Context
Recent media reports suggest that the armed forces are looking at the appointment of a Vice Chief of Defence Staff (VCDS) and a Deputy Chief of Defence Staff (DCDS), highlighting the evolving nature of India’s higher defense management.
Reason for Proposal of New Defence Posts
- Enhancement of Jointness: These posts are proposed to enhance jointness (the sharing of domain expertise and assets) among the armed forces, to streamline inter-service cooperation and improve composite combat capability.
- To Support Chief of Defence Staff (CDS): These posts aim to support the CDS in managing his/her extensive responsibilities, which include being a four-star general, government secretary, and principal adviser to the Defence Minister.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)
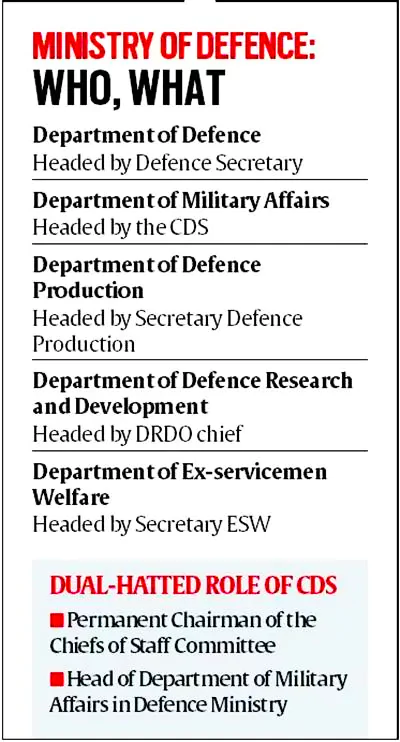
- Refers: The Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) is the first among equals along with the other three service chiefs as a four-star general. The CDS is a high military office that oversees and coordinates the working of the three Services.
- Background & Evolution:
- 1999: The first proposal for a CDS made by the K. Subrahmanyam Committee, also known as Kargil Review Committee (KRC) appointed after the Kargil conflict of 1999 to recommend higher military reforms.
- However, lack of consensus and apprehensions among services meant it never moved forward.
- 2001: Based on the Shri K Subrahmanyam Committee Report, a Group of Ministers (GoM) in 2001 recommended creation of the post of the Chief of Defence Staff.
- 2012: Naresh Chandra Task Force set up by then Prime Minister in 2011, and gave the report in 2012. It recommended that CDS should be designated as the Permanent Chairman Chief of Staff Committee.
- 2016: The CDS is also one of the 99 recommendations made by the Lt General D.B. Shekatkar (retd) Committee.
- 2020: General Bipin Rawat was appointed as the first CDS in January 2020.
- 2022: In October 2022, Lt Gen Anil Chauhan (retd) was appointed the second CDS.
- In the absence of a CDS, the senior most of the three Chiefs functions as the Chairman of Chiefs of Staff Committee (COSC).
- Global Scenario: Many major countries have created the post of the CDS such as Italy, France, China, UK, USA, etc., to bring more jointness and integration in their Armed Forces.
-
Need for Chief of Defence Staff (CDS):
- Effectiveness: Appointment of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) is required to make the military leaner and more effective.
- Single-point Military Advice: It is necessary to have a professional body to render single-point military advice to the government on matters of national security.
- Bridging the Gap: The CDS was envisioned to be a pivotal role, bridging the gap between military and governmental defence operations, thus necessitating a combination of military expertise, bureaucratic skills, and political advisory capabilities.
-
Responsibilities & Mandate of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS):

-
- Advisor to the Government: The Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) is meant to be a single-point military advisor to the government, and to coordinate long-term planning, procurements, training and logistics of the three services.
- Enhance Jointness among Armed Forces: The CDS is also seen as being vital to the creation of “theatre commands”, integrating tri-service assets and personnel like in the US military.
- Prioritising of Inter-Service Procurement Decisions: The Chief of Defence Staff heads the newly created Department of Military Affairs (DMA) in the Ministry of Defence and as the head of DMA, CDS is vested with the authority in prioritising inter-service procurement decisions as Permanent Chairman-COSC.
- Suggest Directives: The CDS is also vested with the authority to provide directives to the three chiefs. However, does not enjoy any command authority over any of the forces.
- CDS is first among equals, he enjoys the rank of Secretary within the Department of Defence and powers are confined to only the revenue budget.
- He also performs an advisory role in the Nuclear Command Authority (NCA).
- The CDS’s Many Hats: The Chief of Defence Staff was accorded a daunting and anomalous institutional profile but this was deemed necessary when the post was conceived.
Significance of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)
- To Maintain Synergy: Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) maintains better cooperation between the Ministry of Defence bureaucracy and the Armed services.
