Context:
Casgevy and Lyfgenia, the first CRISPR-based gene therapies have received approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia treatment.
Casgevy and Lyfgenia: CRISPR-Based Gene Therapies
- Casgevy™ made by Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics, and Lyfgenia™, by Bluebird Bio—is for people 12 and older.
- These two therapies work in different ways however both therapies utilise the Nobel-winning CRISPR/Cas 9 genome editing technology.
-
What Is Casgevy Therapy?
- The therapy uses the patient’s blood stem cells, which are precisely edited using Crispr-Cas9.
- The therapy targets a gene called BCL11A, which is crucial for switching from fetal to adult haemoglobin.
- The therapy uses the body’s mechanisms to produce more foetal haemoglobin, alleviating the symptoms of the two conditions
-
What is Lyfgenia Therapy?
-
- It uses a viral envelope to deliver a healthy hemoglobin-producing gene.
- Lyfgenia works by taking a piece of a virus (a lentivirus, which belongs to the HIV family) and using it to deliver a functional version of a haemoglobin-producing gene.
Gene Therapy
- Technique to replace defective genes with healthy genes to treat genetic disorders.
- Artificial method that introduces DNA into the cells of the human body.
- First developed in 1972, but has limited success.
- There are two Major types of gene therapy: Somatic gene therapy and germline gene therapy.
Gene Editing
- Gene editing is a technique of making specific changes to the DNA at a specific sequence.
- For this DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the genome.
- For this CRISPR CAS9 (Genetic Scissor) is used.
- It involves cutting specific DNA sequences with ‘engineered nucleases’ enzymes.
Germline Editing
- It refers to the process in which the DNA of reproductive cells (such as sperm and eggs) or embryos are modified.
- While somatic cell editing impacts only the treated individual, germline editing can lead to genetic changes for future generations.
|
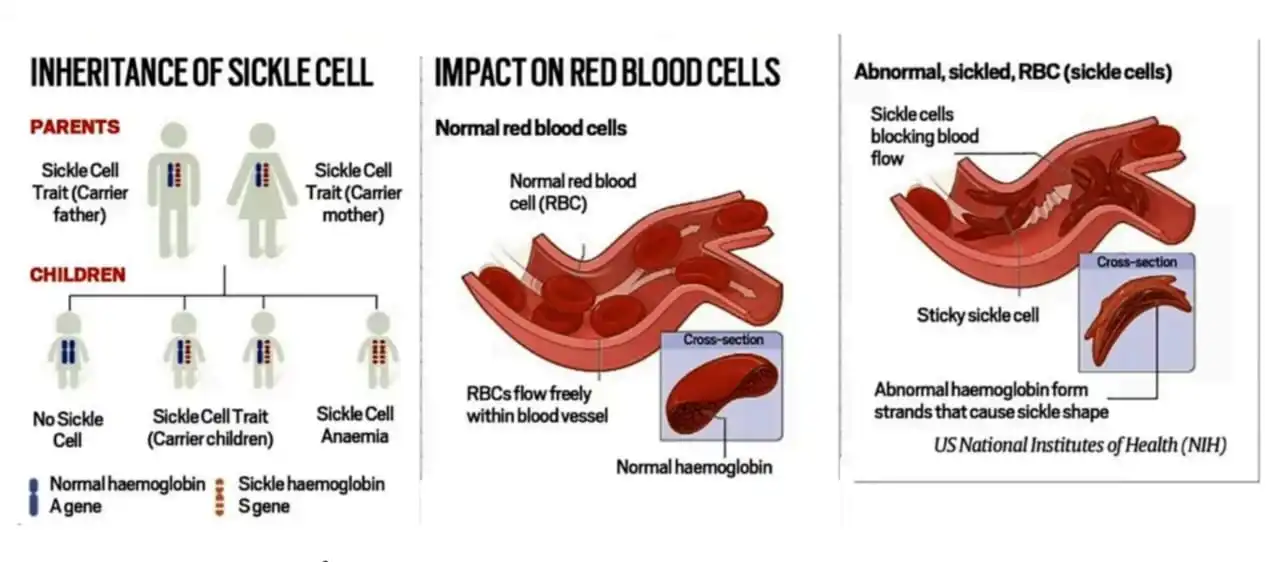
- Genetic Disorder: The genetic error in sickle cell disease leads to red blood cells assuming a crescent shape.
- Unlike the disc-shaped normal cells, the sickle-like cells cannot move around easily in the vessels, resulting in blocked blood flow.
- Symptoms: severe pain, life-threatening infections, anaemia, or a stroke.
- The symptoms manifest in people who inherit a pair of damaged genes from both parents. Those who carry only one copy of the gene from one parent can lead a normal life.
- Prelevance in India: An estimated 30,000-40,000 children in India are born with the disorder every year.
- It is also an inherited (i.e., passed from parents to children through genes) blood disorder caused when the body doesn’t make enough of a protein called haemoglobin.
- Symptoms: Thalassaemia leads to low levels of haemoglobin and shows symptoms like fatigue, nausea, shortness of breath, and irregular heartbeats.
- Prelevance in India: India also has the largest number of children with thalassaemia major in the world about 1-1.5 lakh.
