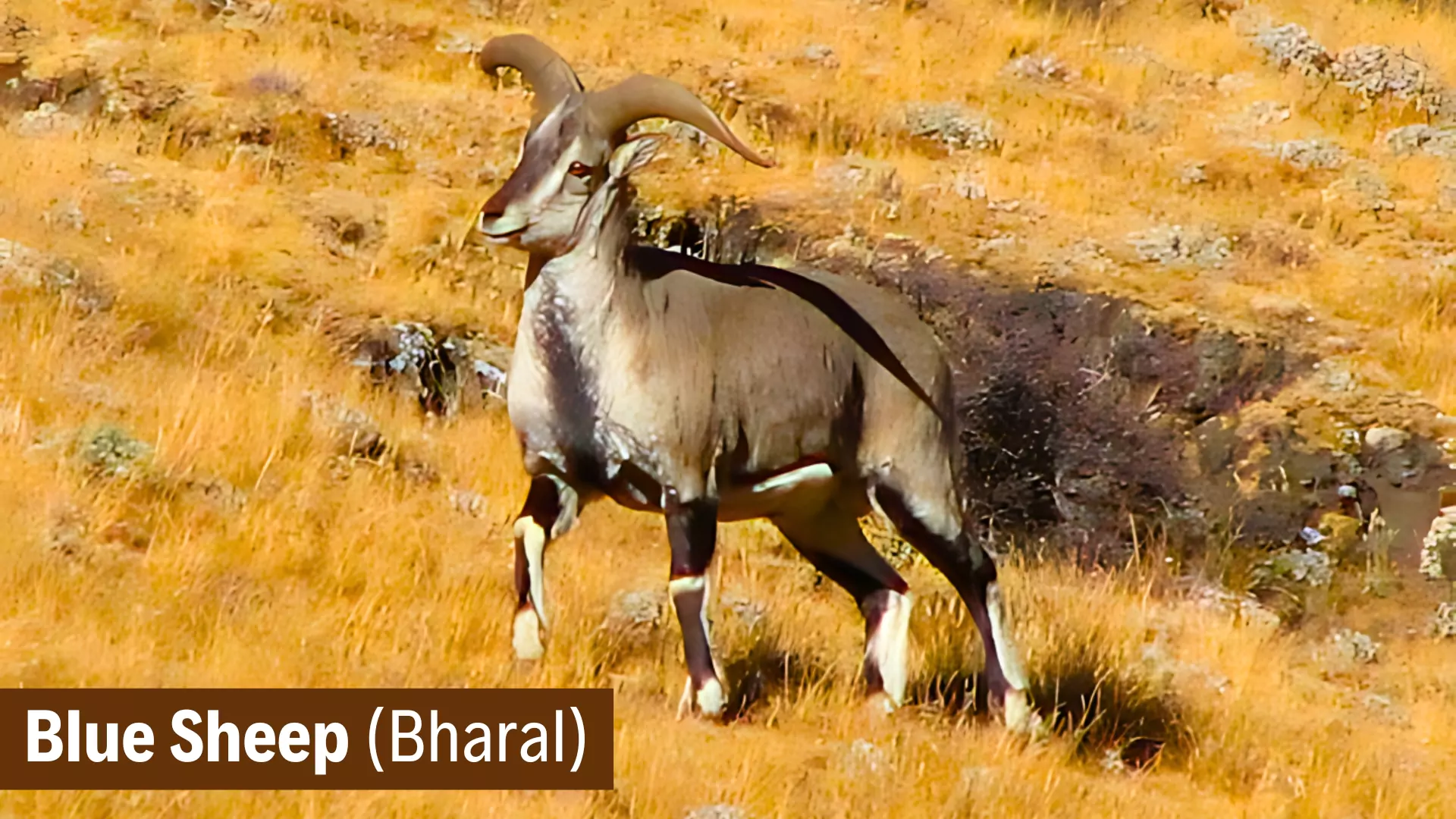

Blue Sheep (Bharal)
- Family group: Solitary or in small groups of less than 20 animals which consist of almost entirely one sex.
- Main Predators: Snow leopard, leopard, mountain fax, tawny eagle..
- Distribution: Montane regions in the Himalayas and the Sichuan region of China.
Additional reading: Snow leapord, WPA, 1972
![]() 24 May 2024
24 May 2024
 Habitat: Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent
Habitat: Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent IUCN Indian status: Least Concern/Uncommon
IUCN Indian status: Least Concern/Uncommon