Context
China has inaugurated the High Energy Photon Source (HEPS), which will be the first fourth-generation synchrotron light source in Asia.
China Inaugurates Next-Generation Synchrotron

- Existing Synchrotrons: Presently there are around 70 synchrotrons across the world that are either in operation or under construction.
- The fourth-generation club: Fourth-generation facilities rely on an array of magnets called a multi-bend achromat lattice to generate X-ray beams that are narrower and therefore brighter. Existing facilities include,
- Sweden’s MAX IV Laboratory,
- Sirius in Campinas, Brazil,
- The European Synchrotron Radiation Facility’s Extremely Brilliant Source in Grenoble, France.
- The Advanced Photon Source in Lemont, Illinois.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About High Energy Photon Source (HEPS)
- Location: It is situated 50 kilometers from Beijing in Huairou.
- Budget: It is a 4.8-billion-yuan (US$665-million) project.
- Objective: To produce a light source that will penetrate deep into samples to reveal their molecular and atomic structure in real time.
- Scope: Users can select from the existing 14 beamlines for experiments in subjects including biomedicine, energy, advanced materials and condensed-matter physics.
- Also, HEPS is expected to accommodate up to 90 beamlines which will impact every scientific field, except maths going forward.
- Feature:
- Produce Hard X Rays: HEPS will accelerate electrons up to energies of 6 gigaelectron volts inside its storage ring, with a circumference of 1.36 kilometres, to produce high-energy, or hard X-rays to measure samples at nanometre scales.
- Enabling Nano measurements: Its time resolution will be 10,000 times better than that achieved by third-generation synchrotrons allowing researchers to make measurements in hundreds of nanoseconds instead of milliseconds
- High Resolution Imaging: HEPS’s electron beam will be the narrowest in the world, allowing it to create particularly intense X-rays enabling researchers to obtain more information from their samples with the same dose of radiation.
- It will further drive scientists’ understanding of the properties of matter and help in the development of new materials.
- Speedy experimentation: HEPS will also allow researchers to rapidly execute experiments that would have taken days to complete at older facilities.
- Example: To determine the atomic structure of proteins, researchers need to purify and coax these molecules into orderly crystal structures that can be visualized with X-rays. Older synchrotrons require large samples that are difficult to produce, making it nearly impossible to study smaller protein crystals
What is synchrotron light?
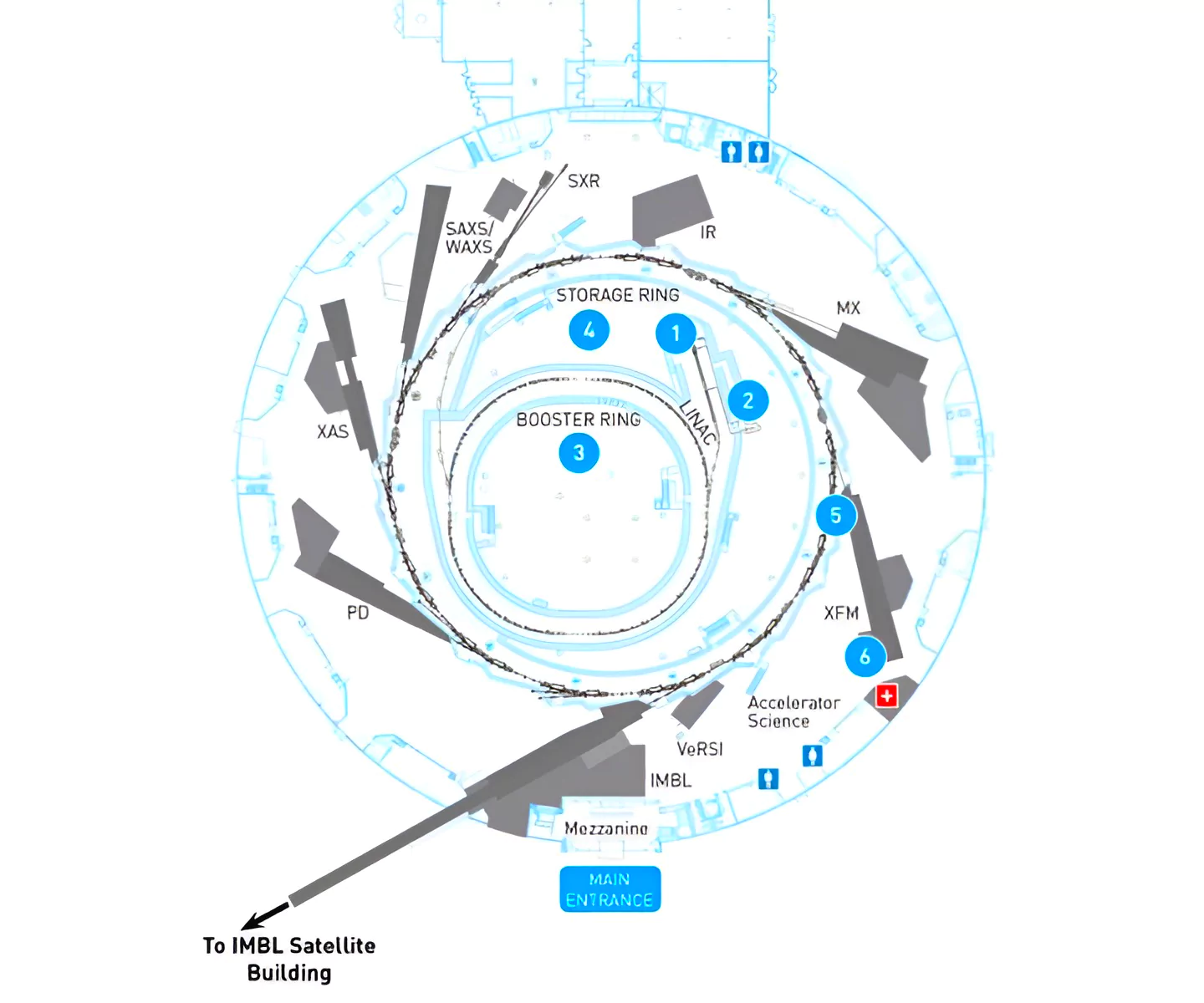
- A synchrotron: It is a type of circular particle accelerator which works by accelerating charged particles (electrons) through sequences of magnets until they reach almost the speed of light.
