Context
Recently, The central board of the Reserve Bank of India approved the transfer of Rs 2.1 lakh crore as surplus to the central government for the accounting year 2023-24.
RBI Surplus Transfer to Government
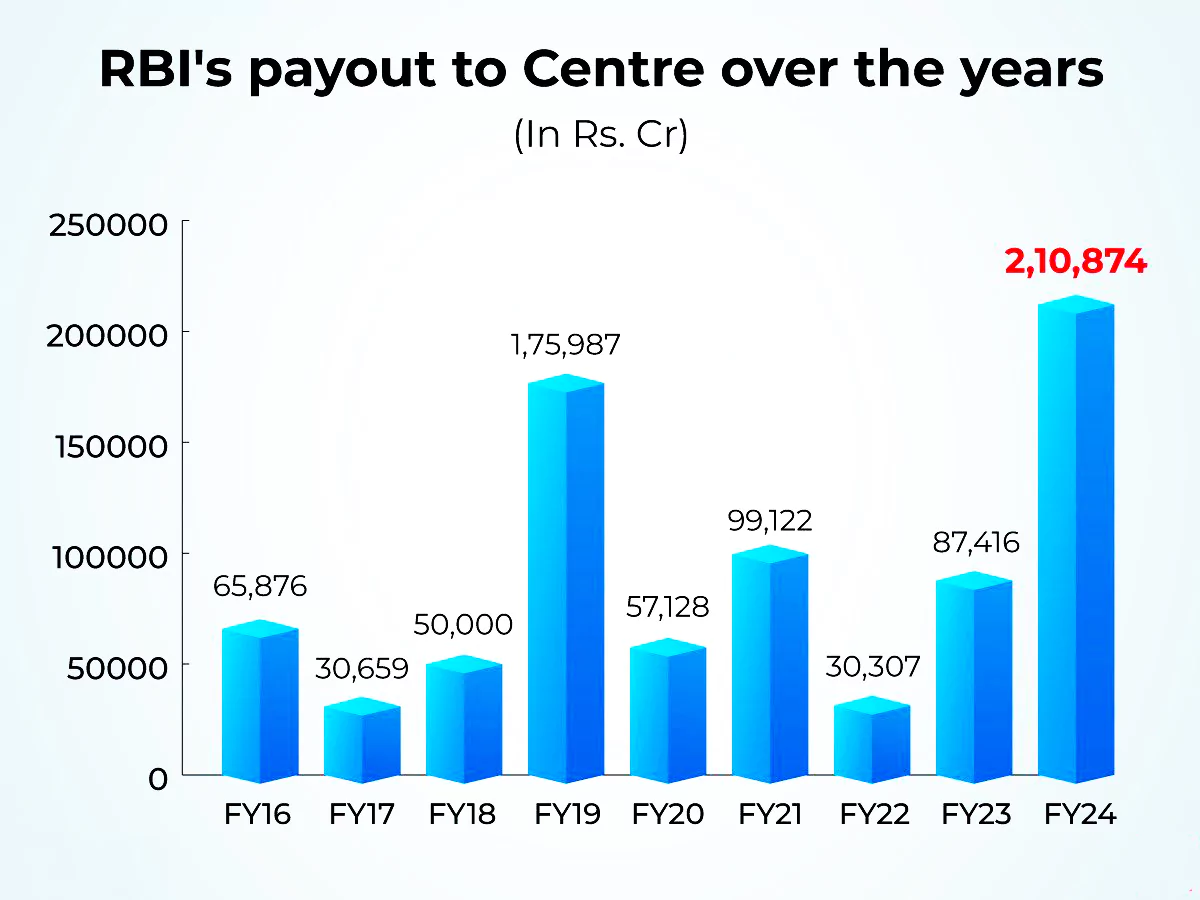
- Surplus Transfer : Every year, the RBI transfers a certain amount to the central government through the surplus income it generates from investments, fluctuations in the valuation of its dollar reserves, and revenue earned from currency printing fees.
- Determination of Surplus : On the basis of the Economic Capital Framework (ECF)
- The surplus amount was adopted by the Reserve Bank of India on August 26, 2019 as per recommendations of the Expert Committee to Review the Economic Capital Framework chaired by former governor Bimal Jalan.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Economic Capital Framework (ECF):
- The economic capital framework provides a methodology for determining the appropriate level of risk provisions and profit distribution to be made under Section 47 of the RBI Act, 1934.
- As per this provision, the central bank is required to pay the balance of its profits to the central government after making provision for bad and doubtful debts, depreciation in assets, and contributions to staff.
- It was developed in 2014-15, operationalised in 2015-16.
- Later, The Central Board of the RBI, in consultation with the government of India, constituted an expert committee chaired by Dr. Bimal Jalan, on December 26, 2018.
- It was tasked with reviewing the Economic Capital Framework of the RBI.
- To recommend an adequate level of risk provisioning for the RBI.
- It aimed to propose a suitable surplus distribution policy, considering all potential situations for the RBI.
- The Central Board of the RBI accepted all recommendations of the committee in its meeting on August 26, 2019.
|
- Contingent Risk Buffer (CRB): As the economy remains robust and resilient, the Board has decided to increase the CRB to 6.50 per cent for FY 2023-24.
- According to the 2019 expert committee, the Contingent Risk Buffer (CRB)should be maintained within a range of 6.5 to 5.5 per cent of the RBI’s balance sheet.
| Contingent Risk Buffer : The contingency risk buffer is a specific provision fund kept by the central bank primarily to be used during any unexpected and unforeseen contingencies. |
What could be the Implications of Surplus Transfer
- The surplus transfer will benefit government finances and liquidity.
- This has created considerable fiscal space for the next government when it presents the full budget for the year after the ongoing national elections.
- It can use this to bring about a steeper decline in the government’s fiscal deficit
- A higher transfer could help offset possible revenue shortfalls in areas such as disinvestment.
- The government can either reduce borrowing in FY25, prioritizing fiscal consolidation, or increase capital expenditure.
- It would be positive for the bond market by improving demand-supply dynamics. Lower borrowing could lead to softer G-Sec yields, reducing the government’s borrowing costs, as bond yields and prices move inversely.
- By Increasing Capital Expenditure : This would reduce reliance on the slow-progressing disinvestment program, providing the government with flexibility to manage welfare and sustain capital expenditures, even if disinvestment receipts fall short.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
![]() 24 May 2024
24 May 2024