- Available Treatment: People with the condition need blood transfusions. The transfusions also lead to excess iron accumulation in the body, which needs chelation.
|
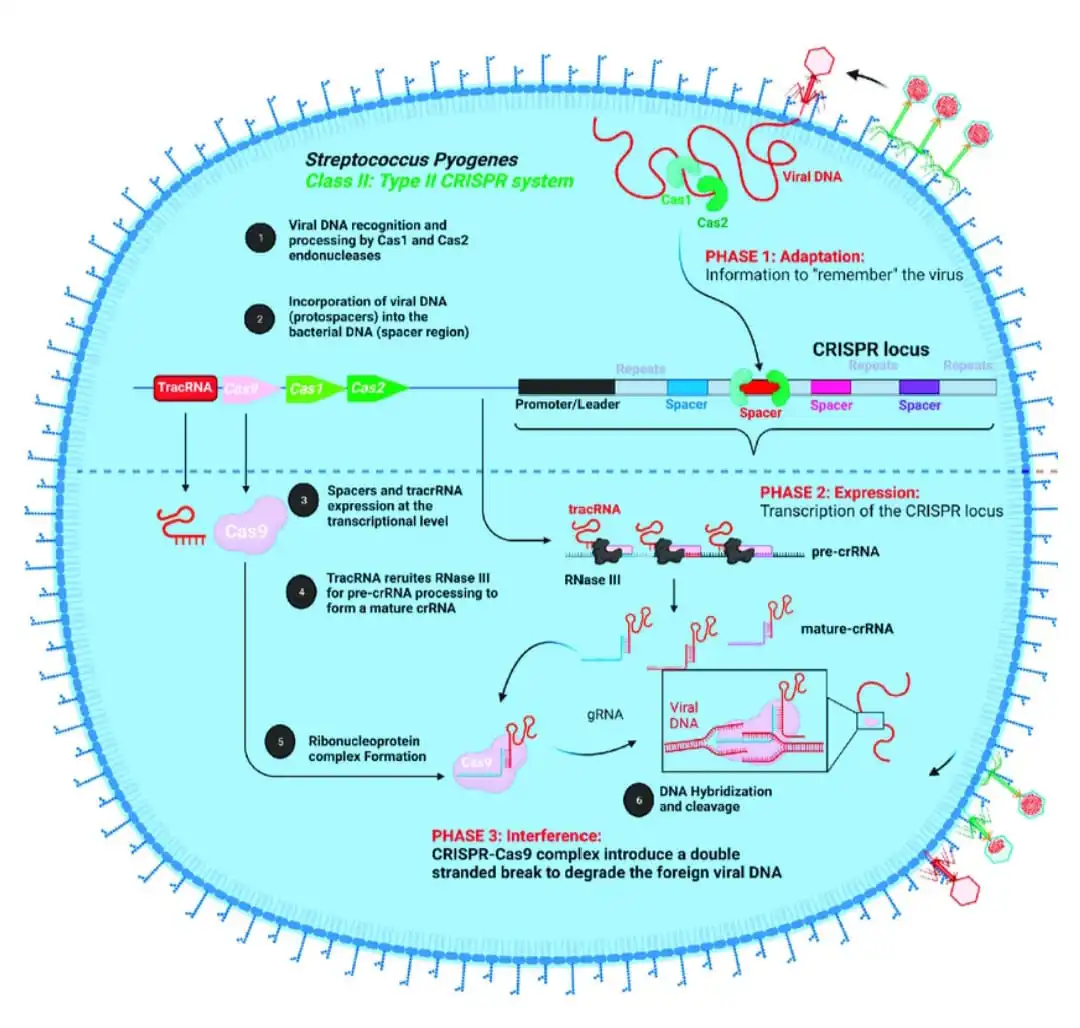
About CRISPR
- CRISPR stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats.
- It’s found in bacteria and archaea, which are simple organisms.
- These sequences come from pieces of viruses that have attacked the organisms before.
- CRISPR helps the organisms recognise and fight off similar viruses in the future.
- CRISPR acts like an immune system. CRISPR helps the organisms recognise and fight off similar viruses in the future.
CRISPR Technology
- This technology helps modify living organisms’ genomes.
- It is based on the antiviral defence system.
- Why is it useful? Researchers use CRISPR to edit DNA precisely. it is used for various purposes
- Treating genetic diseases
- Creating drought-resistant plants
- Modifying food crops
- De-extinction projects.
Regulatory Framework For CRISPR Research in India
- New Drugs and Clinical Trials Rules (2019): CRISPR research in India is governed by strict regulations, with Gene Therapy Products (GTPs) classified as new drugs under the New Drugs and Clinical Trials Rules (2019).
- Central Drugs Standard Control: This organisation approves CRISPR.
- Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM)/Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC): Besides existing regulations, additional rules might be set based on national GTP guidelines and reviewed by relevant committees.
- Further requirements depend on national Gene Therapy Product guidelines and committee oversight.
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR): All biomedical research in India requires ethical approval following ICMR guidelines (2017).
- India mandates ethical conduct for all biomedical research involving human participants (ICMR, 2017).
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 9 Feb 2024
9 Feb 2024
