Context: This article is based on the news “Cyber crime growing at the rate 15-20% annually in India: West Bengal IGP Cyber Cell” which was published in the Economic Times. In 2022, Cyber Crimes in India recorded a 24% increase compared to the previous year, according to the latest data released by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB).
| Relevancy for Prelims: NCRB Data on Cyber Crimes in India, National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC), Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000, National Cyber Security Policy (NCSP), and Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In).
Relevancy for Mains: Growing Cyber Crimes in India: Reasons, Challenges, Government Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
NCRB Data on Cyber Crimes in India
- According to the report ‘Crime in India’, 65,893 cases were registered under cybercrime, showing an increase compared to 52,974 cases in 2021.
- Over 24,000 complaints were registered with the Delhi Police till June 2023. During the same period in 2022, the cops had received 7,500 complaints.
- Preliminary probe data showed that most frauds originated in Mewat (Haryana) and Jamtara (Jharkhand).
- More than 80,000 complaints have been received from West Bengal in 2023 till November end in the national cybercrime reporting portal.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Cyber Crime
- Cybercrime Definition: Any unlawful act where a computer or communication device or computer network is used to commit or facilitate the commission of crime.
- For example, Hacking, identity theft, fraud, and Cyberstalking.
- Cybercrimes comes as a State subject as per the Seventh Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
Increasing Cyber Crimes in India: Major Reasons
- Financial gain: Through stealing financial information, such as credit card numbers and bank accounts, or through demanding ransom in exchange for stolen data or resources.
Manifestations of Cyber Crimes in Real Life
- Cyber Bullying: A form of harassment or bullying inflicted through the use of electronic or communication devices such as computer, mobile phone, laptop, etc.
- Cyber Stalking: Use of electronic communication by a person to follow a person, or attempts to contact a person to foster personal interaction repeatedly despite a clear indication of disinterest by such person.
- Cyber Grooming: It is when a person builds an online relationship with a young person and tricks him/her into doing a sexual act.
- Sexting: It is an act of sending sexually explicit digital images, videos, text messages, or emails, usually by cell phone.
- SIM Swap SCAM: This occurs when fraudsters manage to get a new SIM card issued against a registered mobile number fraudulently through the mobile service provider.
|
-
- For example, Unified Payment Interface (UPI) frauds are the most prevalent online financial frauds reported between January 2020 and June 2023, according to the Future Crime Research Foundation (FCRF) report by IIT-Kanpur.
- Espionage: Some cybercriminals engage in cyber crime to steal confidential or proprietary information for competitive advantage or to damage the reputation of an organization.
- Political or ideological motives: Some cybercriminals target organizations or individuals for political or ideological reasons, such as to promote a particular cause or to advance a particular agenda.
- For example, the Cambridge Analytica scandal (2018) under which the Facebook database was leaked with data of 419 million users including the data of many Indian users.
- Personal motives: Some cybercriminals engage in cybercrime to harass, defame, or harm individuals or organizations.
- Opportunism: Some cybercriminals engage in cybercrime simply because they can, taking advantage of security vulnerabilities in technology or in people to steal information or resources.
- For Example: In June 2023, tech giant Microsoft experienced temporary disruptions to its Outlook and Azure computing services after an attack by a cybercrime group called Anonymous Sudan.
Cyber Crimes in India: Challenges
- Rapid Technological Advancements: The rapid adoption of technology in India has led to an increased attack surface for cybercriminals. As new technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), cloud computing, etc. become more prevalent, the attack vectors for cybercriminals also expand.
What is Cyberterrorism?
- Cyberterrorism is often defined as any premeditated, politically motivated attack against information systems, programs, and data that threatens violence or results in violence.
- The definition is sometimes expanded to include any cyber attack that intimidates or generates fear in the target population. Attackers often do this by damaging or disrupting critical infrastructure.
- For example, ISIS targets military websites, and government websites for spreading hate and propaganda.
|
-
- For instance, Deep Fake and AI-generated voice is a rising challenge as it has become easy to create and superimpose faces and voices.