 Since 1947, there have been three Service Headquarters (SHQ) designated as “Attached Offices” of the Department of Defense (DoD). Due to this, communication between SHQ and DoD takes place largely through the medium of files.
Since 1947, there have been three Service Headquarters (SHQ) designated as “Attached Offices” of the Department of Defense (DoD). Due to this, communication between SHQ and DoD takes place largely through the medium of files.- With the creation of CDS as Principal Military Adviser (PMA) to Defense Minister, the process of decision-making will be accelerated.
- Jointness: Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) is a high military office that oversees and coordinates the working of the three defence Services in India that lead to enhanced security.
- As the CDS is “permanent chairman of COSC”, he/she will be able to devote undivided attention to the administration of tri-service organisations.
- Operationalisation of Theatre Command: Creation of DMA will facilitate the operationalisation of joint/theatre command. Theatre commands would need staff with the knowledge and experience to deploy land, maritime and air forces that would be implemented by the CDS.
- Although a successful template for joint operations was created in the Andaman & Nicobar Command, the lack of political direction and indifference of the COSC has led to inactivity of this joint command.
- Resource Optimisation: Chief of Defence Staff will have to ensure that the “defence rupee” is spent judiciously on warfare-capabilities that are considered vital for national military power.
- The CDS helps in the tackling of threats in an integrated manner and would help in optimal use of available resources.
- Also, policy-making on operations, procurement and joint logistics are improved.
- Holistic Management: The CDS is crucial in holistic management of national security for optimised results and single point military advice on matters of national security including nuclear weapons.
- CDS administers the Strategic Forces Command and it will enhance the credibility of India’s nuclear deterrent.
- The Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) also initiated an early review of India’s Nuclear Doctrine.
Raising Concerns
- Time-Consuming Process: As the Indian Defence Minister has noted, creating theatre commands is a complex and time-consuming process, requiring consensus among different services.
- Also, the government took nine months to appoint a new Chief of Defence Staff when the first Indian CDS Bipin Rawat died in a chopper crash.
- Avoidable Overload on CDS: The existing responsibilities of the CDS is a case of avoidable overload. Serving as the Secretary to the Government of India in the Ministry of Defence entails significant administrative duties that can detract from the CDS from its primary military functions.
- Operational Challenges: One of the primary challenges is to harmonise the interests and operational philosophies of the three services as each branch of the armed forces has its own traditions, priorities, and strategic doctrines.
- Rank Hierarchy: Rank hierarchy is central to the military and if implemented, could disrupt the rank hierarchy and affect the command structure.
- Location Choice: The proposed location for the Maritime Theatre Command in Coimbatore, instead of the previously considered Karwar, raises questions about the strategic use of existing infrastructure.
- Concern over Theaterisation: All three services also have concerns about how theaterisation might dilute the role of the service chiefs.
- Also, the arbitrary changes expanded the pool of eligible candidates for appointment as CDS that may have diminished the dignity of the evolving office.
- Persistence of Security & Sovereignty Challenge: The challenges to national security and sovereignty remain abiding and tenacious.
- With a two-front operational tasking along the land borders (China and Pakistan) and tangled, there are consistent unresolved territorial disputes.
- They have been compounded by the rise of state-sponsored terrorism.
- Examples: Kargil 1999, Mumbai 2008 and Galwan 2020.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Way Forward
- Clear Demarcation of the Roles: There is a need for clarification of the roles and responsibilities of the CDS, VCDS, and other senior military positions to delineate the boundaries of authority and reduce the risk of overlapping duties that can lead to inefficiencies.
- Strengthening of Inter-Service Cooperation: Initiatives to enhance jointness among the services should be prioritised by conducting regular joint training exercises, integrated planning sessions, and shared resources.
- Focus on Strategic Leadership: By delegating bureaucratic responsibilities to the VCDS, the CDS can focus more on strategic leadership and long-term defence planning.
- This will enable the CDS to drive initiatives that enhance the military’s operational capabilities and readiness.
- Maintaining Professional Integrity: Upholding the professional independence of the Chief of Defence Staff is crucial. It needs to ensure that the CDS can provide honest and unbiased advice to the government while also advocating effectively for the needs of the armed forces.
- The military ethos requires that the CDS retains his professional independence and upholds his oath of allegiance to the Constitution.
![]() 18 May 2024
18 May 2024



 Since 1947, there have been three Service Headquarters (SHQ) designated as “Attached Offices” of the Department of Defense (DoD). Due to this, communication between SHQ and DoD takes place largely through the medium of files.
Since 1947, there have been three Service Headquarters (SHQ) designated as “Attached Offices” of the Department of Defense (DoD). Due to this, communication between SHQ and DoD takes place largely through the medium of files.