Context
On May 7, Boeing’s Starliner spaceship will launch two NASA astronauts from the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida to the International Space Station.
- This is the first time Starliner will carry astronauts, testing its ability to do so.
What is Boeing’s Starliner?
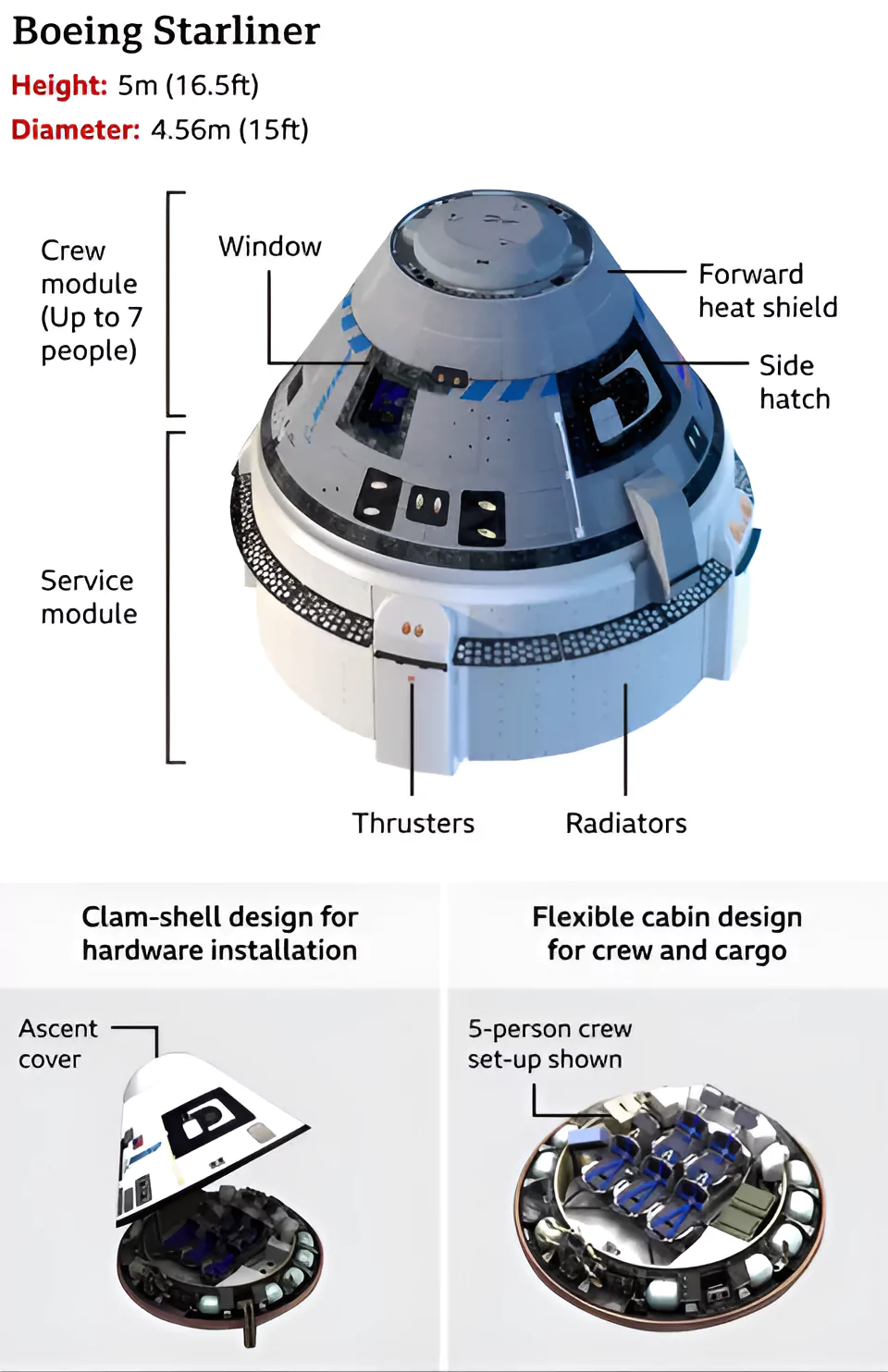
- Boeing’s Starliner is also known as CST-100 (crew space transportation).
- It is a crew capsule designed for space travel.
- It’s partially reusable, meaning it can be used for multiple missions.
- It consists of two modules:
- Crew Module: This is where astronauts stay during the journey.
- Service Module: This part is like the powerhouse of the spacecraft which provides electricity, propulsion (movement), temperature control, air, and water for the astronauts in space.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is the Boeing’s Starline mission?
- Objective: To test how well Starliner performs in space with astronauts on board.
- It aims to dock with the ISS a day after launch and stay there for about 10 days before returning to Earth.
- Key Points about Starliner’s Crewed Test Flight and Return Journey
- The astronauts will test new space suits during the mission.
- These blue suits are around 40% lighter than their predecessors and have touchscreen-sensitive gloves.
- During the return journey, NASA and Boeing will closely monitor Starliner’s heat shield and parachutes.
- They’ll slow down the descent before the airbags open to make the landing softer.
- Unlike many other crew capsules, Starliner will land on the ground, not in the sea.
-
The significance of the mission for NASA and Boeing:
-
NASA:
- Backup Option: Approval of Starliner for routine flights to and from the ISS would provide NASA with a backup option.
- It will reduce dependency on a single company or vehicle for space launches.
-
Boeing:
- Competition with SpaceX: If Starliner achieves its goals, it could enable Boeing to compete more effectively with SpaceX in the commercial space sector.
Also Read: Six Space Missions In 2024: By NASA
![]() 7 May 2024
7 May 2024