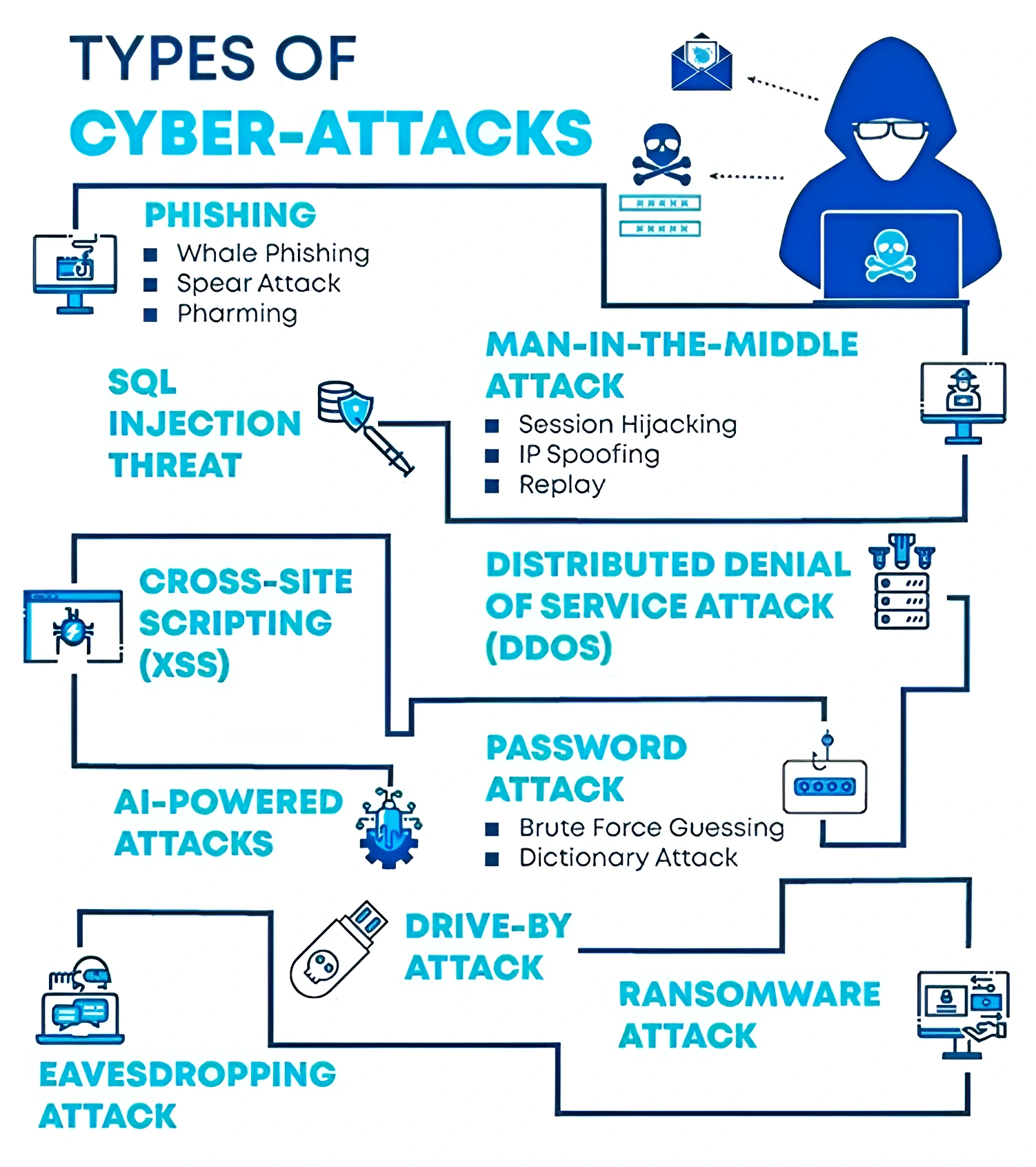
- Sophisticated Cyber Attacks: Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated, using advanced techniques such as ransomware, zero-day exploits, and social engineering to target individuals and organizations.
- A zero-day exploit is a cyberattack technique that takes advantage of an unknown security flaw in computer software, hardware or firmware.
- Cyber Warfare and State-sponsored Attacks: India faces the threat of cyber espionage and state-sponsored cyber attacks increasing the vulnerability of critical infrastructure and sensitive government information.
- For instance, the Malware(Dtrack) attack on Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant (KKNPP) in 2019. It is believed that this malware has been created by a group called Lazarus with links to North Korea.
- Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness: Many individuals and businesses in India may not be fully aware of the risks and preventive measures associated with cybersecurity which makes them more susceptible to falling victim to cybercrimes.
- Inadequate Legal Framework: Although India has made efforts to establish legal frameworks to address cybercrimes, there may still be gaps and challenges in effectively enforcing these laws.
Also Read: What is Deepfake Technology? – Its Types, Impacts, and Security Countermeasures
Cyber Crimes in India: Government Measures
- National Cyber Forensic Laboratory (Investigation): It has been established in New Delhi to provide early-stage cyber forensic assistance to Investigating Officers (IOs) of all State/UT Police both through online and offline modes.‘CyTrain’ portal: Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC) platform for capacity building of all the stakeholders, police officers, judicial officers and prosecutors through online courses on critical aspects of cybercrime investigation, forensics, prosecution, etc. along with certification.
- National Cyber Security Policy (NCSP): It aims to create a secure cyberspace environment and strengthen the country’s cybersecurity.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C): The I4C serves as the nodal point for coordinating efforts to combat cybercrime in India with a focus on enhancing the capabilities of law enforcement agencies to prevent and investigate cybercrimes.
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal: It has been launched to enable the public to report incidents about all types of cyber crimes, with a special focus on cyber crimes against women and children.
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC): NCIIPC is responsible for protecting critical information infrastructure from cyber threats. It identifies critical sectors and formulates policies and guidelines for securing them.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: This initiative focuses on the detection and removal of malware-infected systems, thereby reducing the impact of botnets.
- Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In): CERT-In is the national agency responsible for responding to and mitigating cybersecurity incidents. It issues alerts and advisories to the public and private sectors to enhance cybersecurity awareness.
- Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000: It is a comprehensive legislation that addresses various aspects of electronic governance, digital signatures, data protection, and penalties for cybercrimes.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Global Conventions to Tackle Cybercrime
- Interpol Cybercrime Global Strategy 2022-2025: Reducing the global impact of cybercrime and protecting communities for a safer world. The strategy outlines INTERPOL’s plan to support its member countries in combating cybercrime.
- Potential UN Cybercrime Treaty: UN member states have been negotiating an international treaty on countering cybercrime. If adopted by the UN General Assembly, it would be the first binding UN instrument on a cyber issue.
- Budapest Convention: The treaty focused on harmonizing laws and increasing cooperation across borders so that a range of cybercrime could be prosecuted in the multiple countries affected. India decided not to participate in this convention.
|
Way Forward to Prevent Cyber Crimes in India
- Implement Advanced Cybersecurity Framework: Cybersecurity frameworks offer a range of best practices, policy processes, security protocols, and other necessary tools to secure an organization’s business operations.
- Investing in advanced cybersecurity technologies can help to protect critical information systems and networks.
- Cyber Hygiene Practices: Encourage individuals and organizations to adopt good cyber hygiene practices, such as regular software updates, strong password management, and secure online behavior.
- International Cooperation: Strengthen collaboration with international organizations, law enforcement agencies, and other countries to share threat intelligence, and best practices, and coordinate efforts in investigating and prosecuting cross-border cybercrimes.
- For instance, India and Japan have agreed to step up cooperation to improve skills in securing cyberspace at bilateral and multilateral levels.
- Public Awareness and Education: Conduct widespread awareness campaigns to educate the public about common cyber threats, safe online practices, and the importance of cybersecurity.
- Encourage the Adoption of Cyber Insurance: Cyber insurance policies help cover the financial losses that result from cyber events and incidents. In addition, cyber-risk coverage often helps with the costs associated with remediation, including payment for legal assistance, investigators, crisis communicators, and customer credits or refunds.
Conclusion:
The growing trend of cyber crimes in India demands a comprehensive approach, including advanced cybersecurity measures, international cooperation, public awareness, and the effective implementation of legal frameworks to ensure a secure digital environment for individuals and organizations.
![]() 19 Dec 2023
19 Dec 2023