- Formation of Synchrotron Light: These fast-moving high energy electrons produce very bright light, by the ‘synchronised’ application of strong magnetic fields called synchrotron light.
- This very intense light, predominantly in the X-ray region, is millions of times brighter than light produced from conventional sources and 10 billion times brighter than the sun.
- Significance: The intense light which is produced by the electrons is then filtered and adjusted to travel into experimental workstations, where it is used to study minute matter such as atoms and molecules and reveals the innermost secrets of materials, from human tissue to plants to metals and more.
 Origin:
Origin: -
- The first synchrotron: It was built in 1946 and was designed to study collisions between high energy particles. Example: The Large Hadron Collider at CERN
- The First synchrotron Light experiment: In 1956, the first experiments were carried out using synchrotron light drawn from a particle collider at Cornell in the USA
- The First Dedicated facility: In 1980 UK built the world’s first synchrotron dedicated to producing synchrotron light for experiments at Daresbury in Cheshire.
- Process:
- 1st step: The electrons are generated by the electron gun in the centre of the synchrotron and accelerated to 99.9997% of the speed of light by the linear accelerator, or linac.
- 2nd step: The electrons are then transferred to the booster ring, where in approx. half a second, there is an increase in energy from 100 MeV to 3,000 MeV (or 3 GeV). They are then transferred to the outer storage ring.
- Final step: The electrons are circulated around the storage ring by a series of magnets separated by straight sections. As the electrons are deflected through the magnetic field, electromagnetic radiation is produced.
- Final Synchrotron light: At each bending magnet a beam of synchrotron light is produced and the electromagnetic radiation produced by the synchrotron is emitted in a narrow cone in the forward direction, at a tangent to the electron’s orbit.
- Properties of Synchrotron light:
- High brightness: It is extremely intense (hundreds of thousands of times more intense than that from conventional x-ray tubes) and highly collimated.
- Wide energy spectrum: It can be generated across the range of the electromagnetic spectrum ie. from infrared to visible light to x-rays.
- Tunable: It is possible to obtain an intense beam of any selected wavelength.
- Highly polarised: The synchrotron emits highly polarised radiation, which can be linear, circular or elliptical.
- Very short pulses: Pulses are emitted in typically less than a nano-second (a billionth of a second), enabling time-resolved studies.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
![]() 20 May 2024
20 May 2024

 Origin:
Origin: